Drug Trials Snapshot: CIBINQO
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the key clinical trials that supported the original FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, age, and ethnic groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable). Refer to the CIBINQO Prescribing Information for all of the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
CIBINQO (abrocitinib)
(sih-BIN’ koe)
Pfizer, Inc.
Original Approval date: January 14, 2022
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
CIBINQO is a Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitor that is indicated for the treatment of adults with refractory, moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with other systemic drug products, including biologics, or when use of those therapies is inadvisable.
How is this drug used?
CIBINQO is an oral tablet that is taken once daily. Take 100 mg once daily to start, if an adequate response is not achieved with CIBINQO 100 mg daily after 12 weeks, consider increasing dosage to 200 mg orally once daily. Discontinue therapy if inadequate response is seen after dosage increase to 200 mg once daily.
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved CIBINQO based on evidence from 3 controlled clinical trials enrolling a total of 1615 patients supporting efficacy and safety. Two of the trials enrolled patients 12-years of age and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis and one trial enrolled adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. The trials were conducted at multiple sites in 18 countries (i.e., United States, Canada, Australia, Mexico, Chile, Great Britain, Poland, Germany, Bulgaria, Hungary, Czech Republic, Latvia, Slovakia, Spain, Italy, Japan, Korea, Taiwan).
In addition, safety analyses were performed on the combined results of these 3 controlled clinical trials and one additional controlled study in a total of 1,540 patients.
What are the benefits of this drug?
More patients achieved clear or almost clear skin and a reduction in itch after treatment with CIBINQO in comparison to those who were treated with placebo.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The tables below summarize the efficacy results for the evaluated patients in two monotherapy trials (Trials-AD-1 and Trial-AD-2) and in combination with background topical corticosteroids (Trial-AD-3).
Table 1. Efficacy Results of CIBINQO Monotherapy at Week 12 in Patients 12 years and older with Moderate-to-Severe AD (Trial-AD-1 and Trial-AD-2)
|
Endpoint |
Trial-AD-1 |
Trial-AD-2 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CIBINQO |
Placebo |
CIBINQO |
Placebo |
|||
|
200 mg QD |
100 mg QD |
200 mg QD |
100 mg QD |
|||
|
IGA 0 or 1a |
44% |
24% |
8% |
38% |
28% |
9% |
|
Difference from Placebo (95% CI) |
36% |
16% |
- |
29% |
19% |
- |
|
EASI‑75b |
62% |
40% |
12% |
61% |
44% |
10% |
|
Difference from Placebo (95% CI) |
51% |
28% |
- |
50% |
33% |
- |
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; EASI=Eczema Area and Severity Index; IGA=Investigator Global Assessment; QD=once daily.
a. IGA responders were subjects with IGA score of clear (0) or almost clear (1) (on a 5 point scale) and a reduction from baseline of ≥2 points.
b. EASI -75 responders were patients with ≥75% improvement in EASI from baseline.
The proportion of subjects achieving PP-NRS4 at Week 2 (defined as an improvement of ≥4 points from baseline in Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale [PP-NRS]) was higher in subjects treated with CIBINQO monotherapy 200 mg once daily (28% in Trial-AD-1 and 24% in Trial-AD-2) and 100 mg once daily (11% in both trials) compared to placebo (2% in both trials). A higher proportion of subjects in the CIBINQO monotherapy 100 mg or 200 mg once daily arm compared to placebo achieved improvement in itching at Week 12.
Table 2. Efficacy Results of CIBINQO with Concomitant Topical Corticosteroids at Week 12 in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe AD (Trial-AD-3)*
|
Endpoints |
CIBINQO |
Placebo |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
200 mg QD |
100 mg QD |
||
|
IGA 0 or 1a at Week 12 |
47% |
36% |
14% |
|
Difference from Placebo |
34% |
23% |
- |
|
EASI-75b at Week 12 |
68% |
58% |
27% |
|
Difference from Placebo |
41% |
32% |
- |
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; EASI=Eczema Area and Severity Index; IGA=Investigator Global Assessment; QD=once daily.
