Drug Trials Snapshots: XCOPRI
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to XCOPRI Prescribing Information for complete information.
XCOPRI (cenobamate)
ex koe' pree
SK Life Science, Inc.
Approval date: November 21, 2019
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
XCOPRI is a drug for the treatment of specific type of seizures called partial-onset seizures in adult patients.
Partial-onset seizures occur when clusters of nerve cells (neurons) undergo uncontrolled activation in a limited area of the brain.
How is this drug used?
XCOPRI is a tablet drug that is taken once daily by mouth. An initial low dose may be increased every two weeks according to a special schedule.
What are the benefits of this drug?
Patients taking XCOPRI had less frequent seizures than patients taking placebo.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The table below summarizes efficacy results for the clinical trials.
Table 1. Percent Change from Baseline in Seizure Frequency per 28 Days in the Treatment Period
| N | Median Percent Change from Baseline in Seizure Frequency per 28 Days (%)ƚ | p-value (Compared to Placebo) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trial 1 | |||
| Placebo | 108 | -21.5 | -- |
| 200 mg/day | 113 | -55.6 | < 0.0001* |
| Trial 2 | |||
| Placebo | 106 | -24.3 | -- |
| 100 mg/day | 108 | -36.3 | 0.006* |
| 200 mg/day | 109 | -55.2 | < 0.001* |
| 400 mg/day | 111 | -55.3 | < 0.001* |
ƚ A negative percent change from baseline in seizure frequency indicates reduction in seizure frequency from baseline.
* Statistically significant compared to placebo
XCOPRI Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: XCOPRI worked similarly in men and women.
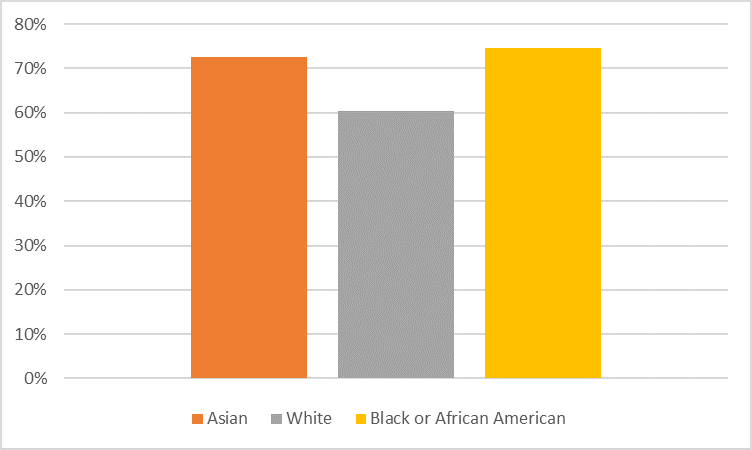
- Race: The majority of patients in the clinical trial were White. Differences in how well XCOPRI worked among different races could not be determined.
- Age: The majority of patients in the clinical trial were younger than 65 years of age. Differences in how well XCOPRI worked between patients below and above 65 years of age could not be determined.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes efficacy results by subgroup. Age differences were not explored because few patients were older than 65 years.
