FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA cautions about dose confusion and medication errors for antibacterial drug Zerbaxa (ceftolozane and tazobactam)
[ 5-20-2015 ]
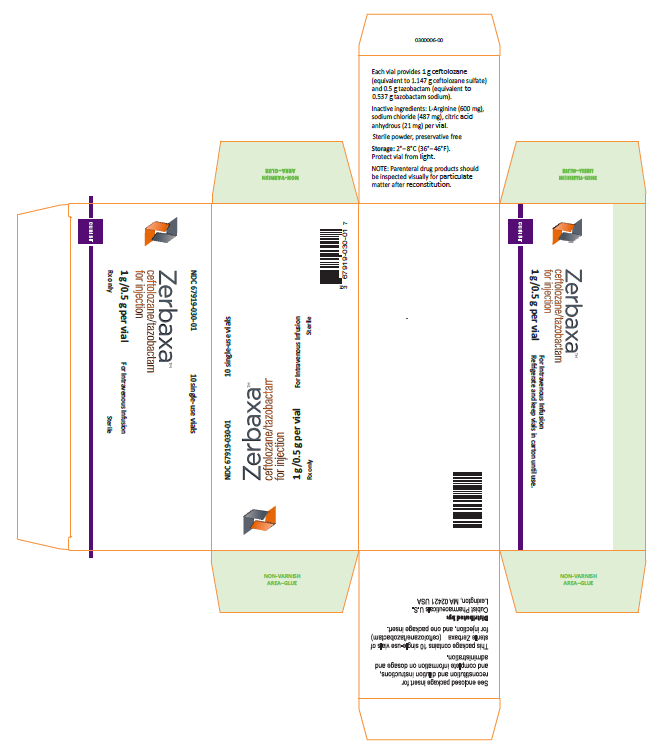
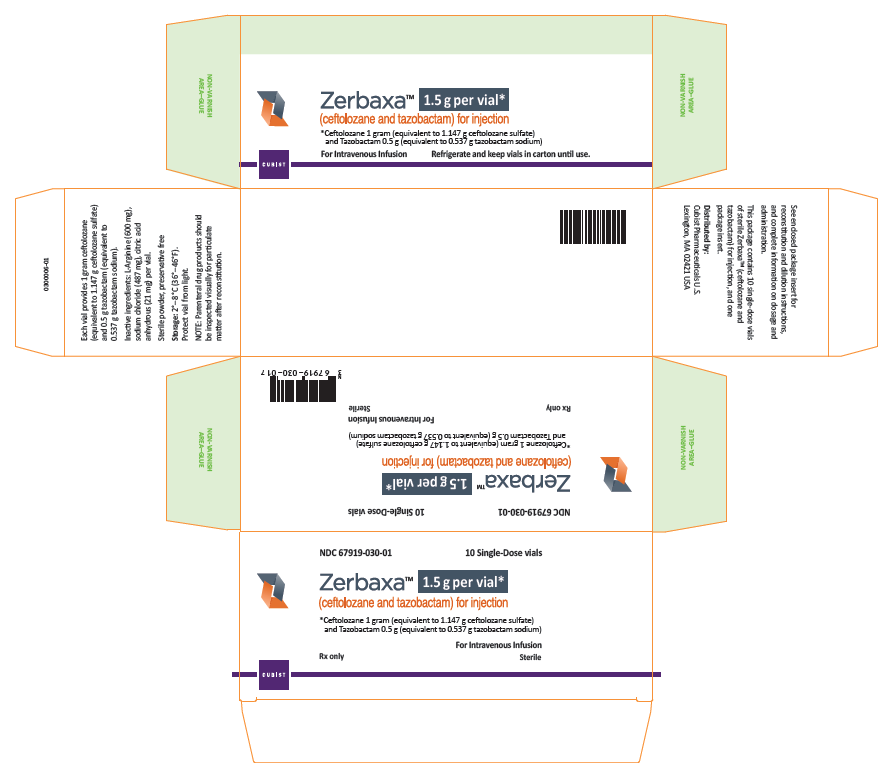
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is warning health care professionals about the risk for dosing errors with the antibacterial drug Zerbaxa (ceftolozane and tazobactam) due to confusion about the drug strength displayed on the vial and carton labeling. Zerbaxa’s vial label was initially approved with a strength that reflects each individual active ingredient (e.g. 1 g/0.5 g); however, the product is dosed based on the sum of these ingredients (e.g. 1.5 g). To prevent future medication errors, the strength on the drug labeling has been revised to reflect the sum of the two active ingredients. Thus, one vial of Zerbaxa will now list the strength as 1.5 grams equivalent to ceftolozane 1 gram and tazobactam 0.5 gram (See Photos).
