Drug Trials Snapshots: Axumin
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to AXUMIN Prescribing Information for complete information.
AXUMIN (fluciclovine F 18)
(ax ue' min)
Blue Earth Diagnostics
Approval date: May 27, 2016
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
AXUMIN is a drug for detection of prostate cancer recurrence in men who have been treated for prostate cancer but have persistently high prostate specific antigen (PSA) in their blood.
High PSA in the blood of these patients is a suspicious sign that cancer is coming back or spreading.
How is this drug used?
AXUMIN is an injection given by a health care provider in the vein (intravenous) in preparation for an imaging test that can help detect cancer (called positron emission tomography or PET scan imaging).
What are the benefits of this drug?
PET imaging done after AXUMIN injection showed sites of prostate cancer recurrence.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The tables below summarize efficacy results for the clinical Trial 1 based on 105 AXIUM scans in comparison to histopathology results from biopsy of the prostate bed and biopsies of lesions suspicious by imaging.
Table 2. Performance of AXUMIN in Patients with Biochemically Suspected Recurrent Prostate Cancer, at the Patient Level and at the Prostate Bed and Extraprostatic Region Levels
| Reader 1 | Reader 2 | Reader 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | N = 104 | N = 105 | N = 99 |
| True Positive | 75 | 72 | 63 |
| False Positive | 24 | 23 | 13 |
| True Negative | 5 | 7 | 15 |
| False Negative | 0 | 3 | 8 |
| Prostate Bed | N = 98 | N = 97 | N = 96 |
| True Positive | 58 | 56 | 47 |
| False Positive | 29 | 26 | 15 |
| True Negative | 10 | 12 | 24 |
| False Negative | 1 | 3 | 10 |
| Extraprostatic | N = 28 | N = 28 | N = 25 |
| True Positive | 25 | 26 | 22 |
| False Positive | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| True Negative | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| False Negative | 1 | 0 | 1 |
N = number of patient scans evaluated
Source: AXUMIN Prescribing Information
In Trial 2 in patients with median PSA value of 1.44 ng/mL the agreement values between the AXUMIN and C11 choline reads were 61%, 67% and 77%, respectively.
Source: AXUMIN Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: All trial participants were men, therefore sex differences cannot be determined.
- Race: The majority of participants in the clinical trials were White. Differences among races could not be determined due to small number of participants from other races. Also, the race was not reported for many participants.
- Age: AXUMIN worked similarly in patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below summarize efficacy results by race and age based on comparison between AXUMIN scans to histopathology readings.
Table 4. Efficacy Subgroup Analysis by Race
| RACE | ||
|---|---|---|
| White (71 Subjects) |
Black (17 Subjects) |
|
| Sensitivity | 96% | 92% |
| Specificity | 38% | 60% |
| PPV | 79% | 85% |
| NPV | 89% (8/9) | 75% (3/4) |
Source: FDA Statistical review
Table 5. Efficacy Subgroup Analysis by Age
| AGE | ||
|---|---|---|
| ≥65 years (62 Subjects) |
<65> (35 Subjects) |
|
| Sensitivity | 96% | 91% |
| Specificity | 31% | 54% |
| PPV | 80% | 78% |
| NPV | 71% (5/7) | 88% (7/8) |
PPV=positive predictive value
NPV=negative predictive value
Source: FDA Statistical review
What are the possible side effects?
The most common side effects are injection site pain and redness, headache and a metallic taste in the mouth.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
Adverse reactions were reported in ≤1% of participants during clinical trials with AXUMIN. The most common adverse reactions were injection site pain, injection site erythema and dysgeusia.
AXUMIN Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: All trial participants were men, therefore sex differences in side effects could not be determined.
- Race: The majority of participants in the clinical trials were White. Differences in side effects among races could not be determined due to small number of participants from other races. Also, the race was not reported for many participants.
- Age: The occurrence of common side effect between patients younger and older than 65 years of age was not tested due to low number of side effects in either group.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The analyses of differences in side effects among race and age groups were not conducted due to overall low number of side effects.
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved AXUMIN based on evidence from two clinical trials of male patients who were treated for prostate cancer in the past. In all patients there was suspicion that cancer was spreading because of rising prostate specific antigen or PSA. The trials were conducted in the USA, Italy and Norway.
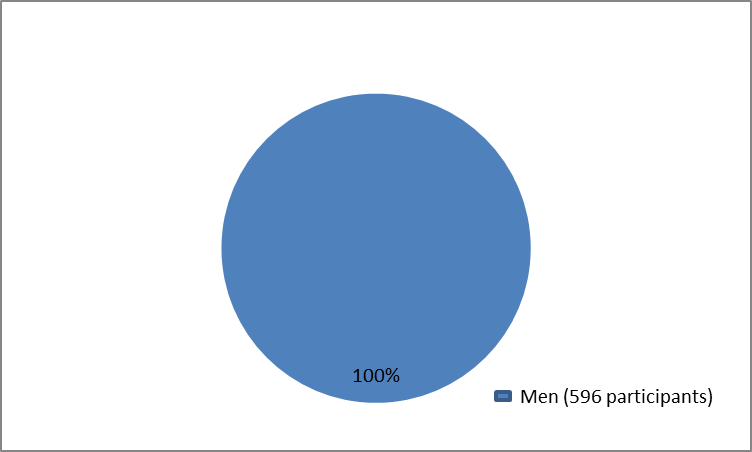
The figure below summarizes how many male participants were in the clinical trials.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Clinical trial data
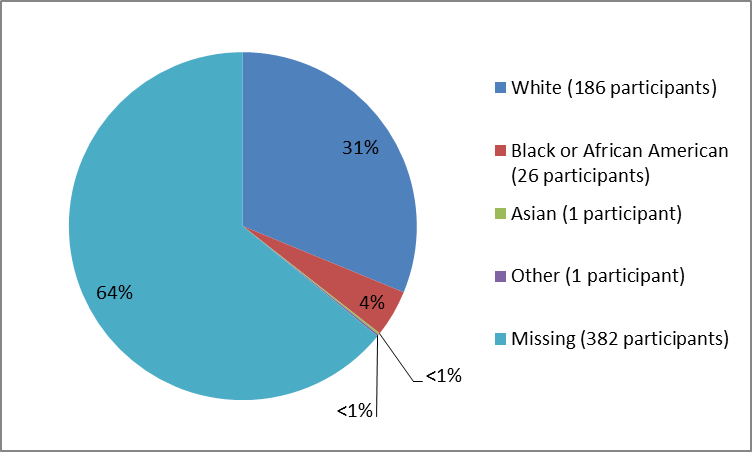
Figure 2 and Table 1 below summarize the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trials.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
Clinical trial data
Table 1. Baseline Demographics by Race
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
| White | 186 | 31% |
| Black or African American | 26 | 4% |
| Asian | 1 | less than 1% |
| Other | 1 | less than 1% |
| Missing | 382 | 64% |
Clinical trial data
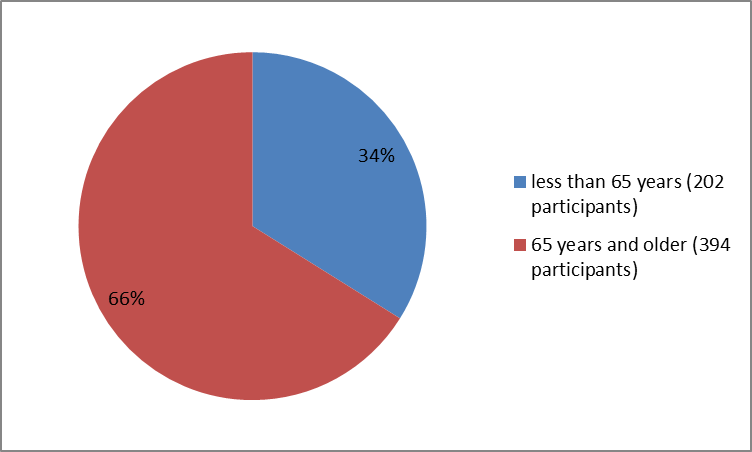
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age group in the clinical trials.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Clinical trial data
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes demographics of patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following prior treatment.
Table 7. Baseline Demographics of Patients in the Clinical Trials (Safety Population)
| Demographic Parameters | Total (N=596) n (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Men | 596 (100%) |
| Age | |
| Mean years (SD) | 66.8 (6.86) |
| Median (years) | 67 |
| Min, max (years) | 42,90 |
| Age Group | |
| < 65="" years=""> | 202 |
| 65 years and older | 394 |
| Race | |
| White | 186 (31%) |
| Black or African American | 26 (4%) |
| Asian | 1 (<1%)> |
| Other | 1 <1%)> |
| Missing | 382 (64%) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Hispanic | 1 (<1%)> |
| Non-Hispanic | 153 (26%) |
| Missing | 442 (74%) |
| Region | |
| United States | 137 |
| Europe | 459 |
Source: Clinical trial data
How were the trials designed?
There were two trials that evaluated benefits and side effects of AXUMIN. The FDA looked at the data from these trials that were published in the medical journals.
The benefit of AXUMIN was evaluated in Trial 1 by measuring the successful detection of cancer lesions using PET/CT imaging in comparison to biopsy results.
The benefit of AXUMIN was evaluated in Trial 2 by comparing agreement in cancer lesion detection between images done with AXUMIN and images done with a different drug called C11 choline.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of AXUMIN were evaluated in two retrospective trials (Trial 1 and Trial 2) in men with suspected recurrence of prostate cancer based on rising PSA levels following radical prostatectomy and/or radiotherapy.
Trial 1 evaluated 105 AXUMIN scans in comparison to histopathology obtained by biopsy of the prostate bed and biopsies of lesions suspicious by imaging. PET/CT imaging generally included the abdomen and pelvic regions. The images were subsequently read by three blinded independent readers.
Trial 2 evaluated the concordance between 96 AXUMIN and C11 choline scans in patients with median PSA value of 1.44 ng/mL (interquartile range = 0.78 to 2.8 ng/mL). The C 11 choline scans were read by on-site readers. The AXUMIN scans were read by the same three blinded independent readers used for Study 1. The agreement values between the AXUMIN and C11 choline reads were 61%, 67% and 77%, respectively.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.