*data in 242 patients randomized to an active control are not presented
a. IGA responders were subjects with IGA score of clear (0) or almost clear (1) (on a 5 point scale) and a reduction from baseline of ³2 points.
b. EASI-75 responders were subjects with ≥75% improvement in EASI, from baseline.
The proportions of subjects achieving PP-NRS4 at Week 2 was higher in subjects treated with CIBINQO 200 mg once daily (30%) and 100 mg once daily (14%) in combination with background medicated topical therapies compared to placebo (8%).
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: CIBINQO worked slightly better in females than males; however, this was not consistent across CIBINQO doses, endpoint and trials.
- Race: CIBINQO worked similarly in White and Asian patients. The number of patients of races other than White and Asian was limited; therefore, differences in response among races could not be determined.
- Age: CIBINQO worked similarly in those <18 years of age and those 18-64 years of age. The number of patients above 65 years of age was limited; therefore, differences in response between patients above and below 65 years of age could not be determined.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below summarize efficacy results at Week 12 by age, sex and race.
Table 3: IGA 0/1 Response at Week 12 by Age, Sex and Race – Trial-AD-1 (FAS; NRI1)
|
|
CIBINQO |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Subgroups |
200 mg |
100 mg |
|||
|
Age (years) |
|||||
|
<18 (33, 34, 17) |
27% |
26% |
12% |
15% (-6%, 37%) |
15% (-7%, 36%) |
|
18-64 (110, 118, 59) |
46% |
20% |
7% |
40% (29%, 51%) |
14% (4%, 23%) |
|
≥65 (11, 4, 1) |
64% |
100% |
0% |
64% (35%, 92%) |
- |
|
Sex |
|||||
|
Male (81, 90, 49) |
36% |
20% |
12% |
24% (10%, 37%) |
8% (-5%, 20%) |
|
Female (73, 66, 28) |
52% |
33% |
0% |
52% (41%, 63%) |
29% (18%, 40%) |
|
Race |
|||||
|
White (104, 113, 62) |
45% |
17% |
10% |
35% (23%, 48%) |
7% (-3%, 17%) |
|
Black/African American |
27% |
5% |
0% |
27% (1%, 54%) |
53% (28%, 79%) |
|
Asian (26, 26, 6) |
38% |
38% |
0% |
38% (20%, 57%) |
38% 920%, 57^) |
|
Other (3, 13, 2) |
54% |
0% |
0% |
54% (27%, 81%) |
- |
|
Overall |
43% |
24% |
8% |
36% (26%, 46%) |
16% (7%, 25%) |
1 Full Analysis Set (FAS) defined as all randomized subjects who were dosed; Missing data imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI)
Table 4: EASI-75 Response at Week 12 by Age, Sex and Race – Trial-AD-1 (FAS; NRI1)
|
|
CIBINQO |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Subgroups |
200 mg |
100 mg |
|||
|
Age (years) |
|||||
|
<18 (33, 34, 17) |
54% |
44% |
12% |
43% (20%, 66%) |
32% (10%, 55%) |
|
18-64 (110, 118, 59) |
64% |
36% |
12% |
52% (40%, 64%) |
25% (13%, 37%) |
|
≥65 (11, 4, 1) |
73% |
100% |
0% |
73% (46%, 99%) |
- |
|
Sex |
|||||
|
Male (81, 90, 49) |
57% |
33% |
41% |
42% (28%, 57%) |
19% (5%, 33%) |
|
Female (73, 66, 28) |
68% |
48% |
7% |
61% (47%, 76%) |
41% (26%, 57%) |
|
Race |
|||||
|
White (104, 113, 62) |
63% |
33% |
13% |
51% (38%, 63%) |
20% (8%, 32%) |
|
Black/African American |
36% |
67% |
17% |
20% (-21%, 61%) |
50% (12%, 88%) |
|
Asian (26, 26, 6) |
58% |
54% |
0% |
58% (39%, 77%) |
54% (35%, 73%) |
|
Other (3, 13, 2) |
85% |
50% |
0% |
85% (65%, 100%) |
50% (-19%, 100%) |
|
Overall |
62% |
40% |
12% |
51% (40%, 61%) |
28% (17%, 39%) |
1 Full Analysis Set (FAS) defined as all randomized subjects who were dosed; Missing data imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI)