Table 2. Subgroup Analyses of Primary End-Point by Sex
| Trial 1 (ITT populationa) |
Trial 2 (mITT populationa) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seizure frequency per 28 days | XCOPRI 200 mg (N = 113) |
Placebo (N = 108) | XCOPRI 400 mg (N = 111) |
XCOPRI 200 mg (N = 109) |
XCOPRI 100 mg (N = 108) |
Placebo (N = 106) |
| Women | ||||||
| n | 58 | 50 | 59 | 55 | 51 | 50 |
| Median at baseline | 8.2 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 16.0 | 10.0 | 9.3 |
| Median of the treatment period | 4.0 | 9.8 | 4.2 | 6.7 | 6.2 | 8.9 |
| Median percent change from baseline | -58.3 | -17.5 | -53.3 | -55.6 | -44.4 | -21.3 |
| Men | ||||||
| n | 55 | 58 | 52 | 54 | 57 | 56 |
| Median at baseline | 6.5 | 5.3 | 9.8 | 9.3 | 8.0 | 7.8 |
| Median of the treatment period | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 6.1 |
| Median percent change from baseline | -44.7 | -30.4 | -58.9 | -53.5 | -32.2 | -25.9 |
Table 3. Subgroup Analyses of Primary End-Point by Race
| Trial 1 (ITT populationa) |
Trial 2 (mITT populationa) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seizure frequency per 28 days | XCOPRI 200 mg (N = 113) |
Placebo (N = 108) |
XCOPRI 400 mg (N = 111) |
XCOPRI 200 mg (N = 109) |
XCOPRI 100 mg (N = 108) |
Placebo (N = 106) |
| Non-White | ||||||
| N | 56 | 51 | 15 | 16 | 19 | 15 |
| Median at baseline | 6.5 | 5.0 | 8.5 | 10.0 | 7.0 | 8.7 |
| Median of the treatment period | 3.3 | 4.9 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 6.1 | 6.1 |
| Median percent change from baseline | -58.3 | -18.4 | -56.0 | -61.3 | -18.1 | -24.4 |
| White | ||||||
| n | 57 | 57 | 96 | 93 | 89 | 91 |
| Median at baseline | 8.5 | 7.0 | 9.0 | 13.0 | 10.0 | 8.2 |
| Median of the treatment period | 4.0 | 5.3 | 3.7 | 5.8 | 5.8 | 7.1 |
| Median percent change from baseline | -44.7 | -23.5 | -55.0 | -52.5 | -39.5 | -23.4 |
aThe primary efficacy analysis population was called the ITT population in Trial 1 and the mITT population in Trial 2
FDA Statistical Review
What are the possible side effects?
XCOPRI may cause serious side effects including life-threatening allergic reactions (called Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms or DRESS), thoughts about suicide or dying, heart rhythm problems (because of a shortened QT interval), and drowsiness which may impair driving ability.
The most common side effects of XCOPRI are drowsiness, dizziness, feeling tired, double vision, and headache.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes adverse reactions in pooled placebo-controlled adjunctive therapy trials in patients with partial-onset seizures.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions in Pooled Placebo-Controlled Adjunctive Therapy Trials in Patients with Partial-Onset Seizures with XCOPRI Frequency in Any Treatment Arm Greater Than 1% Over Placebo
| Adverse Reaction | XCOPRI | Placebo | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg | 200mg | 400mg | ||
| n = 108 % |
n= 223 % |
n=111 % |
n=216 % |
|
| Cardiac Disorders | ||||
| Palpitations | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Ear and Labyrinth Disorders | ||||
| Vertigo | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 |
| Eye Disorders | ||||
| Diplopia | 6 | 7 | 15 | 2 |
| Vision Blurred | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 6 | 6 | 9 | 3 |
| Constipation | 2 | 4 | 8 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 1 | 3 | 5 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 2 | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Dry Mouth | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Abdominal Pain | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Dyspepsia | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||||
| Nasopharyngitis | 2 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Pharyngitis | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 2 | 5 | 0 | 2 |
| Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications | ||||
| Head Injury | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Alanine Aminotransferase Increased | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase Increased | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Weight Decreased | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
| Decreased Appetite | 3 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Back Pain | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
| Musculoskeletal Chest Pain | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Somnolence | 19 | 22 | 37 | 11 |
| Dizziness | 18 | 22 | 33 | 15 |
XCOPRI Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in men and women
- Race: The occurrence of side effects was similar among tested race groups.
- Age: The majority of patients in the clinical trial were younger than 65 years of age. Differences in side effects between patients below and above 65 years of age could not be determined.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The figures below depict adverse events by sex and race subgroup. Age differences were not explored because few patients were older than 65 years.
Figure 4. Subgroup Analysis of Nervous System SOC Events in Pooled Trials by Sex
Adapted from FDA Clinical Review
Figure 5. Subgroup Analysis of Nervous System SOC Events in Pooled Trials by Race
Adapted from FDA Clinical Review
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved XCOPRI based primarily on evidence from two clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT01866111 and Trial2/NCT01397968) of 655 patients with partial-onset seizures.
The trials were conducted at 147 sites in the USA, Europe, Asia, Australia, Israel, and South Africa.
The figure below summarizes how many men and women were in the clinical trials.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Clinical Trial Data
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trials.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
Clinical Trial Data
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age enrolled in the clinical trials.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Clinical Trial Data
Who participated in the trials?
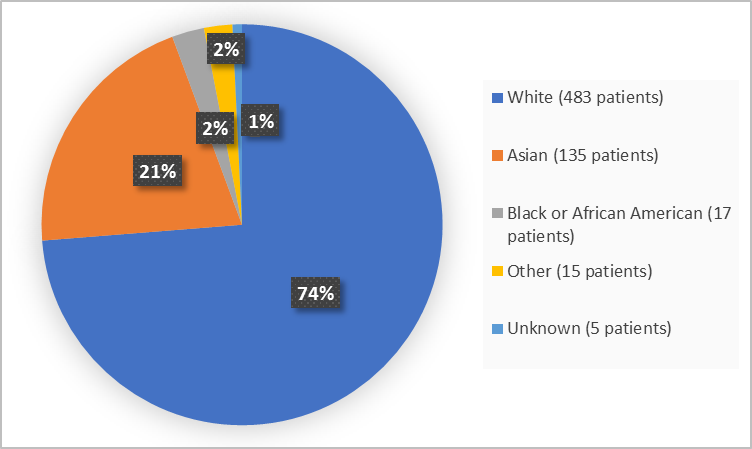
The table below summarizes demographics of patients in the clinical trials.
Table 6. Baseline Demographics of Patients in the Clinical Trials (efficacy population)
| Demographic Characteristic | Trial 1 N=221 |
Trial 2 N=434 |
Total N=655 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Men | 113 (51.1) | 219 (50.5) | 332 (50.7) |
| Women | 108 (48.9) | 215 (49.5) | 323 (49.3) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 114 (51.6) | 369 (85) | 483 (73.7) |
| Black or African American | 5 (2.3) | 12 (2.8) | 17 (2.6) |
| Asian | 94 (42.5) | 41 (9.4) | 135 (20.6) |
| Other | 3 (1.4) | 12 (2.8) | 15 (2.3) |
| Unknown | 5 (2.3) | 0 | 5 (0.8) |
| Age | |||
| Median (Min, Max) | 37 (18,61) | 38 (19,70) | 38 (18,70) |
| Age Group, n (%) | |||
| <65 years | 221 (100) | 424 (97.7) | 645 (98.5) |
| ≥65 years | 0 | 10 (2.3) | 10 (1.5) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 7 (3.2) | 36 (8.3) | 43 (6.5) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 205 (92.8) | 398 (91.7) | 603 (92.1) |
| Not reported | 9 (4.1) | 0 | 9 (1.4) |
| Geographic Region, n (%) | |||
| USA | 86 (38.9) | 109 (25.1) | 195 (29.3) |
| Europe | 43 (19.5) | 250 (57.6) | 293 (44.7) |
| Asia | 41 (18.5) | 39 (9) | 80 (12.2) |
| *Rest of the World | 51 (23.1) | 36 (8.3) | 87 (13.3) |
* Australia, Israel and South Africa
Clinical Trial Data
How were the trials designed?
The benefit and side effects of XCOPRI were evaluated in two clinical trials of patients with partial-onset seizures who were not adequately controlled on their current therapy. Both trials had an 8-week period to assess baseline seizure frequency while patients were taking their usual treatments for seizures. After 8 weeks and in addition to their usual treatments for seizures, patients received either XCOPRI tablets at various doses or placebo tablets for 12 weeks. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which new treatment was being given until after the trial was completed.
The benefit of XCOPRI was evaluated by measuring the difference from baseline in number of seizures per 28 days of treatment and comparing it to the placebo.
Patients from both trials who completed the treatment with either XCOPRI or placebo were eligible to continue taking XCOPRI in order to collect long-term safety data.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of XCOPRI were primarily established in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials. Randomized patients had to have partial-onset seizures that were not adequately controlled with 1 to 3 concomitant antiepileptic drugs.
The trials had an 8-week baseline period followed by a 12-week treatment period. Trial 1 compared a dose of XCOPRI 200 mg/day with placebo. Trial 2 compared doses of XCOPRI 100 mg/day, 200 mg/day, and 400 mg/day with placebo.
The efficacy outcome measure in both trials was the percent reduction from baseline in seizure frequency per 28 days during the treatment period.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.