Drug Trials Snapshot: EVENITY
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the EVENITY Package Insert for complete information.
EVENITY (romosozumab-aqqg)
e-ven-i-tee
Amgen, Inc.
Approval date: April 9, 2019
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
EVENITY is a drug to treat osteoporosis (thinning and weakening of bone) in women after menopause (“change of life”) who:
- are at high risk of breaking a bone (fracture), or
- cannot use another osteoporosis medicine or other osteoporosis medicines did not work well.
How is this drug used?
EVENITY is administered as 2 injections under the skin (subcutaneously) once a month for 12 months.
What are the benefits of this drug?
In Trial 1, patients who received EVENITY had fewer new bone fractures in the spine after 12 months compared to patients who received placebo. Patients who received EVENITY followed by denosumab (another medicine approved to treat osteoporosis) for an additional 12 months also had fewer new bone fractures than patients who received placebo followed by denosumab.
In Trial 2, patients who received EVENITY for 12 months followed by alendronate (another medicine approved to treat osteoporosis) for 12 months had fewer new bone fractures in the spine compared to patients who received alendronate for 24 months.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The tables below summarize efficacy results for clinical Trials 1 and 2 in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. The co-primary efficacy endpoints in Trial 1 were new vertebral fractures at month 12 and month 24. The co-primary efficacy endpoints in Trial 2 were the incidence of vertebral fracture at 24 months and the time to the first clinical fracture.
Table 2. Effect of EVENITY on the Incidence and Risk of Fractures in Trial 1
|
|
Proportion of Women with Fractures |
Absolute Risk Reduction (%) (95% CI)a |
Relative Risk Reduction (%) (95% CI)a |
p‑valueb |
|
|
|
|||||
|
At Month 12
|
Placebo (N = 3591) |
EVENITY (N = 3589) |
|
|
|
|
New vertebral fracture |
1.8% |
0.5% |
1.3 (0.8, 1.8) |
73 (53, 84) |
< 0.001 |
|
At Month 24 |
Placebo Followed by denosumab (N = 3591) |
EVENITY Followed by (N = 3589) |
|
|
|
|
New vertebral fracture |
2.5% |
0.6% |
1.9 (1.3, 2.5) |
75 (60, 84) |
< 0.001 |
N = Number of subjects randomized.
- Absolute and relative risk reduction are based on the Mantel‑Haenszel method adjusting for age and prevalent vertebral fracture strata.
- P‑value is based on logistic regression model adjusting for age and prevalent vertebral fracture strata.
EVENITY Prescribing Information
Table 3. Effect of EVENITY on the Incidence of New Vertebral Fractures in Trial 2
|
|
Proportion of Women with Fracture (%) |
Risk Reduction |
p-valueb |
||
|
|
Alendronate Alone (N = 2047) |
EVENITY Followed by (N = 2046) |
Absolute Risk Reduction (%) (95% CI)a |
Relative Risk Reduction (%) (95% CI)a |
|
|
|
|||||
|
New vertebral fracture through Month 24 |
8.0% |
4.1% |
4.0 (2.5, 5.6) |
50 (34, 62) |
<0.001 |
|
N= Number of subjects randomized |
|||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
|
|||||
EVENITY Prescribing Information
Table 4. Effect of EVENITY on the Risk of Clinical Fractures in Trial 2
|
|
Proportion of Women with Fracture (%)a |
Hazard Ratio (95% CI)c |
p-valuec |
|
|
|
Alendronate Alone (N = 2047) |
EVENITY Followed by (N = 2046) |
||
|
|
||||
|
Clinical fracture through primary analysis periodb |
13.0% |
9.7% |
0.73 (0.61, 0.88) |
<0.001 |
N= Number of subjects randomized
- % = number of subjects who had a clinical fracture through the primary analysis period/N*100%; the duration of follow-up varied across subjects.
- Primary analysis period ended when clinical fracture events were confirmed for at least 330 subjects and all subjects completed the month 24 study visit. The median duration of follow-up for the primary analysis period was 33 months.
- Hazard ratio and P-value are based on Cox proportional hazards model adjusting for age strata, baseline total hip BMD T-score, and presence of severe vertebral fracture at baseline
EVENITY Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: All patients in the trial were women; therefore, differences in how well the drug worked between sexes could not be determined.
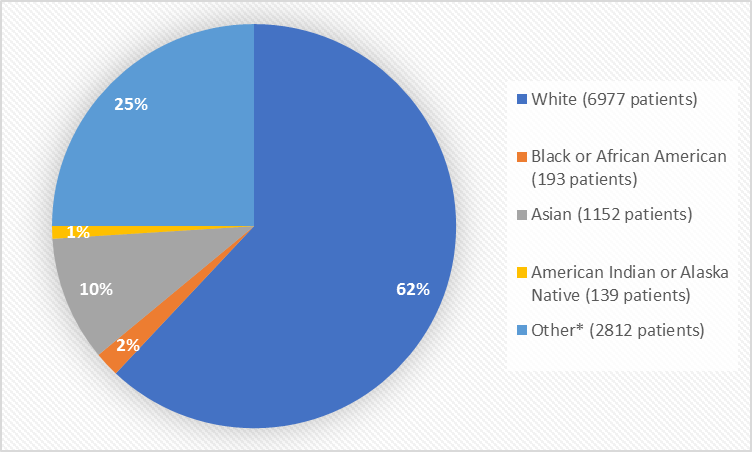
- Race: Most of the patients were White. Differences in bone fractures among races could not be determined because of the limited number of fractures and patients in other races.
- Age: EVENITY worked similarly in women younger and older than 75 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below present efficacy results by subgroup in clinical Trials 1 and 2.
Table 5. New Vertebral Fracture Through Month 12 by Demographics (Trial 1)
|
Subgroup |
EVENITY N a =3589 n/N1b (%) |
Placebo N=3591 n/N1 (%) |
RRRc (95% CI) |
|
Race |
|||
|
White |
10/1871 (0.5) |
40/1870 (2.1) |
74 (49, 87) |
|
Other |
6/1450 (0.4) |
19/1452 (1.3) |
69 (23, 88) |
|
Age |
|||
|
< 65 years |
1/722 (0.1) |
12/709 (1.7) |
92 (37, 99) |
|
> 65 years |
15/2599 (0.6) |
47/2613 (1.8) |
68 (43, 82) |
|
< 75 years |
10/2297 (0.4) |
39/2309 (1.7) |
74 (48, 87) |
|
> 75 years |
6/1024 (0.6) |
20/1013 (2.0) |
70 (27, 88) |
aN=Number of patients randomized
bN1=Number of patients in the primary analysis set for vertebral fractures
cRRR=Relative risk reduction and 95% CI based on the Mantel-Haenszel method adjusted for age strata (when appropriate) and prevalent vertebral fracture (Yes, No) at baseline.
FDA Review
Table 6. New Vertebral Fractures Through Month 24 by Demographics (Trial 1)
|
Subgroup |
EVENITY Followed by Denosumab N a =3589 n/N1b (%) |
Placebo Followed by Denosumab N=3591 n/N1 (%) |
RRRc (95% CI) |
|
Race |
|||
|
White |
12/1874 (0.6) |
54/1874 (2.9) |
77 (58, 88) |
|
Other |
9/1451 (0.6) |
30/1453 (2.1) |
71 (38, 86) |
|
Age |
|||
|
< 65 years |
1/725 (0.1) |
16/710 (2.3) |
94 (54, 99) |
|
> 65 years |
20/2600 (0.8) |
68/2617 (2.6) |
70 (51, 82) |
|
< 75 years |
11/2301 (0.5) |
56/2312 (2.4) |
80 (62, 90) |
|
> 75 years |
10/1024 (1.0) |
28/1015 (2.8) |
65 (28, 83) |
aN=Number of patients randomized
bN1=Number of patients in the primary analysis set for vertebral fractures
cRRR=Relative risk reduction and 95% CI based on the Mantel-Haenszel method adjusted for age strata and prevalent vertebral fracture (Yes, No) at baseline.
FDA Review
Table 7. New Vertebral Fracture Through Month 24 by Demographics (Trial 2)
|
Subgroup |
EVENITY Followed by Alendronate N a =2046 n/N1b (%) |
Alendronate Alone N=2047 n/N1 (%) |
RRRc (95% CI) |
|
Race |
|||
|
White |
61/1278 (4.8) |
112/1260 (8.9) |
47 (28, 61) |
|
Other |
13/547 (2.4) |
35/574 (6.1) |
61 (27, 79) |
|
Age |
|||
|
< 75 years |
37/890 (4.2) |
61/901 (6.8) |
38 (8, 58) |
|
> 75 years |
37/936 (4.0) |
86/933 (9.2) |
68 (39, 71) |
aN=Number of patients randomized
bN1=Number of patients in the primary analysis set for vertebral fractures
cRRR=Relative risk reduction and 95% CI based on the Mantel-Haenszel method adjusted for age strata (when appropriate), baseline total hip BMD T-score (< -2.5, > -2.5) and, presence of severe vertebral fracture at baseline
FDA Review
Table 8. Clinical Fracture Through Primary Analysis Period by Demographics (Trial 2)
|
Subgroup |
EVENITY Followed by Alendronate N a =2046 n/N1b (%) |
Alendronate Alone N=2047 n/N1 (%) |
HRc (95% CI) |
|
Race |
|||
|
White |
156/1447 (10.8) |
196/1415 (13.9) |
0.8 (0.6, 0.9) |
|
Other |
42/599 (7.0) |
70/631 (11.1) |
0.6 (0.4, 0.9) |
|
Age |
|||
|
< 75 years |
87/973 (8.9) |
115/978 (11.8) |
0.8 (0.6, 1.0) |
|
> 75 years |
111/1073 (10.0) |
151/1071 (14.1) |
0.7 (0.6, 0.9) |
aN=Number of patients randomized
bN1=Number of patients in the primary analysis set for vertebral fractures
cHR=Hazard Ratio and 95% CI based on Cox proportional hazards model adjusting forbaseline total hip BMD T-score (< -2.5, > -2.5) and, presence of severe vertebral fracture at baseline
FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
EVENITY may cause serious side effects including heart attack, stroke or death from a cardiovascular (heart or blood vessel) problem.
Other serious side effects include allergic reactions, decreased calcium levels in the blood, jaw problems (osteonecrosis), and unusual thigh bone fractures.
The most common side effects of EVENITY are joint pain and headache.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes adverse reactions in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis in clinical Trials 1 and 2.
Table 9. Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 2% of EVENITY‑treated Women in at least One Trial (Trial 1 and Trial 2)
|
|
Trial 1 |
Trial 2 |
||
|
Preferred Term |
EVENITY (N = 3581) n (%) |
Placebo (N = 3576) n (%) |
Alendronate (N = 2014) n (%) |
EVENITY (N = 2040) n (%) |
|
Arthralgia |
468 (13.1) |
434 (12.1) |
194 (9.6) |
166 (8.1) |
|
Headache |
235 (6.6) |
208 (5.8) |
110 (5.5) |
106 (5.2) |
|
Muscle spasms |
163 (4.6) |
140 (3.9) |
81 (4.0) |
70 (3.4) |
|
Edema peripheral |
86 (2.4) |
67 (1.9) |
38 (1.9) |
34 (1.7) |
|
Asthenia |
84 (2.3) |
79 (2.2) |
53 (2.6) |
50 (2.5) |
|
Neck pain |
80 (2.2) |
54 (1.5) |
42 (2.1) |
34 (1.7) |
|
Insomnia |
72 (2.0) |
68 (1.9) |
36 (1.8) |
34 (1.7) |
|
Paresthesia |
72 (2.0) |
62 (1.7) |
34 (1.7) |
29 (1.4) |
EVENITY Prescribing Infomation
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: All patients in the trial were women; therefore, differences in side effects between sexes could not be determined.
- Race: Most of the patients were White. The occurrence of side effects among White and Asian patients was similar. The occurrence of side effects among other races could not be determined because of the limited number of patients in other races.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar in women younger and older than 75 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below summarize the occurrence of the most common adverse reaction, arthralgia, by race and age group in clinical Trials 1 and 2.
