Drug Trials Snapshots: NUBEQA
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the NUBEQA Package Insert for complete information.
NUBEQA (darolutamide)
NOO-bƏ-kƏ
Bayer
Approval date: July 30, 2019
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
NUBEQA is a drug for the treatment of prostate cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body (non-metastatic) and no longer responds to a medical or surgical treatment that lowers testosterone (castration-resistant).
How is this drug used?
NUBEQA is a tablet. Two tablets are taken twice daily with food.
What are the benefits of this drug?
In patients with medical or previous surgical treatment to lower testosterone, NUBEQA increased the patients’ survival during which time the cancer did not spread [metastasis-free survival (MFS)]. The MFS for patients taking NUBEQA was about 40 months compared to about 18 months for patients taking a placebo.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The table below summarizes efficacy results for the evaluated patients in the clinical trial. The primary endpoint was metastasis-free survival defined as the time from randomization to the time of first evidence of Blinded Independent Central Review (BICR)-confirmed distant metastasis or death due to any cause, whichever occurred first.
Table 2. Efficacy Results from the Clinical Trial|
|
NUBEQA |
Placebo |
|
Metastasis-free survival |
||
|
Number of Events (%) |
221 (23) |
216 (39) |
|
Median, months (95% CI)1 |
40.4 (34.3, NR) |
18.4 (15.5, 22.3) |
|
Hazard Ratio (95% CI)2 |
0.41 (0.34, 0.50) |
|
|
P-value3 |
<0.0001 |
|
NR: not reached
1 Based on Kaplan-Meier estimates
2 Hazard ratio is based on a Cox regression model (with treatment as the only covariate) stratified by PSADT (≤ 6 months vs. > 6 months) and use of osteoclast-targeted therapy (yes vs. no). Hazard ratio < 1 favors NUBEQA.
3 P-value is based on a stratified log-rank test by PSADT (≤ 6 months vs. > 6 months) and use of osteoclast-targeted therapy (yes vs. no)
NUBEQA Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: All the patients were men since NUBEQA is for the treatment of prostate cancer.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. NUBEQA worked similarly in White and Asian patients. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in how well NUBEQA worked among races could not be determined.
- Age: NUBEQA worked similarly in all age groups tested.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below shows metastasis-free survival by subgroup
Table 3. MFS in Demographic Subgroups.
|
Variable and Subgroup |
N |
HR [95% CI] |
Median (months) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Total |
Events |
Censored |
|
NUBEQA |
Placebo |
|
| Race |
||||||
|
White |
1194 |
361 |
833 |
0.432 (0.351, 0.533) |
40.37 |
18.36 |
|
Black or African |
52 |
11 |
41 |
0.000 (0.000, NE) |
NE |
12.42 |
|
Asian |
193 |
45 |
148 |
0.324 (0.177, 0.593) |
NE |
21.81 |
|
Other |
15 |
5 |
10 |
0.484 (0.077, 3.047) |
NE |
14.82 |
| Age Group (years) |
||||||
|
<65 |
197 |
72 |
125 |
0.591 (0.368, 0.948) |
26.02 |
17.15 |
|
65 – 74 |
589 |
170 |
419 |
0.349 (0.257, 0.473) |
NE |
18.3 |
|
75 – 84 |
593 |
155 |
438 |
0.432 (0.313, 0.595) |
40.37 |
25.16 |
|
≥85 |
130 |
40 |
90 |
0.509 (0.271, 0.958) |
40.51 |
18.33 |
HR=Hazard Ratio; CI=Confidence Interval; NE=Non-Estimable
FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
NUBEQA can cause harm to a fetus and loss of pregnancy in female sexual partners.
The most common side effects are fatigue, pain in extremity, and rash.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below shows the adverse reactions in patients who received at least one dose of treatment and were included in the safety assessment (safety population).
Table 4. Adverse Reactions|
Adverse Reaction2 |
NUBEQA |
Placebo |
||
|
All Grades |
Grades > 3 |
All Grades |
Grade > 3 |
|
|
Fatigue1 |
16 |
0.6 |
11 |
1.1 |
|
Pain in extremity |
6 |
0 |
3 |
0.2 |
|
Rash |
3 |
0.1 |
1 |
0 |
1 Includes fatigue and asthenia
2 Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03.
NUBEQA Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: All the patients were men since NUBEQA is for the treatment of prostate cancer.
- Race: The occurrence of side effects was similar among White and Asian patients. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, the occurrence of side effects among other races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar in all age groups tested.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes the occurrence of the most frequent adverse reaction, fatigue, by subgroup.
Table 5. Pooled Subgroup Analysis of Fatigue1|
Demographic Characteristic |
NUBEQA |
Placebo |
|---|---|---|
|
Race |
||
|
White |
128/760 (16.8) |
59/434 (13.6) |
|
Black or African American |
4/28 (14.3) |
3/24 (12.5) |
|
Asian |
16/122 (13.1) |
5/71 (7.0) |
|
Other |
5/45 (11.1) |
3/25 (12.0) |
| Age Group |
||
|
< 65 years |
20/113 (17.7) |
7/84 (8.3) |
|
65 to 74 years |
54/373 (14.5) |
22/216 (10.2) |
|
75 to 84 |
56/384 (14.6) |
27/209 (12.9) |
|
> 85 years |
21/85 (24.7) |
8/45 (17.8) |
Clinical Trial Data
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved NUBEQA based on evidence from one clinical trial (NCT02200614) of 1509 patients with non-metastatic, castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
The trial was conducted in Asia Pacific, Australia, Canada, Europe, Latin America, South Africa, and the United States.
Figure 1 summarizes how many men were in the clinical trial.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
FDA Review
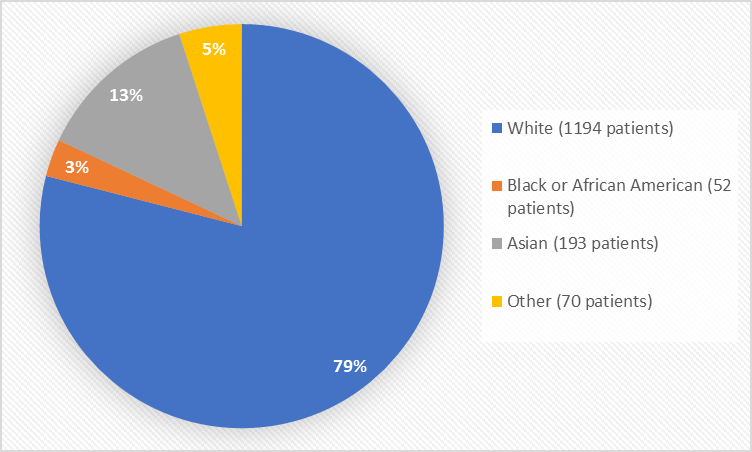
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trial.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
FDA Review
Table 1. Demographics of Clinical Trial by Race
|
Race |
Number of |
Percent |
|
White |
1194 |
79 |
|
Black or African American |
52 |
3 |
|
Asian |
193 |
13 |
|
Other |
15 |
1 |
|
Missing |
55 |
4 |
FDA Review
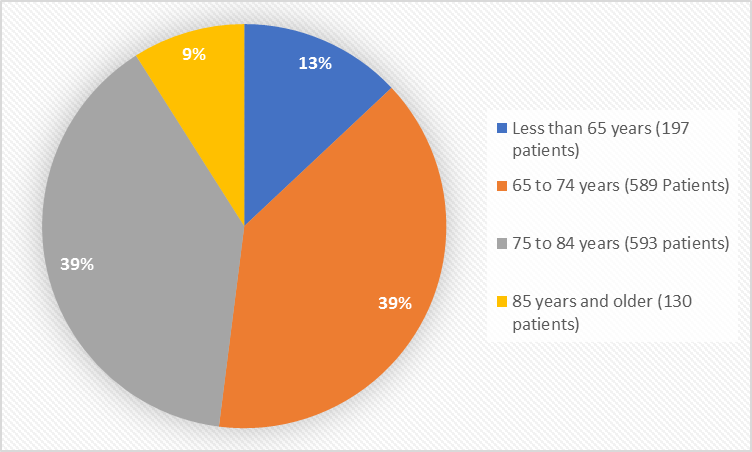
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age groups in the clinical trial.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
The table below shows the trial demographics.
Table 6. Trial Demographics|
|
NUBEQA |
Placebo |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex |
|||
|
Men |
955 (100.0%) |
554 (100.0%) |
1509 (100.0%) |
| Race |
|||
|
White |
760 (79.6%) |
434 (78.3%) |
1194 (79.1%) |
|
Black or African American |
28 (2.9%) |
24 (4.3%) |
52 (3.4%) |
|
Asian |
122 (12.8%) |
71 (12.8%) |
193 (12.8%) |
|
Missing |
36 (3.8%) |
19 (3.4%) |
55 (3.6%) |
|
Other |
9 (0.9%) |
6 (1.1%) |
15 (1.0%) |
| Age Group (years) |
|||
|
<65 |
113 (11.8%) |
84 (15.2%) |
197 (13.1%) |
|
65 – 74 |
373 (39.1%) |
216 (39.0%) |
589 (39.0%) |
|
75 – 84 |
384 (40.2%) |
209 (37.7%) |
593 (39.3%) |
|
≥85 |
85 (8.9%) |
45 (8.1%) |
130 (8.6%) |
| Age (years) |
|||
|
Mean ± SD |
73.9 ± 7.8 |
73.2 ± 8.2 |
73.6 + 8.0 |
|
Median |
74.0 |
74.0 |
74.0 |
|
Range |
48-95 |
50-92 |
48-95 |
| Ethnicity |
|||
|
Hispanic |
32 (3.4%) |
15 (2.7%) |
47 (3.1%) |
|
Not Reported |
923 (96.6%) |
539 (97.3%) |
1462 (96.9%) |
| Geographic Region |
|||
|
Canada |
28 (2.9%) |
17 (3.1%) |
45 (3.0%) |
|
Asia Pacific |
119 (12.5%) |
67 (12.1%) |
186 (12.3%) |
|
United States |
80 (8.4%) |
59 (10.6%) |
139 (9.2%) |
|
Rest of the World |
728 (76.2%) |
411 (74.2%) |
1139 (75.5%) |
Clinical Trial Data
How were the trials designed?
The benefit and side effects of NUBEQA were evaluated in one clinical trial. The trial enrolled men aged 48 to 95 years with prostate cancer that had not spread outside the prostate and that had not responded to castration. Patients were assigned to receive NUBEQA or placebo by mouth twice daily. Neither the patient nor the healthcare provider knew which treatment was given until after the trial was completed. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable side effects. All patients received either hormone therapy or had previous surgery to lower the amount of testosterone in their body.
The benefit of NUBEQA was assessed by measuring the length of time after the start of treatment that the cancer did not spread to other parts of the body and that the patient was still alive (metastasis-free survival [MFS]).
How were the trials designed?
The efficacy and safety of NUBEQA were established in one randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial in men aged 48 to 95 years of age with non-metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer with a prostate specific antigen doubling time (PSADT) of 10 months or less. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive NUBEQA 600 mg or matching placebo orally twice daily. Treatment continued until radiographic disease progression as assessed by BICR, unacceptable toxicity or withdrawal. All patients received a gonadotropin-releasing hormone analog concurrently or had previously undergone a bilateral orchiectomy.
The primary efficacy endpoint was metastasis free survival (MFS). MFS was defined as the time from randomization to the time of first evidence of BICR-confirmed distant metastasis or death due to any cause, whichever occurred first.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.