Drug Trials Snapshots: XADAGO
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the XADAGO Prescribing Information for complete information.
XADAGO (safinamide)
(ZA-da-go)
Newron Pharmaceuticals
Approval date: March 21, 2017
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
XADAGO is a drug for the treatment of “off episodes” in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). XADAGO is to be added to drugs for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease that contain levodopa/carbidopa combination.
An “off” episode” is a time when a patient’s medications are not working well, leading to an increase in Parkinson’s symptoms, such as tremor and difficulty walking.
How is this drug used?
XADAGO is a tablet taken by mouth once a day.
What are the benefits of this drug?
On average, patients taking XADAGO experienced more “ON” time, a time when Parkinson’s symptoms are reduced, without troublesome involuntary movement (dyskinesia), compared to those receiving a placebo.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The tables below summarize the efficacy results for individual trials based on difference in average time without any dyskinesia plus the time with non-troublesome dyskinesia
Table 2. Change in Mean Total Daily “ON” Time† in Trial 1
| N | Baseline (hours) (mean ± SD) | Change from Baseline to Endpoint (LSD* vs. placebo) (95% CI)** p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | 212 | 9.3 ± 2.2 | -- |
| XADAGO 50 mg once daily | 217 | 9.4 ± 2.2 | 0.50 (0.03, 0.96) p=0.0356 |
| XADAGO 100 mg once daily | 216 | 9.6 ± 2.5 | 0.53 (0.07, 1.00) p=0.0238 |
† “ON” Time = “ON” Time without dyskinesia plus “ON” Time with non-troublesome dyskinesia
*LSD: Least squares difference; a positive value indicates improvement
**95% CI: 95% Confidence Interval
XADAGO Prescribing Information
Table 3. Change in Mean Total Daily “ON” Time† in Trial 2
| N | Baseline (hours) (mean ± SD) | Change from Baseline to Endpoint (LSD* vs. placebo) (95% CI)** | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | 273 | 9.1 ± 2.5 | -- | -- |
| XADAGO 100 mg once daily | 270 | 9.3 ± 2.4 | 0.99 (0.58, 1.39) | <> |
† ON time = ON time without dyskinesia plus ON time with non-troublesome dyskinesia
*LSD: Least squares difference; a positive value indicates improvement
**95% CI: 95% Confidence Interval
XADAGO Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: XADAGO worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: XADAGO worked similarly in White and Asian patients. The number of patients of other races was limited; therefore, differences in response could not be determined.
- Age: XADAGO worked similarly in patients above and below age 65.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Subgroup analyses of the primary endpoint by sex, age and race groups are presented below for each trial separately.
Table 4. Analysis of the Primary Endpoint by Sex, MMRM, mITT population-Trial 1
| Sex | Change from Baseline to Week 24 in total daily “on” time | Placebo | XADAGO 50 mg/day | XADAGO 100 mg/day |
| Women | N | 60 | 65 | 59 |
| Means (SD) a | 1.16 (2.191) | 1.15 (2.419) | 1.35 (2.545) | |
| LS mean b | 0.68 | 1.00 | 1.13 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) b | 0.32 (0.455) | 0.45 (0.459) | ||
| Men | N | 152 | 152 | 157 |
| Means (SD) a | 0.90 (2.455) | 1.46 (2.876) | 1.38 (2.669) | |
| LS mean c | 0.77 | 1.47 | 1.36 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) c | 0.70 (0.283) | 0.59 (0.278) |
LS: least squares; mITT: modified intent-to-treat; MMRM: mixed effect model repeated measures; N: number of patients in the mITT population; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error.
a Obtained from all observations in the sex specific mITT population that were on treatment at Week 24, without imputation for missing data.
b Obtained from MMRM on all female patients in the mITT population, with treatment, center, visit, and treatment-by-center interaction as fixed effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach was used.
c Obtained from MMRM on all male patients in the mITT population, with treatment, center, visit, and treatment-by-center interaction as fixed effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach was used.
Adapted from FDA Statistical review
Table 5. Analysis of the Primary Endpoint by Sex, ANCOVA, LOCF, mITT population-Trial 2
| Sex | Change from Baseline to Week 24 in total daily “on” time | Placebo | XADAGO 50-100 mg/day |
| Women | N | 111 | 100 |
| Means (SD) a | 0.59 (2.415) | 1.71 (2.615) | |
| LS mean b | 0.45 | 1.84 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) b | 1.39 (0.330) | ||
| Men | N | 162 | 168 |
| Means (SD) a | 0.50 (2.457) | 1.28 (2.915) | |
| LS mean c | 0.64 | 1.35 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) c | 0.71 (0.269) |
ANCOVA: analysis of covariance; LOCF: last observation carried forward; LS: least squares; mITT: modified intent-to-treat; N: number of patients in the mITT population; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error.
a Obtained from all observations in the sex specific mITT population that were on treatment at Week 24, with LOCF imputation for missing data.
b Obtained from ANCOVA model on all female patients in the mITT population, with treatment and region effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach and the LOCF method were used.
c Obtained from ANCOVA model on all male patients in the mITT population, with treatment and region effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach and the LOCF method were used.
Adapted from FDA Statistical review
Table 6. Analysis of the Primary Endpoint by Age, MMRM, mITT population-Trial 1
| Age | Change from Baseline to Week 24 in total daily “on” time | Placebo | XADAGO 50 mg/day | XADAGO 100 mg/day |
| < 65=""> | N | 143 | 142 | 144 |
| Means (SD) a | 1.01 (2.488) | 1.50 (2.799) | 1.35 (2.538) | |
| LS mean b | 0.77 | 1.38 | 1.31 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) b | 0.60 (0.290) | 0.53 (0.290) | ||
| ≥ 65 years | N | 69 | 75 | 72 |
| Means (SD) a | 0.90 (2.183) | 1.09 (2.642) | 1.42 (2.837) | |
| LS mean c | 0.79 | 1.28 | 1.30 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) c | 0.49 (0.438) | 0.50 (0.440) |
LS: least squares; mITT: modified intent-to-treat; MMRM: mixed effect model repeated measures; N: number of patients in the mITT population; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error.
a Obtained from all observations in the age group specific mITT population that were on treatment at Week 24, without imputation for missing data.
b Obtained from MMRM on all patients < 65="" years="" in="" the="" mitt="" population,="" with="" treatment,="" center,="" visit="" and="" treatment-by-center="" interaction="" as="" fixed="" effects="" and="" baseline="" value="" of="" the="" total="" daily="" “on”="" time="" as="" the="" covariate.="" the="" “on="" treatment”="" approach="" was="">
c Obtained from MMRM on all patients ≥ 65 years in the mITT population, with treatment, center, visit and treatment-by-center interaction as fixed effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach was used.
Adapted from FDA Statistical review
Table 7. Analysis of the Primary Endpoint by Age, ANCOVA, LOCF, mITT population-Trial 2
| Age | Change from Baseline to Week 24 in total daily “on” time | Placebo | XADAGO 50-100 mg/day |
| < 65=""> | N | 156 | 157 |
| Means (SD) a | 0.60 (2.461) | 1.41 (2.883) | |
| LS mean b | 0.50 | 1.45 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) b | 0.96 (0.271) | ||
| ≥ 65 years | N | 117 | 111 |
| Means (SD) a | 0.44 (2.409) | 1.48 (2.714) | |
| LS mean c | 0.50 | 1.57 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) c | 1.08 (0.323) |
ANCOVA: analysis of covariance; LOCF: last observation carried forward; LS: least squares; mITT: modified intent-to-treat; N: number of patients in the mITT population; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error.
a Obtained from all observations in the age group specific mITT population that were on treatment at Week 24, with LOCF imputation for missing data.
b Obtained from ANCOVA model on all patients < 65="" years="" in="" the="" mitt="" population,="" with="" treatment="" and="" region="" effects="" and="" baseline="" value="" of="" the="" total="" daily="" “on”="" time="" as="" the="" covariate.="" the="" “on="" treatment”="" approach="" and="" the="" locf="" method="" were="">
c Obtained from ANCOVA model on all patients ≥ 65 years in the mITT population, with treatment and region effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach and the LOCF method were used.
Table 8. Analysis of the Primary Endpoint by Race, MMRM, mITT population-Trial 1
| Race | Change from Baseline to Week 24 in total daily “on” time | Placebo | XADAGO 50 mg/day | XADAGO 100 mg/day |
| Asian | N | 171 | 176 | 173 |
| Means (SD) a | 1.07 (2.371) | 1.54 (2.702) | 1.49 (2.606) | |
| LS mean b | 0.85 | 1.49 | 1.39 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) b | 0.64 (0.252) | 0.54 (0.250) | ||
| White | N | 41 | 41 | 43 |
| Means (SD) a | 0.61 (2.421) | 0.71 (2.860) | 0.90 (2.713) | |
| LS mean c | 0.41 | 0.56 | 0.93 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) c | 0.15 (0.603) | 0.53 (0.609) |
LS: least squares; mITT: modified intent-to-treat; MMRM: mixed effect model repeated measures; N: number of patients in the mITT population; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error.
a Obtained from all observations in the race specific mITT population that were on treatment at Week 24, without imputation for missing data.
b Obtained from MMRM on all Asian patients in the mITT population, with treatment, center, visit, and treatment-by-center interaction as fixed effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach was used.
c Obtained from MMRM on all White patients in the mITT population, with treatment, center, visit, and treatment-by-center interaction as fixed effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach was used.
Adapted from FDA Statistical review
Table 9. Analysis of the Primary Endpoint by Race, ANCOVA, LOCF, mITT population-Trial 2
| Race | Change from Baseline to Week 24 in total daily “on” time | Placebo | XADAGO 50-100 mg/day |
| Asian | N | 85 | 87 |
| Means (SD) a | 0.71 (2.267) | 1.20 (2.749) | |
| LS mean b | 1.20 | 2.03 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) b | 0.83 (0.323) | ||
| White | N | 186 | 178 |
| Means (SD) a | 0.45 (2.523) | 1.55 (2.862) | |
| LS mean c | 0.50 | 1.60 | |
| LS diff. vs. placebo (SE) c | 1.10 (0.266) |
ANCOVA: analysis of covariance; LOCF: last observation carried forward; LS: least squares; mITT: modified intent-to-treat; N: number of patients in the mITT population; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error.
a Obtained from all observations in the race specific mITT population that were on treatment at Week 24, with LOCF imputation for missing data.
b Obtained from ANCOVA model on all Asian patients in the mITT population, with treatment and region effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach and the LOCF method were used.
c Obtained from ANCOVA model on all White patients in the mITT population, with treatment and region effects and baseline value of the total daily “on” time as the covariate. The “on treatment” approach and the LOCF method were used.
Adapted from FDA Statistical review
What are the possible side effects?
When taken with certain other medications, XADAGO may cause a serious, life- threatening condition called serotonin syndrome. Other serious side effects include an increase in blood pressure, falling asleep during activities of daily living (watching television, driving a car, etc.), hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not real), behavioral problems, and confusion.
The most common side effects are uncontrolled involuntary movements (dyskinesia), fall, nausea, and difficulty sleeping.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes common adverse reactions during clinical trials based on Safety population defined as all patients from Trials 1 and 2 who received at least one dose of the drug.
Table 10. Percentage of Patients with Adverse Reactions with an Incidence ≥ 2% in the XADAGO 100 mg/day Group and Greater than Placebo in Trials 1 and 2
| XADAGO 50 mg/day (N = 223) | XADAGO 100 mg/day (N = 498) | Placebo (N = 497) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | (%) | (%) | (%) |
| Dyskinesia | 21 | 17 | 9 |
| Fall | 4 | 6 | 4 |
| Nausea | 3 | 6 | 4 |
| Insomnia | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| Orthostatic hypotension | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Anxiety | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Cough | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Dyspepsia | 0 | 2 | 1 |
XADAGO Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of some side effects was higher in women than in men.
- Race: The occurrence of side effects was similar between White and Asian patients. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in side effects among other races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar in patients above and below age 65.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes “dyskinesia” adverse reaction in the Safety population defined as all patients who received at least at least one dose of the drug.
Table 11. Subgroup Analysis of Adverse Reaction “Dyskinesia”
| Demographic Subgroup | XADAGO N=721 x/n* (%) | Placebo N=497 x/n* (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Age Group | ||
| Race | ||
| Overall | 134/721 (17) | 44/497 (9) |
| Men | 84/491 (17) | 30/323 (9) |
| Women | 50/230 (22) | 14/174 (8) |
| <65> | 92/454 (20) | 33/307 (11) |
| >= 65 years | 42/267 (16) | 11 /190 (6) |
| White | 46/271 (17) | 18/230 (8) |
| Asian | 88/447 (20) | 26/265 (10) |
| Black or African American | 0/3 (0) | 0/2 (0) |
Clinical trial data
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved XADAGO based on evidence from two clinical trials of 1218 patients with PD whose symptoms were not well controlled while receiving their regular PD treatment. The trials were conducted in 178 centers in North America, Europe, Asia and Latin America.
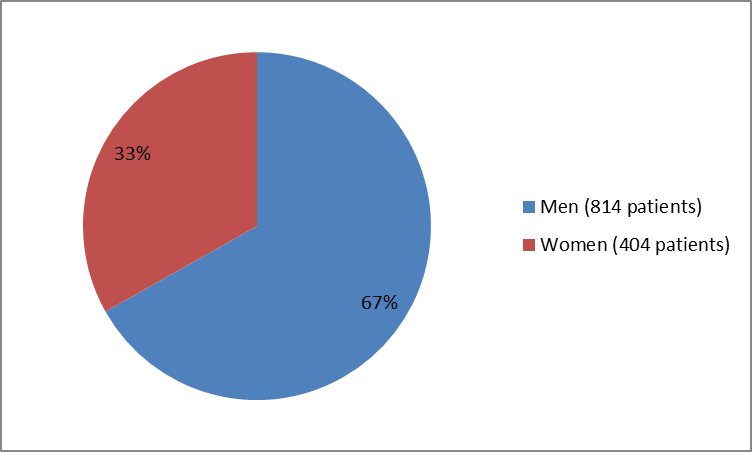
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were enrolled in the clinical trials.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Clinical trial data
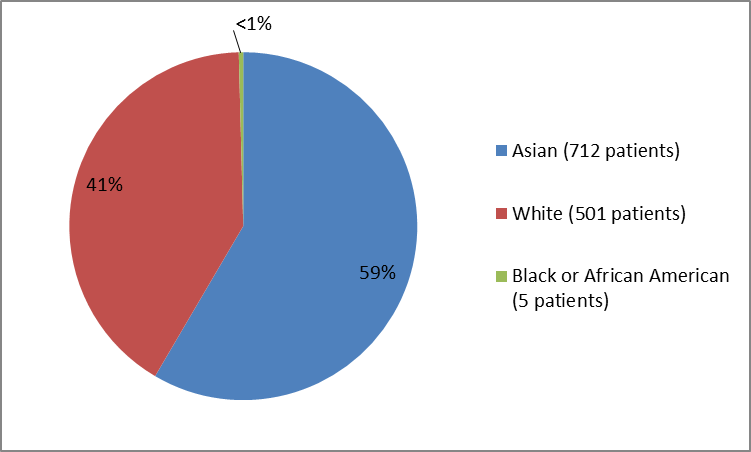
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trials.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
Clinical trial data
Table 1. Baseline Demographics by Race
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Asian | 712 | 59 |
| White | 501 | 41 |
| Black or African American | 5 | less than 1 |
Clinical trial data
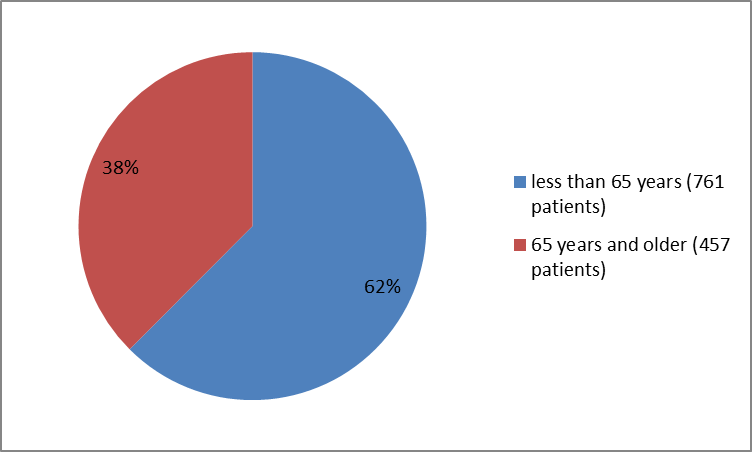
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age that were enrolled in the clinical trials.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Clinical trial data
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes demographics of all randomized patients in clinical Trials 1 and 2 combined.
Table 12. Baseline and Demographics (Randomized Population)
| XADAGO N=721 | Placebo N=497 | Total N=1218 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||
| Age Group, n (%) | |||
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Race, n (%) | |||
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Geographic Region, n (%) | |||
| Min, Max | 35, 80 | 30, 79 | 30, 80 |
| Median | 61 | 61 | 61 |
| <65> | 454 (63) | 307 (62) | 761 (62) |
| ≥ 65 years | 267 (37) | 190 (38) | 457 (38) |
| Men | 491 (68) | 323 (65) | 814 (67) |
| Women | 230 (32) | 174 (35) | 404 (33) |
| White | 271 (38) | 230 (46) | 501 (41) |
| Asian | 447 (62) | 265 (53) | 712 (58) |
| Black or African American | 3 (<> | 2 (<> | 5 (<> |
| Hispanic or Latino | 12 (2) | 9 (2) | 21 (2) |
| Non-Hispanic or Latino | 709 (98) | 488 (98) | 1197 (98) |
| North America | 51 (7) | 51 (10) | 102 (8) |
| Western Europe | 126 (18) | 117 (24) | 243 (20) |
| Other | 544 (76) | 329 (66) | 873 (72) |
Clinical trial data
How were the trials designed?
There were two 24-week trials conducted in PD patients with inadequate control of their Parkinson’s symptom (“OFF” time) while receiving carbidopa/levodopa and other PD medications. Patients were randomly selected to receive either XADAGO or placebo pill once a day for 24 weeks. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which new treatment was being given until the trial was completed 24 weeks later.
In both trials, the benefit was evaluated by measuring the change from baseline in total daily “ON” time in XADAGO and placebo receiving patients. “ON” time was defined as time without any dyskinesia plus the time with non-troublesome dyskinesia and was based on the 18-hour diaries completed by patients for at least 3 days before each of the scheduled visits.
How were the trials designed?
Two double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-national, 24-week trials (Trials 1 and 2) were conducted in PD patients experiencing “OFF” time during treatment with carbidopa/levodopa and other PD medications.
In both trials, the primary measure of effectiveness was the change from baseline in total daily “ON” time without troublesome dyskinesia (i.e., “ON” time without dyskinesia plus “ON” time with non-troublesome dyskinesia), based on the 18-hour diaries completed by patients for at least 3 days before each of the scheduled visits.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION