Drug Trials Snapshots: BYFAVO
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the BYFAVO Prescribing Information for complete information.
BYFAVO (remimazolam)
by-FAV-o
Acacia Pharma
Approval date: July 2, 2020
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
BYFAVO is a drug used to start and maintain sedation in adults undergoing short (less than 30 minutes) procedures.
How is this drug used?
BYFAVO is given as an injection through a vein (intravenous) by a healthcare provider.
What are the benefits of this drug?
BYFAVO provides sedation in adult patients undergoing short procedures.
What are the benefits of this drug?
The tables below depict efficacy results from the individual trials. Patients were defined to be treatment successes if they met all of the following criteria:
- No rescue sedative medication usage;
- Successful completion of the study procedure;
- No more than 5 top-up doses within any 15-minute window (BYFAVO or placebo);
Table 1. Colonoscopy Sedation Success Rate – Trial 1
| Cohort | Sedation Success Rate n/N (%) |
|---|---|
| BYFAVO | 272/298 (91.3%) |
| Placebo | 1/60 (1.7%) |
n/N = number of successes/number of patients in group
Table 2. Bronchoscopy Success Rates-Trial 2
| Cohort | Total Success Rate n/N (%) |
|---|---|
| BYFAVO | 250/310 (80.6%) |
| Placebo | 3/63 (4.8%) |
n/N = number of successes/number of patients in group
Colonoscopy Sedation Success Rate –Trial 3
Patients who received BYFAVO for sedation during scheduled colonoscopy responded at a numerically greater rate than patients who received placebo (randomized analysis population – BYFAVO: 27/32 [84.4%]; placebo: 5/16 [15.6%]).
BYFAVO Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: BYFAVO worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: BYFAVO worked similarly in White and Black or African American patients.
- Age: BYFAVO worked similarly in patients below and above 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Subgroup efficacy analyses based on sedation success rates are presented below.
Table 3. Bayesian Logistic Regression Analyses of the Success Rates by Demographic Subgroup – Trial 1
| Posterior Mean | SD | 2.5% Percentile |
Posterior Median | 97.5% Percentile |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 0.898 | 0.028 | 0.831 | 0.902 | 0.940 | |
| Sex | Women | 0.874 | 0.038 | 0.785 | 0.879 | 0.933 |
| Men | 0.928 | 0.030 | 0.852 | 0.934 | 0.972 | |
| Race | White | 0.890 | 0.029 | 0.823 | 0.894 | 0.936 |
| Black or African American | 0.928 | 0.039 | 0.836 | 0.935 | 0.985 | |
| Other | 0.925 | 0.061 | 0.780 | 0.937 | 0.992 | |
| Age | < 65 years | 0.887 | 0.028 | 0.823 | 0.889 | 0.932 |
| ≥ 65 years | 0.975 | 0.040 | 0.876 | 0.986 | 1.000 |
Table 4. Bayesian Logistic Regression Analyses of the Success Rates by Demographic Subgroup – Trial 2
| Posterior Mean | SD | 2.5% Percentile |
Posterior Median | 97.5% Percentile |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 0.793 | 0.037 | 0.710 | 0.796 | 0.856 | |
| Sex | Women | 0.795 | 0.039 | 0.703 | 0.799 | 0.863 |
| Men | 0.804 | 0.054 | 0.680 | 0.816 | 0.878 | |
| Race | White | 0.787 | 0.037 | 0.707 | 0.792 | 0.848 |
| Black or African American | 0.803 | 0.083 | 0.601 | 0.817 | 0.928 | |
| Other | 0.897 | 0.082 | 0.694 | 0.918 | 0.992 | |
| Age | < 65 years | 0.791 | 0.043 | 0.707 | 0.797 | 0.866 |
| ≥ 65 years | 0.782 | 0.053 | 0.672 | 0.787 | 0.868 |
Table 5. Bayesian Logistic Regression Analyses of the Success Rates by Demographic Subgroup – Trial 3
| Posterior Mean | SD | 2.5% Percentile |
Posterior Median | 97.5% Percentile |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 0.880 | 0.059 | 0.746 | 0.889 | 0.968 | |
| Sex | Women | 0.816 | 0.103 | 0.572 | 0.835 | 0.964 |
| Men | 0.978 | 0.039 | 0.865 | 0.994 | 1.000 | |
| Race | White | 0.853 | 0.071 | 0.692 | 0.864 | 0.961 |
| Black or African American | 0.991 | 0.039 | 0.901 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| Age | < 65 years | 0.833 | 0.097 | 0.601 | 0.849 | 0.971 |
| ≥ 65 years | 0.938 | 0.064 | 0.763 | 0.958 | 0.999 |
FDA Statistical Review
What are the possible side effects?