Table 5: IGA 0/1 Response at Week 12 by Age, Sex and Race – Trial-AD-2 (FAS; NRI1)
|
|
CIBINQO |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Subgroups |
200 mg |
100 mg |
|||
|
Age (years) |
|||||
|
<18 (15, 17, 8) |
40% |
12% |
0% |
40% (15%, 65%) |
12% (-3%, 27%) |
|
18-64 (133, 130, 69) |
38% |
29% |
10% |
27% (17%, 38%) |
18% (8%, 29%) |
|
≥65 (11, 7, 1) |
43% |
48% |
0% |
43% (6%, 79%) |
45% (16%, 75%) |
|
Sex |
|||||
|
Male (88, 94, 47) |
28% |
29% |
8% |
20% (7%, 32%) |
20% (8%, 32%) |
|
Female (67, 64, 31) |
51% |
27% |
10% |
41% (25%, 57%) |
17% (2%, 32%) |
|
Race |
|||||
|
White (91, 101, 40) |
38% |
30% |
10% |
28% (15%, 42%) |
20% (7%, 33%) |
|
Black/African American |
33% |
22% |
0% |
33% (-4%, 71%) |
22% (-5%, 49%) |
|
Asian (26, 26, 6) |
35% |
24% |
10% |
25% (8%, 42%) |
14% (-3%, 30%) |
|
Other (4, 2, 3) |
75% |
50% |
0% |
75% (3%, 100%) |
50% (-19%, 100%) |
|
Overall |
38% |
28% |
9% |
30% (19%, 39%) |
19% (9%, 28%) |
1 Full Analysis Set (FAS) defined as all randomized subjects who were dosed; Missing data imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI)
Table 6: EASI-75 Response at Week 12 by Age, Sex and Race – Trial-AD-2 (FAS; NRI1)
|
|
CIBINQO |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Subgroups |
200 mg |
100 mg |
|||
|
Age (years) |
|||||
|
<18 (15, 17, 8) |
60% |
41% |
0% |
60% (35%, 85%) |
41% (18%, 66%) |
|
18-64 (133, 130, 69) |
59% |
42% |
12% |
48% (36%, 59%) |
31% (19%, 42%) |
|
≥65 (11, 7, 1) |
86% |
64% |
0% |
86% (60%, 100%) |
64% (35%, 92%) |
|
Sex |
|||||
|
Male (88, 94, 47) |
51% |
46% |
11% |
40% (27%, 54%) |
35% (22%, 48%) |
|
Female (67, 64, 31) |
73% |
41% |
10% |
63% (49%, 78%) |
31% (15%, 47%) |
|
Race |
|||||
|
White (91, 101, 40) |
60% |
45% |
10% |
50% (37%, 64%) |
35% (22%, 49%) |
|
Black/African American |
50% |
33% |
0% |
50% (10%, 70%) |
33% (2%, 64%) |
|
Asian (26, 26, 6) |
61% |
41% |
14% |
47% (29%, 65%) |
27% (8%, 46%) |
|
Other (4, 2, 3) |
75% |
50% |
0% |
50% (35%, 66%) |
50% (-19%, 49%) |
|
Overall |
61% |
44% |
10% |
50% (40%, 61%) |
33% (23%, 44%) |
1 Full Analysis Set (FAS) defined as all randomized subjects who were dosed; Missing data imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI)
Table 7: IGA 0/1 Response at Week 12 by Age, Sex and Race – Trial-AD-3 (FAS; NRI1)
|
|
CIBINQO |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Subgroups |
200 mg |
100 mg |
|||
|
Age (years) |
|||||
|
18-64 (211, 224, 21) |
48% |
36% |
15% |
33% (24%, 42%) |
21% (12%, 30%) |
|
≥65 (15, 14, 10) |
33% |
43% |
0% |
33% (9%, 57%) |
43% (17%, 69%) |
|
Sex |
|||||
|
Male (104, 120, 77) |
46% |
32% |
10% |
36% (24%, 47%) |
21% (10%, 32%) |
|
Female (122, 118, 54) |
47% |
41% |
18% |
29% (15%, 43%) |
22% (8%, 36%) |
|
Race |
|||||
|
White (161, 182, 87) |
47% |
37% |
17% |
29% (18%, 40%) |
20% (9%, 31%) |
|
Black/African American |
44% |
50% |
0% |
44% (12%, 77% |
50% (10%, 90%) |
|
Asian (53, 48, 31) |
49% |
31% |
6% |
43% (27%, 59%) |
25% 99%, 40%) |
|
Other (3, 2, 7) |
33% |
0% |
14% |
19% (-40%, 78%) |
-14% (-40%, 12%) |
|
Overall |
47% |
36% |
14% |
33% (42%) |
22% (14%, 31%) |
1 Full Analysis Set (FAS) defined as all randomized subjects who were dosed; Missing data imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI)
Table 8: EASI-75 Response at Week 12 by Age, Sex and Race – Trial-AD-3 (FAS; NRI1)
|
|
CIBINQO |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Subgroups |
200 mg |
100 mg |
|||
|
Age (years) |
|||||
|
18-64 (211, 224, 21) |
69% |
57% |
26% |
43% (33%, 53%) |
31% (30%, 41%) |
|
≥65 (15, 14, 15, 10) |
53% |
71% |
30% |
23% (-15%, 61%) |
41% (4%, 78%) |
|
Sex |
|||||
|
Male (104, 120, 77) |
65% |
56% |
22% |
43% (30%, 56%) |
34% (21%, 47%) |
|
Female (122, 118, 54) |
70% |
60% |
33% |
37% (22%, 52%) |
27% (11%, 42%) |
|
Race |
|||||
|
White (161, 182, 87) |
66% |
57% |
34% |
32% (20%, 44%) |
23% (10%, 35%) |
|
Black/African American |
78% |
67% |
17% |
61% (21%, 100%) |
50% (2%, 98%) |
|
Asian (53, 48, 31) |
74% |
62% |
10% |
64% (48%, 80%) |
53% (36%, 70%) |
|
Other (3, 2, 7) |
66% |
57% |
34% |
61% (47%, 75%) |
49% (33%, 65%) |
|
Overall |
68% |
58% |
27% |
41% (32%, 51%) |
31% (21%, 41%) |
1 Full Analysis Set (FAS) defined as all randomized subjects who were dosed; Missing data imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI)
What are the possible side effects?
The most common side effects of CIBINQO in clinical trials were nasopharyngitis, nausea, headaches, herpes simplex (including oral herpes, ophthalmic herpes, herpes dermatitis and genital herpes), and increase in blood creatine phosphokinase.
CIBINQO can cause serious infections, malignancy, major cardiac events, thrombosis and other laboratory abnormalities including thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, and lipid elevations.
Patients should not receive live vaccines while being treated with CIBINQO.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes safety results up to Week 16 for the evaluated patients in clinical trials with CIBINQO.
Table 9. Adverse Reactions from Placebo-Controlled Trials Reported in ≥1% of CIBINQO Treated Subjects with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis and at Higher Rate than Placebo for up to 16 Weeks
|
Weeks 0-16 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
CIBINQO |
CIBINQO |
Placebo |
|
|
Nasopharyngitis |
51 (8.7) |
75 (12.4) |
27 (7.9) |
|
Nausea |
86 (14.5) |
37 (6.0) |
7 (2.1) |
|
Headache |
46 (7.8) |
36 (6.0) |
12 (3.5) |
|
Herpes simplexb |
25 (4.2) |
20 (3.3) |
6 (1.8) |
|
Increased blood creatinine phosphokinase |
17 (2.9) |
14 (2.3) |
5 (1.5) |
|
Dizziness |
17 (2.9) |
11 (1.8) |
3 (0.9) |
|
Urinary tract infection |
13 (2.2) |
10 (1.7) |
4 (1.2) |
|
Fatigue |
8 (1.3) |
10 (1.6) |
2 (0.5) |
|
Acne |
28 (4.7) |
10 (1.6) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Vomiting |
19 (3.2) |
9 (1.5) |
3 (0.9) |
|
Impetigo |
3 (0.5) |
9 (1.5) |
1 (0.3) |
|
Oropharyngeal pain |
6 (1.0) |
8 (1.4) |
2 (0.6) |
|
Hypertension |
5 (0.8) |
7 (1.2) |
2 (0.7) |
|
Influenza |
6 (1.1) |
7 (1.2) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Gastroenteritis |
8 (1.3) |
7 (1.1) |
2 (0.6) |
|
Dermatitis contact |
3 (0.5) |
6 (1.1) |
1 (0.3) |
|
Abdominal pain upper |
11 (1.9) |
4 (0.6) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Abdominal discomfort |
7 (1.2) |
3 (0.5) |
1 (0.3) |
|
Herpes zoster |
7 (1.2) |
2 (0.3) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
9 (1.5) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
a Study size adjusted percentages
b Herpes simplex also includes oral herpes, ophthalmic herpes, herpes dermatitis, genital herpes.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in males and females
- Race: The occurrence of side effects was similar in White, Asian, Black or African American patients.
- Age: The number of patients above 65 years of age was limited; therefore, differences in adverse event rates between patients above and below 65 years of age could not be determined.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 10: Adverse Events by Sex in Primary Safety Pool through Week 16
|
|
CINBIQO 100 mg QD |
CIBINQO 200 mg QD |
ALL CIBINQO |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Event |
Female |
Male |
Female |
Male |
Female |
Male |
|
Any TEAE, n (%) |
161 (59.0) |
210 (62.7) |
211 (73.0) |
192 (63.8) |
372 (66.2) |
402 (63.2) |
|
SAE, n (%) |
8 (2.9) |
11 (3.3) |
6 (2.1) |
5 (1.7) |
14 (2.5) |
16 (2.5) |
Abbreviations: TEAE = Treatment Emergent Adverse Event; SAE = Serious Adverse Event
Primary Safety Pool Includes Studies: B7451006, B7451012, B7451013, B7451029
Table 11: Adverse Events by Race in Primary Safety Pool through Week 16
|
|
CINBIQO 100 mg QD |
CIBINQO 200 mg QD |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Event |
White |
Black |
Asian |
White |
Black |
Asian |
|
Any TEAE, n (%) |
266 (61.0) |
25 (67.6) |
75 (58.6) |
272 (69.2) |
25 (64.1) |
91 (65.9) |
|
SAE, n (%) |
15 (3.4) |
0 |
1 (0.7) |
9 (2.3) |
1 (2.6) |
1 (0.7) |
Abbreviations: TEAE = Treatment Emergent Adverse Event; SAE = Serious Adverse Event
Primary Safety Pool Includes Studies: B7451006, B7451012, B7451013, B7451029
Table 12: Adverse Events by Age in Primary Safety Pool Week 16
|
|
CINBIQO 100 mg QD |
CIBINQO 200 mg QD |