Zerbaxa is used to treat complicated infections in the urinary tract, or in combination with the antibacterial drug metronidazole to treat complicated infections in the abdomen. Antibacterial drugs work by killing or stopping the growth of bacteria that can cause illness.
We evaluated seven reported cases of medication error that occurred during preparation of the dose in the pharmacy due to confusion with the display of the strength of individual ingredients on Zerbaxa’s vial label and carton labeling. Listing the individual drug strengths led to confusion because it was different from labeling for other beta-lactam/beta-lactamase antibacterial drugs that express strength as the sum of the two active ingredients. In some cases, this led to administration of 50% more drug than was prescribed. No adverse events were reported among these seven cases.
We urge health care professionals and patients to report side effects and medication errors involving Zerbaxa to the FDA MedWatch program, using the information in the “Contact FDA” box at the bottom of the page.
- Zerbaxa is a combination product consisting of ceftolozane, a cephalosporin antibacterial drug and tazobactam, an inhibitor of certain beta-lactamase enzymes.
- Zerbaxa is approved to treat complicated urinary tract infections, and for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections in combination with metronidazole.
- Each vial contains 1.5 grams of Zerbaxa [ceftolozane 1 gram (equivalent to 1.147 g ceftolozane sulfate) and tazobactam 0.5 g (equivalent to 0.537 g tazobactam sodium].
- Due to reports of medication errors associated with Zerbaxa, the vial and carton labeling have been revised to indicate that each vial contains Zerbaxa 1.5 grams equivalent to ceftolozane 1 gram (equivalent to 1.147 g ceftolozane sulfate) and tazobactam 0.5 g (equivalent to 0.537 g tazobactam sodium).
- Zerbaxa is approved to treat complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis, and in combination with metronidazole to treat complicated intra-abdominal infections caused by susceptible bacterial pathogens.
- In order to reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain antibacterial effectiveness, Zerbaxa should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria.
- The dose of Zerbaxa needs to be adjusted in patients with renal impairment.
- Report adverse reactions and medication errors involving Zerbaxa to the FDA MedWatch program, using the information in the “Contact FDA” box at the bottom of the page.
FDA evaluated seven cases of medication errors for Zerbaxa (ceftolozane and tazobactam) reported to us since its approval in December 2014. In four of the seven reported cases, an incorrect dose was given to the patient, although no adverse events were reported. In the other three cases, the pharmacists identified the error before the drug was administered to patients.
The presentation of the drug strength on the Zerbaxa vial label and carton labeling, displayed as 1g/0.5g, was cited as the reason for the medication errors. In all cases, the total dose of Zerbaxa prescribed was either 1.5 grams or 3 grams, which the prescriber intended to represent the sum of the two ingredients. However, the dose to be administered to the patient was calculated based on the amount of ceftolozane in the Zerbaxa vial, which is 1 gram, resulting in a 50% overdose.
Our evaluation determined that previously approved beta-lactam/beta-lactamase antibacterial drug products express the strength as the sum of the two active ingredients in the labeling; for example, 1.5 grams or 3 grams of ampicillin/sulbactam. Therefore, pharmacists and prescribers are familiar with this convention for expressing the strength of beta-lactam/beta-lactamase antibacterial drugs as the sum of the two active ingredients. Confusion arose when the vial label and carton labeling of Zerbaxa expressed the strength to reflect the individual active ingredients.
Before
After
Drug Safety Communication (PDF - 223KB)