BYFAVO may cause serious side effects including:
- Severe and life-threatening allergic reactions;
- Like other similar drugs, BYFAVO may cause sedation in newborns after being used during pregnancy;
- Life-threatening, deep sedation if used with opiates.
The most common adverse reactions are low blood pressure, high blood pressure and low blood oxygen level (hypoxia).
What are the possible side effects?
The table below summarizes adverse reactions in the individual trials.
Table 6. Common Adverse Reactions in Colonoscopy Trial 1 (Incidence > 2%), ASA PS Class I to III
| Adverse Reaction | BYFAVO N = 296 n (%) |
Placebo* (with Midazolam Rescue‡) N = 60 n (%) |
Midazolam N = 102 n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypotension§ | 115 (39%) | 25 (42%) | 63 (62%) |
| Hypertension† | 59 (20%) | 17 (28%) | 18 (18%) |
| Bradycardia | 33 (11%) | 7 (12%) | 16 (16%) |
| Diastolic Hypertension† | 29 (10%) | 6 (10%) | 9 (9%) |
| Tachycardia | 23 (8%) | 7 (12%) | 13 (13%) |
| Diastolic Hypotension§ | 23 (8%) | 4 (7%) | 9 (9%) |
| Systolic Hypertension† | 16 (5%) | 5 (8%) | 6 (6%) |
ASA-PS=American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status
‡ 57/60 (95%) patients received midazolam rescue.
† Hypertension defined as an increase in systolic BP to ≥ 180 mmHg or in diastolic BP to ≥ 100 mmHg, or an increase of systolic or diastolic BP of 20% or more over baseline or necessitating medical intervention.
§ Hypotension defined as a fall in systolic BP to ≤ 80 mmHg or in diastolic BP to ≤ 40 mmHg, or a fall in systolic or diastolic BP of 20% or more below baseline or necessitating medical intervention.
Table 7. Common Adverse Reactions in Bronchoscopy Trial 2 (Incidence > 2%)
| Adverse Event | BYFAVO N = 303 n (%) |
Placebo (with Midazolam Rescue‡) N = 59 n (%) |
Midazolam N = 69 n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypotension§ | 99 (33%) | 28 (47%) | 23 (33%) |
| Hypertension† | 85 (28%) | 9 (15%) | 19 (28%) |
| Diastolic hypertension† | 77 (25%) | 15 (25%) | 16 (23%) |
| Systolic hypertension† | 67 (22%) | 13 (22%) | 17 (25%) |
| Hypoxia | 66 (22%) | 12 (20%) | 13 (19%) |
| Respiratory rate increased | 43 (14%) | 6 (10%) | 10 (14%) |
| Diastolic hypotension§ | 41 (14%) | 17 (29%) | 16 (23%) |
| Nausea | 12 (4%) | 2 (3%) | 2 (3%) |
| Bradycardia | 11 (4%) | 4 (7%) | 4 (6%) |
| Pyrexia | 11 (4%) | 1 (2%) | 1 (1%) |
| Headache | 8 (3%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (4%) |
‡ 57/59 (97%) patients received midazolam rescue.
† Hypertension defined as an increase in systolic BP to ≥ 180 mmHg or in diastolic BP to ≥ 100 mmHg, or an increase of systolic or diastolic BP of 20% or more over baseline or necessitating medical intervention.
§ Hypotension defined as a fall in systolic BP to ≤ 80 mmHg or in diastolic BP to ≤ 40 mmHg, or a fall in systolic or diastolic BP of 20% or more below baseline or necessitating medical intervention.
Table 8. Common Adverse Reactions in Colonoscopy Trial 3 (Incidence > 2%), ASA PS Class III and IV
| Adverse Event | BYFAVO N = 31 n (%) |
Placebo (with Midazolam Rescue‡) N = 16 n (%) |
Midazolam N = 30 n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypotension§ | 18 (58%) | 11 (69%) | 17 (57%) |
| Hypertension† | 13 (42%) | 6 (38%) | 13 (43%) |
| Respiratory acidosis | 6 (19%) | 2 (13%) | 8 (27%) |
| Diastolic hypertension† | 3 (10%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Systolic hypertension† | 2 (6%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Bradycardia | 1 (3%) | 1 (6%) | 4 (13%) |
| Respiratory rate decreased | 1 (3%) | 1 (6%) | 2 (7%) |
| Diastolic hypotension§ | 1 (3%) | 1 (6%) | 0 (0%) |
| Blood pressure diastolic increased | 1 (3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Blood pressure increased | 1 (3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Blood pressure systolic increased | 1 (3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 1 (3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
‡ 16/16 (100%) patients received midazolam rescue.
† Hypertension defined as an increase in systolic BP to ≥ 180 mmHg or in diastolic BP to ≥ 100 mmHg, or an increase of systolic or diastolic BP of 20% or more over baseline or necessitating medical intervention.
§ Hypotension defined as a fall in systolic BP to ≤ 80 mmHg or in diastolic BP to ≤ 40 mmHg, or a fall in systolic or diastolic BP of 20% or more below baseline or necessitating medical intervention.
BYFAVO Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in men and women.
- Race: The occurrence of side effects was similar in White and Black or African American patients.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was higher in patients 65 years of age and above compared to those below 65 years.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below summarize subgroup analyses for the most common adverse events.
Table 9. Subgroup Analysis of Selected Adverse Events by Sex in Pooled Clinical Trials
| Preferred Term | BAYFAVO | Midazolam | Placebo | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men N=303 | Women N=327 | Men N=95 |
Women N=106 | Men N=61 |
Women N=74 | |
| Any TEAE | 76% | 87% | 91% | 91% | 79% | 87% |
| Hypotension | 36% | 38% | 53% | 50% | 51% | 45% |
| Hypertension | 24% | 26% | 23% | 26% | 26% | 22% |
| Bradycardia | 8% | 6% | 10% | 14% | 5% | 12% |
| Hypoxia | 10% | 12% | 10% | 5% | 12% | 10% |
Table 10. Subgroup Analysis of Selected Adverse Events by Race in Pooled Clinical Trials
| Preferred Term | BAYFAVO | Midazolam | Placebo | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White N=508 | Black N=91 |
White N=144 | Black N=43 | White N=102 |
Black N=27 |
|
| Any TEAE | 83% | 75% | 90% | 93% | 82% | 85% |
| Hypotension | 37% | 37% | 51% | 47% | 46% | 48% |
| Hypertension | 26% | 24% | 25% | 26% | 21% | 37% |
| Bradycardia | 7% | 7% | 13% | 9% | 8% | 11% |
| Hypoxia | 13% | 4% | 8% | 7% | 10% | 11% |
Table 11. Subgroup Analysis of Selected Adverse Events by Age in Pooled Clinical Trials
| Preferred Term | BAYFAVO | Midazolam | Placebo | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <65 y N=426 |
65-74y N=154 |
≥75 y N=50 |
<65 y N=143 |
65-74y N=44 |
≥75 y N=14 |
<65y N=94 |
65-74y N=32 |
≥75 y N=9 |
|
| Any TEAE | 78% | 89% | 94% | 90% | 93% | 93% | 82% | 91% | 67% |
| Hypotension | 35% | 41% | 38% | 52% | 48% | 50% | 46% | 53% | 44% |
| Hypertension | 23% | 27% | 38% | 19% | 41% | 36% | 25% | 28% | 0% |
| Bradycardia | 9% | 5% | 0% | 13% | 9% | 14% | 9% | 6% | 22% |
| Hypoxia | 6% | 19% | 26% | 6% | 7% | 21% | 10% | 9% | 22% |
TEAE=treatment emergent adverse event
Adapted from FDA Review
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the trials?
The FDA approved BYFAVO based on evidence from three clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT02290873, Trial 2/NCT02296892 and Trial 3/NCT02532647) in adult patients undergoing short procedures. Trials were conducted at 32 sites in the United States.
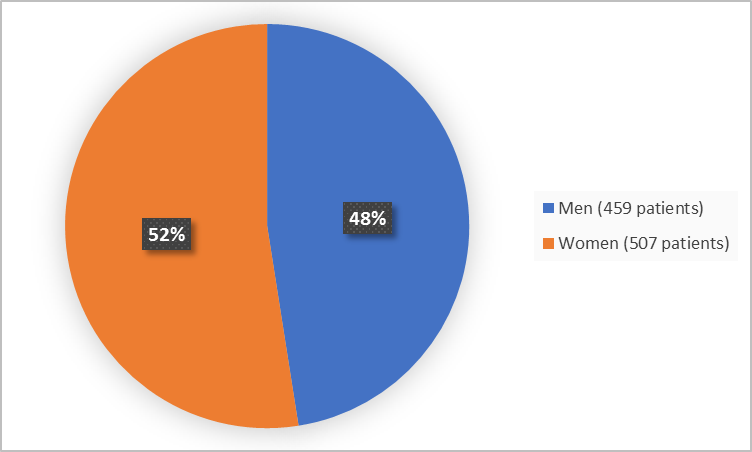
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were in the clinical trials used to evaluate the side effects of BYFAVO (also called the Safety Population).
Figure 1. Demographics by Sex (Safety Population)
Adapted from FDA Review
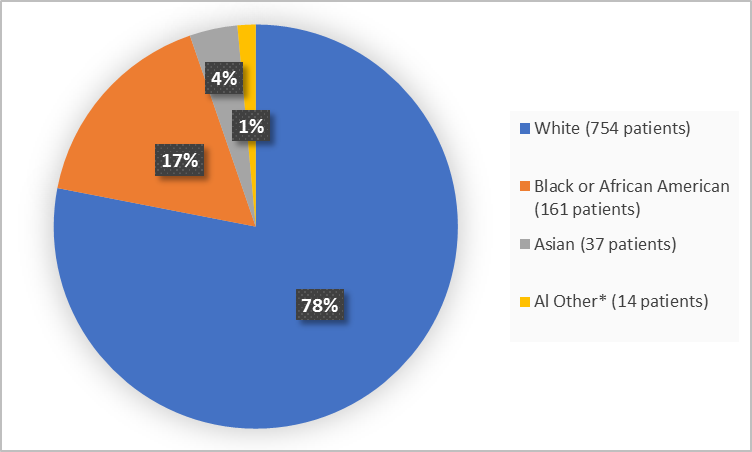
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trials used to evaluate the side effects of BYFAVO.
Figure 2. Demographics by Race (Safety Population)
*includes American Indian or Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, Multiple and Other
Adapted from FDA Review
The figure below summarizes how many patients by age were in the trials used to evaluate the side effects of BYFAVO.
Figure 3. Demographics by Age (Safety Population)
Adapted from FDA Review
The figure below summarizes how many patients by ethnicity were in the trials used to evaluate the side effects of BYFAVO.
Figure 4. Demographics by Ethnicity (Safety Population)
Adapted from FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes the demographics for patients in the pooled safety population.