ALL CIBINQO |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Event |
<65 |
≥ 65 |
<65 |
≥ 65 |
<65 |
≥ 65 |
|
Any TEAE, n (%) |
318 (61.0) |
8 (35.3) |
337 (67.3) |
28 (54.9) |
655 (64.1) |
48 (62.3) |
|
SAE, n (%) |
17 (3.7) |
1 (2.8) |
7 (1.4 |
1 (2.4) |
24 (2.3) |
2 (2.6) |
Abbreviations: TEAE = Treatment Emergent Adverse Event; SAE = Serious Adverse Event
Primary Safety Pool Includes Studies: B7451006, B7451012, B7451013, B7451029
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
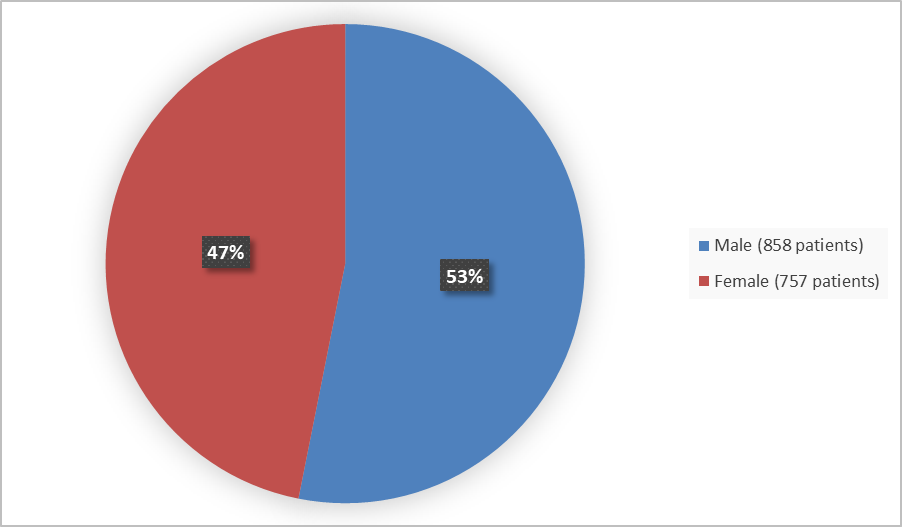
Figure 1 summarizes how many males and females were enrolled in the combined clinical trials used to evaluate the efficacy of CIBINQO.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex (Full Analysis Set)
Adapted from FDA Review
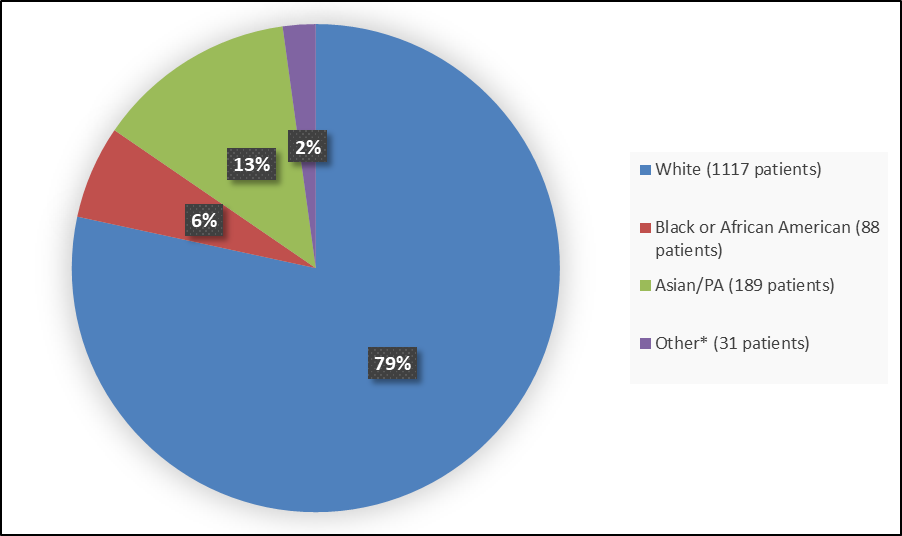
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the combined clinical trials used to evaluate the efficacy of CIBINQO.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race (Full Analysis Set)
* Includes American Indian or Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander and multiple races.
Adapted from FDA Review
Figure 3 summarizes how many patients by race were in the combined trials used to evaluate the side effects of CIBINQO.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age (Full Analysis Set)
Adapted from FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes demographics for the randomized and dosed patients in the three clinical trials (FAS population).
Table 11: Demographics– Trial-AD-1, Trial-AD-2 and Trial-AD-3 (FAS1)
|
|
Trial-AD-1 |
Trial-AD-2 |
Trial-AD-3 |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CIBINQO |
|
CIBINQO |
|
CIBINQO |
|
||||
|
200 mg |
100 mg |
200 mg |
100 mg |
200 mg |
100 mg |
||||
|
Age (years) |
|||||||||
|
Mean (SD) |
33.0 (17.3) |
32.6 (15.4) |
31.5 (14.4) |
33.5 (14.7) |
37.4 (15.8) |
33.4 (13.8) |
38.8 (14.5) |
37.3 (14.7) |
37.4 (15.2) |
|
Median |
27 |
30.5 |
29.0 |
29.0 |
35.0 |
29.0 |
36 |
33 |
34 |
|
Range |
12 – 84 |
12 – 73 |
12 - 65 |
12 – 76 |
12 – 83 |
13 – 71 |
18 – 80 |
18 – 82 |
18 – 84 |
|
Categories, n (%) |
|||||||||
|
12-<18 |
33 (21%) |
34 (22%) |
17 (22%) |
15 (10%) |
17 (11%) |
8 (10%) |
- |
- |
- |
|
18-<65 |
110 (71%) |
118 (76%) |
59 (77%) |
133 (86%) |
130 (82%) |
69 (88%) |
211 (93%) |
224 (94%) |
121 (92%) |
|
≥65 |
11 (7%) |
4 (3%) |
1 (1%) |
7 (4%) |
11 (7%) |
1 (1%) |
15 (7%) |
14 (6%) |
10 (8%) |
|
Sex, n (%) |
|||||||||
|
Male |
81 (53%) |
90 (58%) |
49 (64%) |
88 (57%) |
94 (59%) |
47 (60%) |
104 (46%) |
120 (50%) |
77 (59%) |
|
Female |
73 (47%) |
66 (42%) |
28 (36%) |
67 (43%) |
64 (40%) |
31 (40%) |
122 (54%) |
118 (50%) |
54 (41%) |
|
Race2, n (%) |
|||||||||
|
White |
104 (67%) |
113 (72%) |
62 (80%) |
91 (59%) |
101 (64%) |
40 (51%) |
161 (71%) |
182 (76%) |
87 (66%) |
|
Black or African American |
11 (7%) |
15 (10%) |
6 (8%) |
6 (4%) |
9 (6%) |
6 (8%) |
9 (4%) |
6 (2%) |
6 (5%) |
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
4 (3%) |
1 (1%) |
1 (1%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
1 (<1%) |
2 (1%) |
|
Asian |
26 (17%) |
26 (17%) |
6 (8%) |
54 (35%) |
46 (29%) |
29 (27%) |
1 (<1%) |
0 (0%) |
1 (1%) |
|
Multiple |
6 (4%) |
1 (1%) |
1 (1%) |
2 (1%) |
1 (1%) |
1 (1%) |
53 (23%) |
48 (20%) |
31 (24%) |
|
Missing |
2 (1%) |
0 (0%) |
1 (1%) |
2 (1%) |
1 (1%) |
2 (3%) |
1 (<1%) |
0 (0%) |
3 (2%) |
1 Full Analysis Set (FAS) defined as all randomized subjects who were dosed
2 Missing race information for 3 subjects in Trial B7451012 (two in the 200 mg arm and one in the placebo arm) and 5 subjects in Trial B7451013 (two in the 200 mg arm, one in the 100 mg arm and two in placebo arm).
How were the trials designed?
The benefit and side effects of CIBINQO were evaluated in three clinical trials of 12 year and older patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis not adequately controlled by topical medications(s). Trial-AD-1 and Trial-AD-2 were monotherapy trials in adolescents and adults, while Trial-AD-3 was a trial with background topical therapy in adults only.
All three trials evaluated two doses of CIBINQO: 100mg and 200mg. The monotherapy trials were identically designed, 16-week, randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group, phase 3 trials. Trial-AD-3 with concomitant background therapy was a 24-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active-comparator (dupilumab) and placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. In this trial, at Week 16, subjects previously receiving placebo were re-randomized to receive CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg, subjects previously receiving CIBINQO continued on their respective dose and subjects previously receiving dupilumab continued to take placebo.
The benefit of CIBINQO to placebo was assessed after 12 weeks of treatment using the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scale that measures the severity of disease on a scale from 0 to 4 and the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) for all three trials.
How were the trials designed?
The efficacy of CIBINQO was evaluated in three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. All patients had moderate to severe atopic dermatitis defined as a score of ≥3 using an Investigator’s Global Assessment [IGA] severity scale of 0 to 4, an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score ≥16 on a scale of 0 to 72, and a minimum body surface area involvement of ≥10%.
For all three phase 3 trials, the protocols specified the following co-primary efficacy endpoints:
- IGA 0/1: Proportion of subjects with IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with a reduction of ≥2 points at Week 12
- EASI-75: Proportion of subjects with at least 75% reduction in EASI score from baseline to Week 12
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.