Drug Trials Snapshots: UPTRAVI
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the UPTRAVI Prescribing Information for complete information.
UPTRAVI (selexipag)
up-TRA-vee
Actelion Therapeutics
Approval date: December 21, 2015
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
UPTRAVI is a drug used for the treatment of adults with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare, chronic, and progressive lung disease in which there is abnormally high blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, the blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the lungs. PAH can lead to death or the need for transplantation.
How is this drug used?
UPTRAVI is a tablet that is taken two times a day.
What are the benefits of this drug?
UPTRAVI slowed down the progression of the disease and lowered the risk of being hospitalized for PAH.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The table below summarizes efficacy results for the clinical trial.
Table 2. Combined Efficacy in the Clinical Trial (efficacy population*)
| UPTRAVI N = 574 n (%) | Placebo N = 582 n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Patients with a primary endpoint event** | 155 (27.0) | 242 (41.6) |
| Component as first event Hospitalization for PAH Disease Progression Death i.v./s.c. prostanoid or chronic oxygen therapy Need for lung transplantation or atrial septostomy | 78 (13.6) 38 (6.6) 28 (4.9) 10 (1.7) 1 (0.2) | 109 (18.7) 100 (17.2) 18 (3.1) 13 (2.2) 2 (0.3) |
*includes 4 randomized patients who were not dosed
**p>
i.v. = intravenous, PAH = pulmonary arterial hypertension, s.c. = subcutaneous.
UPTRAVI Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
Subgroup analyses were conducted for sex, race, and age.
- Sex: UPTRAVI worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: Most of the patients in the trial were White and Asian. Differences in response to UPTRAVI among races could not be determined.
- Age: UPTRAVI worked similarly in patients below and above 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
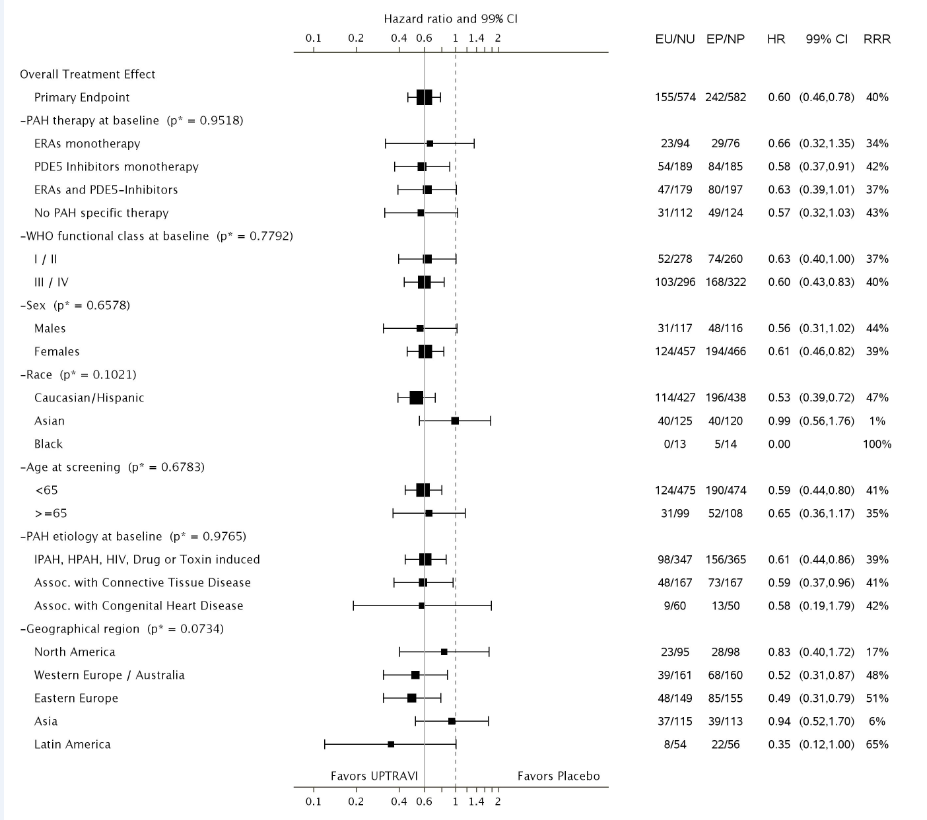
The table below summarizes efficacy results by subgroup.
Figure 4. Subgroup Efficacy Analysis (efficacy population*)
*includes 4 randomized patients who were not dosed
UPTRAVI Prescribing Information
What are the possible side effects?
The most common side effects are headache, diarrhea, jaw pain, nausea, muscle pain, vomiting, pain in the arms and legs, and flushing.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes adverse reactions in the clinical trial.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions More Frequent on UPTRAVI than on Placebo by >3% (safety population)
| Adverse Reaction | UPTRAVI N=575 | Placebo N=577 |
|---|---|---|
| Headache | 65% (375) | 32% (182) |
| Diarrhea | 42% (244) | 18% (106) |
| Jaw pain | 26% (148) | 6% (33) |
| Nausea | 33% (192) | 18% (105) |
| Myalgia | 16% (92) | 6% (34) |
| Vomiting | 18% (104) | 9% (49) |
| Pain in Extremity | 17% (97) | 8% (44) |
| Flushing | 12% (70) | 5% (28) |
| Arthralgia | 11% (62) | 8% (44) |
| Anemia | 8% (48) | 5% (31) |
| Decreased appetite | 6% (34) | 3% (19) |
| Rash | 11% (64) | 8% (48) |
UPTRAVI Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
Subgroup analyses were conducted for sex, race, and age.
- Sex: The risk of side effects was similar in men and women.
- Race: Most of the patients in the trials were White and Asian. The risk of side effects was similar in Whites and Asians. Differences in side effects among other races could not be determined.
- Age: The risk of side effects was similar in patients below and above 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
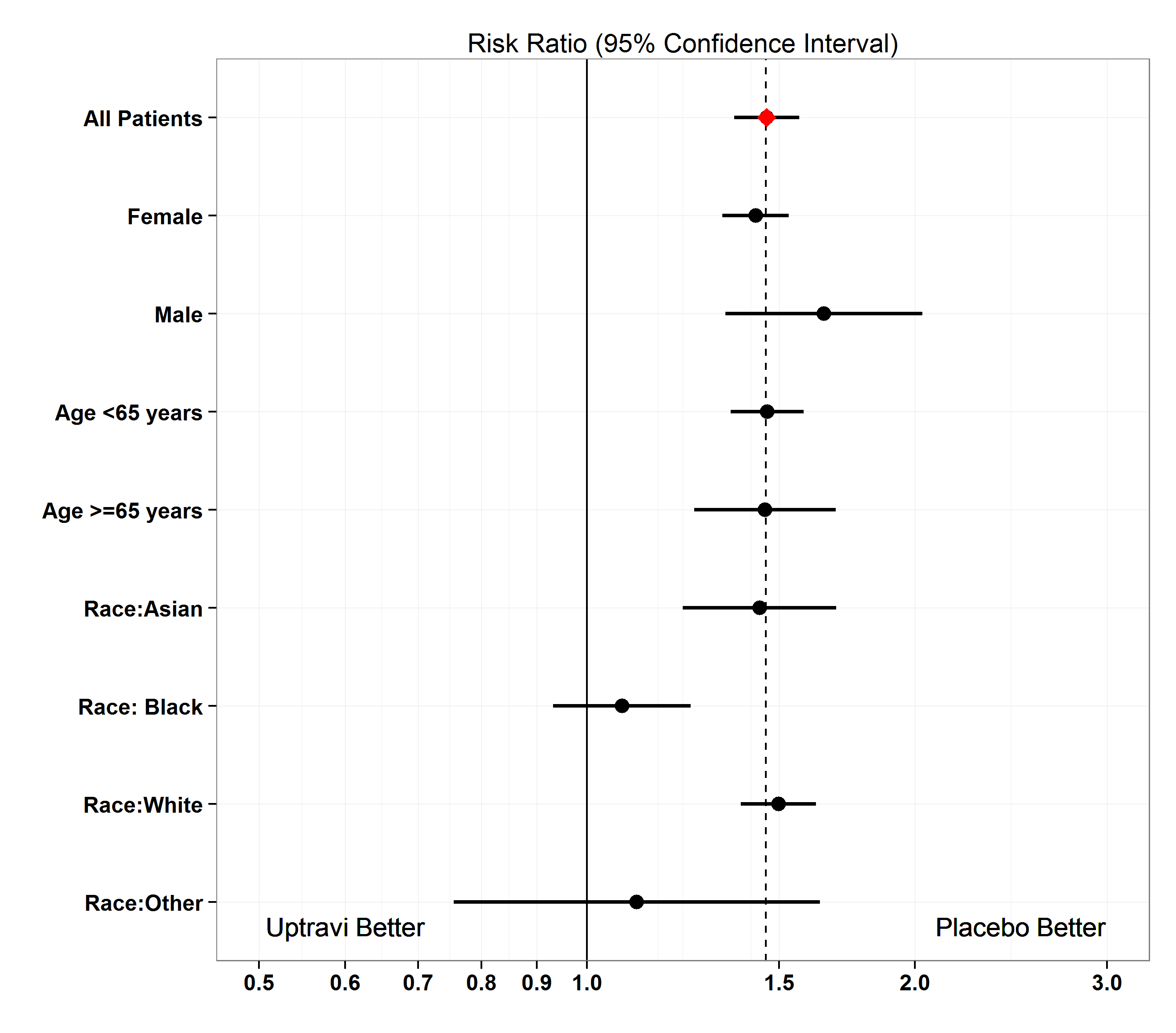
The table below summarizes combined adverse reactions from the Table 4 by subgroup.
Figure 5. Subgroup Analysis of Adverse Reactions (safety population)
Clinical trial data
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved UPTRAVI based on the evidence from one clinical trial of 1156 patients with PAH. The trial was conducted in North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Australia, and Asia.
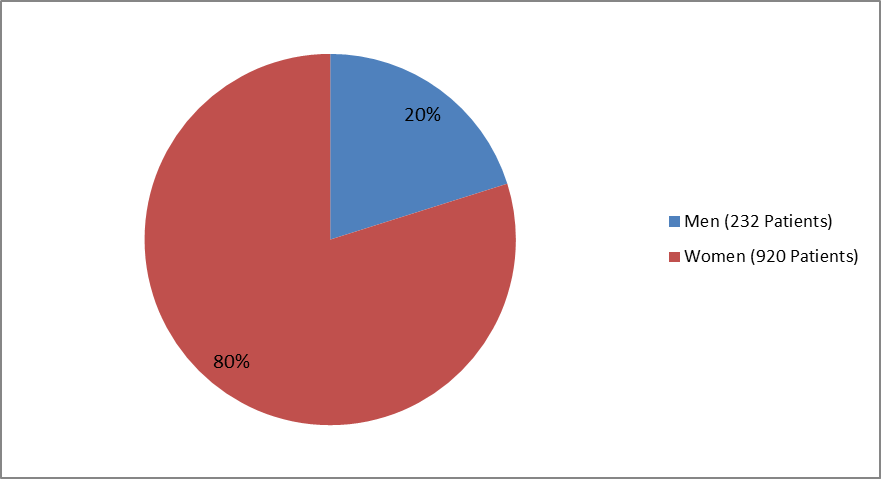
The figure below summarizes how many men and women were in the clinical trial.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex (safety population)
Clinical trial data
Figure 2 and Table 1 summarize the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race (safety population)
Clinical trial data
Table 1. Demographics of Trials by Race (safety population)
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 861 | 75% |
| Black or African American | 27 | 2% |
| Asian | 245 | 21% |
| Other | 19 | 2% |
Clinical trial data
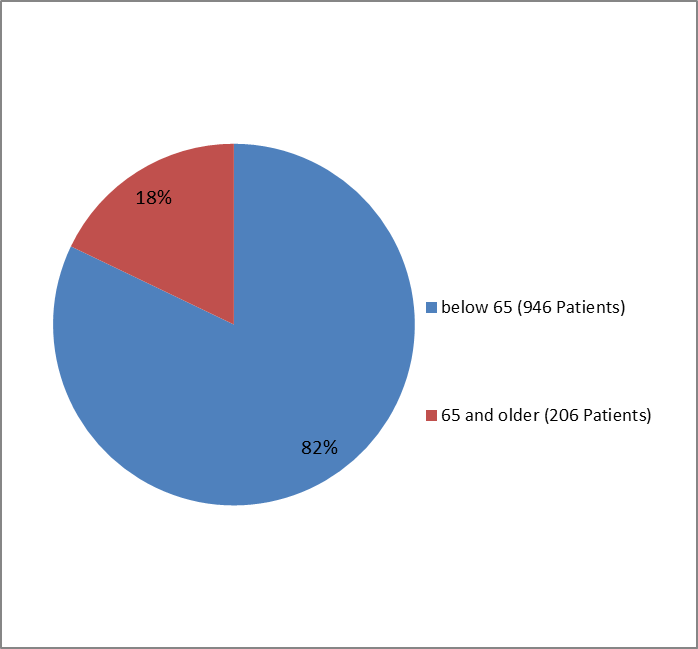
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age in the clinical trial.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age (safety population)
Clinical trial data
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes demographics of patients in the clinical trial.
Table 6. Baseline Demographics of Patients in the Clinical Trials (safety population)
| Demographic Subgroup | UPTRAVI (N=575) | Placebo (N=577) | Total (N=1152) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 117 (20.3%) | 115 (19.9%) | 232 (20.1%) |
| Female | 458 (79.7%) | 462 (80.1%) | 920 (79.9%) |
| Age Group, n (%) | |||
| 18 - 64 years | 476 (82.8%) | 470 (81.5%) | 946 (82.1%) |
| >=65 years | 99 (17.2%) | 107 (18.5%) | 206 (17.9%) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 428 (74.4%) | 433 (75.0%) | 861 (74.7%) |
| Black or African American | 13 (2.3%) | 14 (2.4%) | 27 (2.3%) |
| Asian | 125 (21.7%) | 120 (20.8%) | 245 (21.3%) |
| Other | 9 (1.6%) | 10 (1.7%) | 19 (1.6%) |
Clinical trial data
How were the trials designed?
The benefits and side effects of UPTRAVI were evaluated in one clinical trial. The patients received either UPTRAVI or placebo. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trials were completed. The benefit of UPTRAVI was evaluated by measuring the time to the first occurrence of either death, hospitalization for PAH, or PAH worsening.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of UPTRAVI were established in 1156patients who were treated in one multi-center, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group, event-driven trial. The patients had symptomatic PAH World Health Organization Functional Class I-IV.
The primary efficacy outcome was the time to first occurrence up to end-of-treatment of: a) death, b) hospitalization for PAH, c) PAH worsening resulting in need for lung transplantation, or balloon atrial septostomy, d) initiation of parenteral prostanoid therapy or chronic oxygen therapy, or e) other disease progression based on a 15% decrease from baseline in 6-Minute Walk Distance plus worsening of Functional Class or need for additional PAH-specific therapy.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.