Table 10. Adverse Reactions of Arthralgia by Race (Trial 1 and Trial 2)
|
Adverse Event |
White |
Asian |
Black |
Other |
||||
|
Control (N=3467) n (%) |
EVENITY (N=3510) n (%) |
Control (N=590) n (%) |
EVENITY (N=562) n (%) |
Control (N=97) n (%) |
EVENITY (N=96) n (%) |
Control (N=1484) n (%) |
EVENITY (N=1467) n (%) |
|
|
Arthralgia |
298 (8.6) |
325 (9.3) |
55 (9.3) |
70 (12.4) |
27 (27.8) |
20 (20.8) |
248 (16.7) |
219 (14.3) |
Control=placebo or alendronate
N=number of patients in the analysis set
n=number of patients reporting > 1 event
Clinical Trial Data
Table 11. Adverse Reactions of Arthralgia by Age Group (Trial 1 and Trial 2)
|
Adverse Event |
< 65 years |
> 65 – 74 years |
> 75 – 84 years |
> 85 years |
||||
|
Control (N=993) n (%) |
EVENITY (N=1003) n (%) |
Control (N=2433) n (%) |
EVENITY (N=2431) n (%) |
Control (N=1899) n (%) |
EVENITY (N=1914) n (%) |
Control (N=265) n (%) |
EVENITY (N=273) n (%) |
|
|
Arthralgia |
115 (11.6) |
131 (13.1) |
269 (11.1) |
287 (11.8) |
215 (11.3) |
191 (10.0) |
29 (10.9) |
25 (9.2) |
Control=placebo or alendronate
N=number of patients in the analysis set
n=number of patients reporting > 1 event
WHO WAS IN THE STUDIES?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved EVENITY based on evidence from two clinical trials of 11273 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. The trials were conducted in Asia, Canada, Central and Latin America, South America, Europe, Mexico, New Zealand, and the United States.
Figure 1 summarizes how many women were enrolled in the clinical trials.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trials.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
*Other includes Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Island, Mixed, Multiple, and Missing
FDA Review
Table 1. Demographics by Race
|
Race |
Number of Patients |
Percentage |
|---|---|---|
|
White |
6977 |
62 |
|
Black or African American |
193 |
2 |
|
Asian |
1152 |
10 |
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
139 |
1 |
|
Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander |
3 |
Less than 1 |
|
Other |
1454 |
13 |
|
Multiple/Mixed |
1354 |
12 |
|
Missing |
1 |
Less than 1 |
FDA Review
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes demographics of the patients in the combined clinical trials .
Table 12. Baseline Demographics for Trials 1 and 2
|
|
Trial 1
|
Trial 2
|
Total (N=11273)
|
||
|
EVENITY (N=3589) |
Placebo (N=3591) |
EVENITY (N=2046)
|
Alendronate (N=2047)
|
||
|
Sex - n (%) |
|||||
|
Women |
3589 (100.0) |
3591 (100.0) |
2046 (100) |
2047 (100) |
11273 (100) |
|
Race - n (%) |
|||||
|
White |
2063 (57.5) |
2052 (57.1) |
1447 (70.7) |
1415 (69.1) |
6977 (61.9) |
|
Asian |
425 (11.8) |
441 (12.3) |
137 (6.7) |
149 (7.3) |
1152 (10.2) |
|
Black or African American |
77 (2.1) |
74 (2.1) |
19 (0.9) |
23 (1.1) |
193 (1.7) |
|
American Indian or Alaska native |
64 (1.8) |
63 (1.8) |
5 (0.2) |
7 (0.3) |
139 (1.2) |
|
Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander |
0 (0) |
1 (<0.1) |
0 (0) |
2 (<0.1) |
3 (<0.1) |
|
Multiple/Mixed |
623 (17.4) |
636 (17.7) |
50 (2.4) |
45 (2.2) |
1354 (12.0) |
|
Other |
337 (9.4) |
324 (9.0) |
388 (19.0) |
405 (18.9) |
1454 (12.9) |
|
Missing |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1 (<0.1) |
1 (<0.1) |
|
Age Group - n (%) |
|||||
|
<65 years |
768 (21.4) |
757 (21.1) |
239 (11.7) |
240 (11.7) |
2004 (17.8) |
|
> 65 to 74 years |
1704 (47.5) |
1719 (47.9) |
737 (36.0) |
758 (37.0) |
4918 (43.6) |
|
≥75 years |
1117 (31.1) |
1115 (31.0) |
1070 (52.3) |
1049 (51.2) |
4351 (38.6) |
|
Age (years) |
|||||
|
Mean (SD) |
70.9 (7.0) |
70.8 (6.9) |
74.4 (7.5) |
74.2 (7.5) |
72.6 (7.2) |
|
Median (min., max.) |
70.0 (55, 90) |
70.0 (55, 90) |
75.0 (55, 90) |
75.0 (55, 90) |
72.0 (55, 90) |
|
Ethnicity - n (%) |
|||||
|
Hispanic/Latino |
1427 (39.8) |
1416 (39.4) |
631 (30.8) |
662 (32.3) |
4136 (36.7) |
|
Not Hispanic/Latino |
2162 (60.2) |
2175 (60.6) |
1415 (69.2) |
1385 (67.7) |
7137 (63.3) |
|
Geographic Region - n (%) |
|||||
|
Central and Eastern Europe and Middle East |
1043 (29.1) |
1050 (29.2) |
835 (40.8) |
798 (39.0) |
3726 (33.0) |
|
Central/Latin America |
1550 (43.2) |
1534 (42.7) |
674 (32.9) |
727 (35.5) |
4485 (13.4) |
|
Western Europe and Australia/New Zealand |
482 (13.4) |
497 (13.6) |
269 (13.1) |
264 (12.9) |
1512 (39.8) |
|
Asia Pacific and South Africa |
410 (11.4) |
419 (11.7) |
213 (10.4) |
216 (10.6) |
1258 (11.2) |
|
North America |
104 (2.9) |
91 (2.5) |
55 (2.7) |
42 (2.1) |
292 (2.6) |
|
United States |
69 (66.3) |
63 (69.2) |
33 (1.6) |
24 (1.2) |
189 (1.7) |
|
Canada |
35 (33.7) |
28 (30.8) |
22 (1.1) |
18 (0.9) |
103 (0.9) |
Clinical Trial Data
How were the trials designed?
The benefits and side effects of EVENITY were evaluated in two clinical trials of postmenopausal women aged 55 to 90 years with osteoporosis. All women took daily calcium and vitamin D supplements.
In Trial 1, women were randomly assigned to receive either EVENITY or placebo as an injection under the skin once monthly for 12 months. Neither the women nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given. After the initial 12-month treatment period, women in both groups received denosumab (another approved medication for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis) as an injection under the skin once every 6 months for an additional 12 months. The benefit of EVENITY was evaluated by measuring the occurrence of new spine fractures at 12 months and 24 months.
In Trial 2, women were randomly assigned to receive either EVENITY as an injection under the skin once monthly or alendronate (another approved medication for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis) once weekly by mouth for 12 months. Neither the women nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given. After the initial 12-month treatment period, women in both groups received alendronate by mouth through the end of the trial. The benefit of EVENITY was evaluated by measuring the occurrence of new spine fractures through 24 months. The trial also measured the occurrence of clinical fractures (defined as fractures in bones other than the spine or fractures in the spine that caused symptoms). Clinical fractures were assessed when at least 330 patients had a clinical fracture and all patients completed at least 24 months of the trial.
How were the trials designed?
The efficacy and safety of EVENITY were evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, clinical trials. All patients were postmenopausal women aged 55 to 90 years. All women received daily calcium and vitamin D supplements.
Trial 1 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in women with bone mineral density (BMD) T-scores less than or equal to -2.5 at the total hip or femoral neck. Women were randomized to receive EVENITY 210 mg or placebo subcutaneously (SC) for 12 months. After 12 months, women in both groups received open label denosumab 60 mg SC every 6 months for an additional 12 months. The co-primary efficacy endpoints were new vertebral fractures at month 12 and month 24.
Trial 2 was a randomized, double-blind, alendronate-controlled trial. At baseline, women had one of the following:
- BMD T-score less than or equal to -2.5 at the total hip or femoral neck and either one moderate or severe vertebral fracture or two mild vertebral fractures
- BMD T-score less than or equal to -2.0 at the total hip or femoral neck and either two moderate or severe vertebral fractures or a history of a proximal femur fracture.
Women were randomized to receive monthly SC injections of EVENITY 210 mg or weekly alendronate 70 mg orally for 12 months. After the initial 12-month treatment period, women in both arms received open-label oral alendronate 70 mg weekly through the end of the trial. The total treatment duration varied for individual patients (the median study duration was 33 months). The co-primary efficacy endpoints were new vertebral fractures at month 24 and the time to the first clinical fracture (composite endpoint of non-vertebral fracture or symptomatic vertebral fracture). The time to the first clinical fracture was evaluated when at least 330 patients had a clinical fracture and all patients completed at least 24 months of the study.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.