Table 12. Demographics for the Clinical Trials 1-3 (Safety Population)
| Demographic Category | Trial 1 N=458 |
Trial 2 N=431 |
Trial 3 N=77 |
Total N=966 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | ||||
| Men | 218 (48) | 198 (46) | 43 (56) | 459 (48) |
| Women | 240 (52) | 233 (54) | 34 (44) | 507 (52) |
| Race, n (%) | ||||
| White | 339 (74) | 358 (83) | 57 (74) | 754 (78) |
| Black or African American | 80 (17) | 62 (14) | 19 (25) | 161 (17) |
| Asian | 31 (7) | 5 (1) | 1 (1) | 37 (4) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 1(<1) | 1(<1) | 0 | 2 (<1) |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 1 (<1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (<1) |
| Multiple | 2 (<1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (<1) |
| Other | 4 (1) | 5 (1) | 0 | 9 (1) |
| Age (years) | ||||
| Median | 56 | 64 | 63 | 59 |
| Min, Max | 19,92 | 22, 95 | 42,84 | 19, 95 |
| Age category, n (%) | ||||
| <65 years | 395 (86) | 222 (52) | 46 (60) | 663 (69) |
| ≥ 65 years | 63 (14) | 209 (48) | 31 (40) | 303 (31) |
| ≥ 75 years | 3 (1) | 63 (15) | 7 (9) | 73 (8) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | ||||
| Hispanic or Latino | 73 (16) | 8 (2) | 0 | 81 (8) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 385 (84) | 423 (92) | 77 (100) | 885 (92) |
| Region n (%), | ||||
| USA | 458 (100) | 431 (100) | 77 (100) | 966 (100) |
Adapted from FDA Review
How were the trials designed?
There were three clinical trials that provided data for BYFAVO approval.
Trials 1 and 3 were conducted in patients undergoing colonoscopy and Trial 2 was conducted in patients undergoing bronchoscopy procedures.
In the trials, patients were randomly divided in three groups: one group received BYFAVO, one group received placebo and one group received midazolam (similar, but approved drug). In the first two groups, neither patients nor investigators knew which medications were given and patients could also receive midazolam as a rescue drug when needed for sedation. In the third group, all patients received midazolam only. Additionally, in all three trials patients received a medication for pain control.
Trials 1 and 2 compared patients who received BYFAVO to patients in the other two groups, measuring the success of sedation with the set of pre-determined criteria. Data from Trial 3 were used primarily to assess the side effects of BYFAVO when multiple dosing is used.
How were the trials designed?
FDA approved BYFAVO based on three, randomized, double-blind, multi-center trials conducted in adult patients receiving procedural sedation.
Trials 1 and 2 were conducted in American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status (ASA PS) class I to III patients undergoing colonoscopy or bronchoscopy, respectively. BYFAVO 5 mg (2 mL) i.v. was administered as an initial bolus, followed by 2.5 mg (1 mL) top-up doses versus placebo 2 mL administered as an initial bolus, followed by 1 mL top-up doses. Midazolam rescue was dosed per investigator discretion in both treatment groups. Fentanyl was administered as an analgesic pre-treatment at an initial dose of 50 to 75 mcg i.v. (or a reduced dose for debilitated patients) immediately prior to administration of the initial dose of study medication.
The primary efficacy endpoint for BYFAVO versus placebo in both trials was success of the procedure, defined as a composite of the following:
- Completion of the procedure, and
- No requirement for a rescue sedative medication, and
- No requirement for more than 5 doses of study medication within any 15-minute window.
Trial 3 was conducted in ASA PS class III and IV patients undergoing colonoscopy. BYFAVO 2.5 mg (1 mL) to 5 mg (2 mL) i.v. was administered as an initial bolus, followed by 1.25 mg (0.5 mL) to 2.5 mg (1 mL) top-up doses versus placebo 1 to 2 mL administered with midazolam rescue, dosed per investigator discretion. Fentanyl was administered as an analgesic pre-treatment at an initial maximum dose of 50 mcg (with dose reduction for debilitated patients), immediately prior to administration of the initial dose of study medication. The primary objective of this trial was to assess the safety of multiple doses of BYFAVO compared to placebo and midazolam. Procedure success was a secondary objective.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION