Drug Trial Snapshot: BRIDION
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the BRIDION Prescribing Information for complete information.
BRIDION (sugammadex)
BRY--DEE–ON
Merck
Approval date: December 15, 2015
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
BRIDION is an injection intended to reverse the effects of certain neuromuscular blocking drugs, called rocuronium bromide and vecuronium bromide, which are used during certain types of surgery in adults. Neuromuscular blocking drugs are used to paralyze the vocal cords when patients require an artificial airway or breathing tube for surgery. They can also be used to prevent patients from moving during surgery while they are receiving general anesthesia.
How is this drug used?
BRIDION is given as an injection through a vein (intravenous).
What are the benefits of this drug?
The return to recovery time was faster overall for patients receiving BRIDION compared to patients receiving a different drug to reverse the neuromuscular blockade. Most patients recovered within 5 minutes of routine use of BRIDION.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The two figures below depict efficacy results from Trial 1 (moderate blockade).
Figure 4. Time (Minutes) from Administration of BRIDION or Neostigmine at the Reappearance of T2 after Rocuronium to Recovery of the T4/T1 Ratio to 0.9
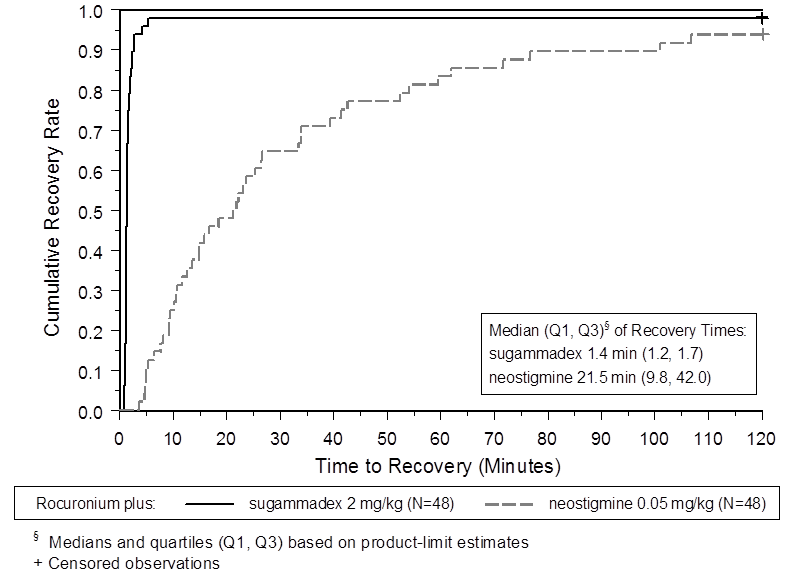
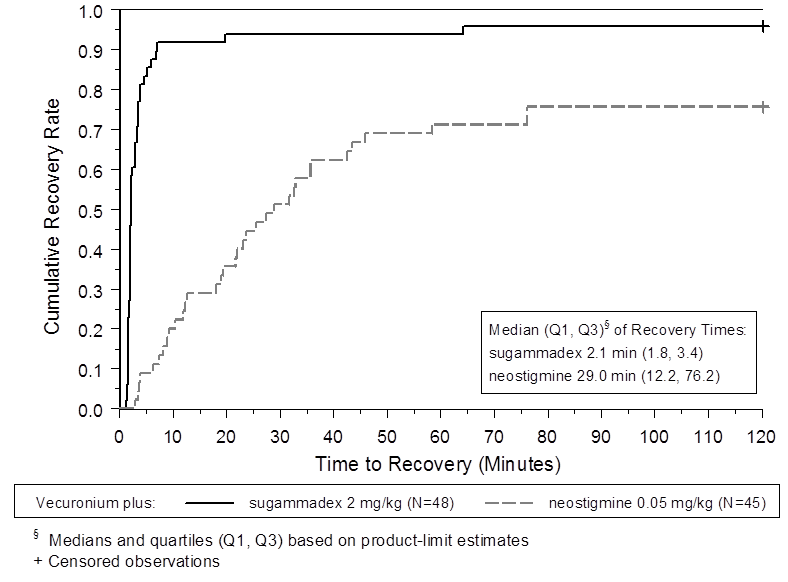
Figure 5. Time (Minutes) from Administration of BRIDION or Neostigmine at the Reappearance of T2 after Vecuronium to Recovery of the T4/T1 Ratio to 0.9
Efficacy results from Trial 2 (deep blockade) are summarized below:
Return of the T4/T1 ratio to 0.9 in patients with 1 to 2 PTCs with BRIDION 4 mg/kg had a wider range of recovery times but the median time to recovery was comparable to the study of reversal at T2 (2.7 minutes with 25th and 75th percentiles of 2.1 and 4.3 minutes for rocuronium [N=37], and 3.3 minutes with 25th and 75th percentiles of 2.3 and 6.6 minutes for vecuronium [N=47]). There were 7 and 6 censored observations in the rocuronium and vecuronium groups, respectively.
BRIDION Prescribing Information
The table below summarizes results of Trial 3 that compared to succinylcholine to rocuronium plus BRIDION.
Table 2. Time (minutes) from Start of Administration of Rocuronium or Succinylcholine to Recovery of T1 to 10% of Baseline
| Treatment Regimen | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rocuronium (1.2 mg/kg) and BRIDION (16 mg/kg) | Succinylcholine (1 mg/kg) | |
| N | 55 | 55 |
| Mean (SD) | 4.4 (0.7) | 7.1 (1.6) |
| Median (Range) | 4.2 (3.5 – 7.7) | 7.1 (3.8 – 10.5) |
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
Subgroup analyses were conducted for sex, race and age.
- Sex: BRIDION was similarly effective in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients in the trials were White. Differences in response among races could not be determined.
- Age: BRIDION was similarly effective in patients below and above 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes the efficacy subgroup analysis for Trials 1, 2, and the dedicated trial in older adults.
Table 3. Primary Efficacy Endpoint Results, by Subgroup--Pooled Data for Trial 1, Trial 2, and dedicated trial in older adults.
| Demographic | BRIDION | Comparator |
|---|---|---|
| N=330 | N=166 | |
| Sex, n | ||
|
Male |
N=160 | N=83 |
| 2:26 (2:12, 2:42) |
29:56 (23:59, 37:23) |
|
|
Female |
N=170 | N=83 |
| 2:57 (2:40, 3:17) |
29:28 (24:25, 35:35) |
|
| Age Group, n | ||
|
17 - 64 years |
N=194 | N=140 |
| 2:35 (2:20, 2:53) |
28:09 (24:10, 32:46) |
|
|
>=65 years |
N=136 | N=26 |
| 2:51 (2:36, 3:07) |
39:43 (25:56, 60:51) |
|
| Race, n | ||
|
White |
N=289 | N=158 |
| 2:39 (2:27, 2:51) |
28:32 (24:38, 33:03) |
|
|
Black or African American |
N=32 | N=2 |
| 2:45 (2:16, 3:20) |
40:30 (8:00, 205:00) |
|
|
Asian |
N=1 | N=6 |
| 18:39 | 77:02 (36:10, 164:02) |
|
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
N=1 | N=0 |
| 3:25 | N/A | |
|
Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander |
N=0 | N=0 |
| N/A | N/A | |
|
Other |
N=7 | N=0 |
| 3:48 (1:05, 13:26) |
N/A | |
Note: Values are geometric mean times (mm:ss) from treatment administration to recovery of TOF >=0.9 (95% CI); Protocol 305 was a dedicated geriatric trial
Clinical Trial Data
The table below separately summarizes the subgroup efficacy analysis for the trial that compared BRIDION to spontaneous reversal after succinylcholine.
Table 4. Primary Efficacy Endpoint Results, by Subgroup for Trial 3
| Demographic | BRIDION | Comparator |
|---|---|---|
| N=330 | N=166 | |
| Sex, n | ||
|
Male |
N=160 | N=83 |
| 2:26 (2:12, 2:42) |
29:56 (23:59, 37:23) |
|
|
Female |
N=170 | N=83 |
| 2:57 (2:40, 3:17) |
29:28 (24:25, 35:35) |
|
| Age Group, n | ||
|
17 - 64 years |
N=194 | N=140 |
| 2:35 (2:20, 2:53) |
28:09 (24:10, 32:46) |
|
|
>=65 years |
N=136 | N=26 |
| 2:51 (2:36, 3:07) |
39:43 (25:56, 60:51) |
|
| Race, n | ||
|
White |
N=289 | N=158 |
| 2:39 (2:27, 2:51) |
28:32 (24:38, 33:03) |
|
|
Black or African American |
N=32 | N=2 |
| 2:45 (2:16, 3:20) |
40:30 (8:00, 205:00) |
|
|
Asian |
N=1 | N=6 |
| 18:39 | 77:02 (36:10, 164:02) |
|
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
N=1 | N=0 |
| 3:25 | N/A | |
|
Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander |
N=0 | N=0 |
| N/A | N/A | |
|
Other |
N=7 | N=0 |
| 3:48 (1:05, 13:26) |
N/A | |
Note: Values are geometric mean times (mm:ss) from treatment administration to recovery of TOF >=0.9 (95% CI)
Clinical Trial Data
What are the possible side effects?
The most common adverse reactions are vomiting, low blood pressure, pain, headache, and nausea.
BRIDION may temporarily reduce how well hormonal contraceptives work. Therefore, women should use a different method of birth control for a period of time after receiving BRIDION.
Severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reactions were reported in the clinical trials.
There have been cases of abnormally slow heart rate (bradycardia), some of which have resulted in cardiac arrest, that have been observed within minutes after the administration of BRIDION.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes adverse reactions in the Phase 1 to 3 trials that supported the side effect profile of BRIDION.
Table 5. Percent of Subject Exposures in Pooled Phase 1 to 3 Studies with Adverse Reactions Incidence ≥ 2%
| Body System Preferred Term |
Sugammadex | Placebo | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg/kg (N=895) n (%) |
4 mg/kg (N=1921) n (%) |
16 mg/kg (N=98) n (%) |
(N=544) n (%) |
|
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | ||||
| Incision site pain | 58 (6) | 106 (6) | 4 (4) | 6 (1) |
| Procedural complication | 13 (1) | 27 (1) | 8 (8) | 3 (1) |
| Airway complication of anesthesia | 11 (1) | 13 (1) | 9 (9) | 0 |
| Anesthetic complication | 8 (1) | 14 (1) | 9 (9) | 1 (<> |
| Wound hemorrhage | 5 (1) | 38 (2) | 0 | 8 (1) |
| Recurrence of neuromuscular blockade | 0 | 1 (<> | 2 (2) | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 208 (23) | 503 (26) | 23 (23) | 127 (23) |
| Vomiting | 98 (11) | 236 (12) | 15 (15) | 57 (10) |
| Abdominal pain | 48 (5) | 68 (4) | 6 (6) | 17 (3) |
| Flatulence | 17 (2) | 51 (3) | 1 (1) | 10 (2) |
| Dry mouth | 9 (1) | 5 (<> | 2 (2) | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Pain | 434 (48) | 993 (52) | 35 (36) | 207 (38) |
| Pyrexia | 77 (9) | 109 (6) | 5 (5) | 17 (3) |
| Chills | 30 (3) | 61 (3) | 7 (7) | 27 (5) |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Headache | 61 (7) | 99 (5) | 10 (10) | 42 (8) |
| Dizziness | 44 (5) | 67 (3) | 6 (6) | 13 (2) |
| Hypoesthesia | 12 (1) | 24 (1) | 3 (3) | 9 (2) |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Oropharyngeal pain | 42 (5) | 66 (3) | 5 (5) | 27 (5) |
| Cough | 13 (1) | 49 (3) | 8 (8) | 11 (2) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Pain in extremity | 13 (1) | 35 (2) | 6 (6) | 15 (3) |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 16 (2) | 33 (2) | 1 (1) | 6 (1) |
| Myalgia | 5 (1) | 17 (1) | 2 (2) | 3 (1) |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 20 (2) | 103 (5) | 5 (5) | 22 (4) |
| Anxiety | 14 (2) | 19 (1) | 3 (3) | 1 (<> |
| Restlessness | 3 (<> | 17 (1) | 2 (2) | 2 (<> |
| Depression | 2 (<> | 5 (<> | 2 (2) | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Red blood cell count decreased | 13 (1) | 34 (2) | 1 (1) | 2 (<> |
| Electrocardiogram QT interval abnormal | 13 (1) | 7 (<> | 6 (6) | 4 (1) |
| Blood creatine phosphokinase increased | 9 (1) | 14 (1) | 2 (2) | 1 (<> |
| Vascular disorders | ||||
| Hypertension | 48 (5) | 96 (5) | 9 (9) | 38 (7) |
| Hypotension | 33 (4) | 102 (5) | 13 (13) | 20 (4) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Pruritus | 17 (2) | 50 (3) | 2 (2) | 9 (2) |
| Erythema | 5 (1) | 31 (2) | 0 | 6 (1) |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Hypocalcemia | 15 (2) | 12 (1) | 0 | 4 (1) |
| Cardiac disorders | ||||
| Tachycardia | 17 (2) | 29 (2) | 5 (5) | 4 (1) |
| Bradycardia | 9 (1) | 21 (1) | 5 (5) | 6 (1) |
| Surgical and medical procedures | ||||
| Hysterectomy | 0 | 0 | 2 (2) | 0 |
| Hypertension | 48 (5) | 96 (5) | 9 (9) | 38 (7) |
| Hypotension | 33 (4) | 102 (5) | 13 (13) | 20 (4) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Pruritus | 17 (2) | 50 (3) | 2 (2) | 9 (2) |
| Erythema | 5 (1) | 31 (2) | 0 | 6 (1) |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Hypocalcemia | 15 (2) | 12 (1) | 0 | 4 (1) |
| Cardiac disorders | ||||
| Tachycardia | 17 (2) | 29 (2) | 5 (5) | 4 (1) |
| Bradycardia | 9 (1) | 21 (1) | 5 (5) | 6 (1) |
| Surgical and medical procedures | ||||
| Hysterectomy | 0 | 0 | 2 (2) | 0 |
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
Subgroup analyses were conducted for sex, race and age.
- Sex: The risk of overall side effects was similar in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients in the trials were White. Differences in the risk of side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The risk of overall side effects was higher in patients 65 years of age and above compared to those below 65 years. This was seen in patients receiving BRIDION as well as in patients receiving a different drug.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes the subgroup analysis for overall treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) in the pooled Phase 1 through Phase 3 trials.
Table 6. Subgroup Analysis for Safety--Overall TEAEs by Subgroup in Pooled Phase 1-3 Clinical Trials
| Demographic | BRIDION | Comparator |
|---|---|---|
| N=2914 | N=544 | |
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 1080/1378 (78) | 225/284 (79) |
| Female | 1315/1536 (86) | 222/260 (85) |
| Age Group, n (%) | ||
| 17 - 64 years | 1689/2118 (80) | 271/345 (79) |
| >=65 years | 706/796 (89) | 176/199 (88) |
| Race, n (%) | ||
| Black or African American | 91/94 (97) | 0/0 (0) |
| Asian | 289/400 (72) | 25/25 (100) |
| Caucasian | 1994/2399 (83) | 417/513 (81) |
| Other | 20/20 (100) | 5/6 (83) |
| Missing | 1/1 (100) | 0/0 (0) |
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved BRIDION based on evidence from clinical trials that evaluated the benefits and the side effects of BRIDION.
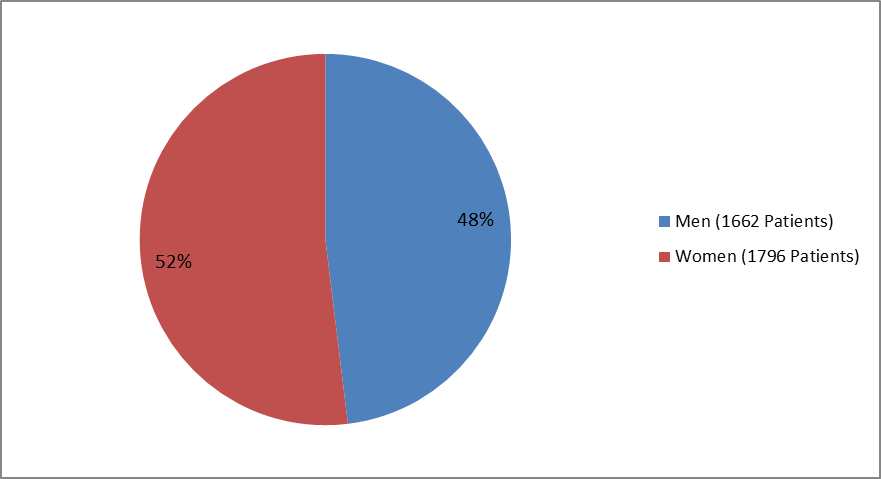
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were enrolled in the clinical trials used to evaluate the side effects of BRIDION (also called the Safety Population). The population of patients used to evaluate the benefits of BRIDION (called the Efficacy Population) is described in the MORE INFO section.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex—Safety Population
Clinical Trial Data
Figure 2 and Table 1 summarize the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trials used to evaluate the side effects of BRIDION.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race—Safety Population
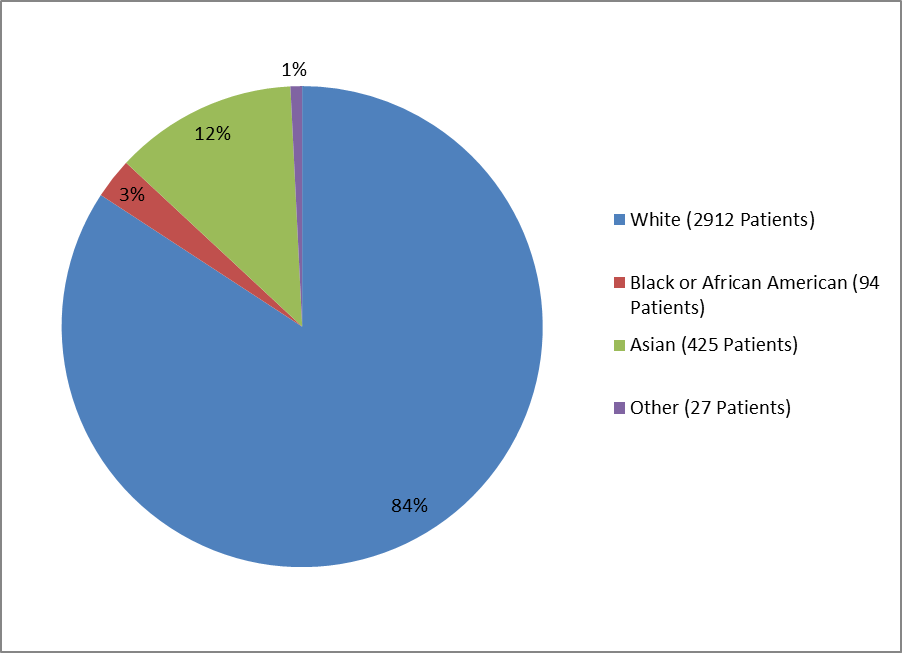
Table 1. Demographics by Race—Safety Population
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 2912 | 84% |
| Black or African American | 94 | 3% |
| Asian | 425 | 12% |
| Other | 26 | 1% |
| Missing | 1 | <> |
Clinical Trial Data
The figure below summarizes how many patients by age were enrolled in the trials used to evaluate the side effects of BRIDION.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age—Safety Population

Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes the demographics for patients in the pooled Safety population.
Table 7. Baseline Demographics for the Clinical Trials (Safety Population)
| Demographic | BRIDION | Comparator | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total N | 2914 | 544 | 3458 |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 1378 (47) | 284 (52) | 1662 (48) |
| Female | 1536 (53) | 260 (48) | 1796 (52) |
| Age Group, n (%) | |||
| <17> | |||
| 17 - 64 years | 2118 (73) | 345 (63) | 2463 (71) |
| >=65 years | 796 (27) | 199 (37) | 995 (29) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| Black or African American | 94 (3) | 0 (0) | 94 (3) |
| Asian | 400 (14) | 25 (5) | 425 (12) |
| Caucasian | 2399 (82) | 513 (94) | 2912 (84) |
| Other | 20 (1) | 6 (1) | 26 (1) |
| Missing | 1 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 80 (3) | 5 (1) | 85 (2) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 2571 (88) | 485 (89) | 3056 (88) |
| Missing | 263 (9) | 54 (10) | 317 (9) |
Clinical Trial Data
The table below summarizes demographic information from the pooled efficacy trials (Trial 1, Trial 2, and the dedicated trial in older adults). Because of a different clinical trial design, the table excludes patients from the third clinical trial (comparing succinylcholine to rocuronium plus BRIDION) and demographics of that trial are presented separately.
Table 8. Baseline Demographics for Efficacy Trials (Trial 1, Trial 2, and dedicated trial in older adults)
| Demographic Subgroup | BRIDION | Comparator | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| N=330 | N=166 | N=496 | |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 160 (48) | 83 (50) | 243 (49) |
| Female | 170 (52) | 83 (50) | 253 (51) |
| Age Group, n (%) | |||
| <17> | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 17 - 64 years | 194 (59) | 140 (84) | 334 (67) |
| >=65 years | 136 (41) | 26 (16) | 162 (33) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 289 (88) | 158 (95) | 447 (90) |
| Black or African American | 32 (10) | 2 (1) | 34 (7) |
| Asian | 1 (0) | 6 (4) | 7 (1) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 1 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0) |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Other | 7 (2) | 0 (0) | 7 (2) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 22 (7) | 22 (13) | 44 (9) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 308 (93) | 144 (87) | 452 (91) |
Clinical Trial Data
Table 9. Baseline Demographics for the Third Efficacy Trial (Comparing BRIDION/Rocuronium versus Succinylcholine)
| Demographic Subgroup | BRIDION | Comparator | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| N=55 | N=55 | N=110 | |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 23 (42) | 23 (42) | 46 (42) |
| Female | 32 (58) | 32 (58) | 64 (58) |
| Age Group, n (%) | |||
| 17 - 64 years | 55 (100) | 54 (98) | 109 (99) |
| >=65 years | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 1 (1) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 41 (75) | 45 (82) | 86 (78) |
| Black or African American | 10 (18) | 6 (11) | 16 (15) |
| Asian | 4 (7) | 3 (5) | 7 (6) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Other | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 1 (1) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 15 (27) | 17 (31) | 32 (29) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 40 (73) | 38 (69) | 78 (71) |
How were the trials designed?
There were three main Phase 3 clinical trials that supported the benefits of BRIDION. In two of these trials (called Trial 1 and Trial 2 in this Snapshot), patients who received neuromuscular blockade with vecuronium or rocuronium were randomly assigned to have their neuromuscular blockade reversed with either BRIDION or a drug called neostigmine. The time to recovery from neuromuscular blockade was measured.
In a third Phase 3 trial (called Trial 3 in this Snapshot), patients were randomly assigned to receive the neuromuscular blocking drug rocuronium followed 3 minutes later with BRIDION for reversal or a different neuromuscular blocking drug, succinylcholine, which reverses spontaneously. The time to recovery from neuromuscular blockade was measured.
There was also a study specifically looking at the benefits and side effects of BRIDION in older adults compared to younger adults (65-74 year-olds and >75 year-olds compared with 18-64 year-olds). In this trial, younger and older groups received rocuronium followed by BRIDION. The time to recovery from neuromuscular blockade was compared between these groups.
How were the trials designed?
Trial 1 was a multicenter, randomized, parallel-group, active-controlled, safety-assessor blinded study comparing BRIDION and neostigmine. Patients were randomly assigned to the rocuronium or vecuronium group and underwent elective surgical procedures under general anesthesia that required endotracheal intubation and maintenance of neuromuscular blockade. The surgical procedures were mainly endocrine, ocular, ENT, abdominal (gynecological, colorectal, urological), orthopedic, vascular, or dermatological. At the reappearance of T2, after the last dose of rocuronium or vecuronium, 2 mg/kg BRIDION or 50 mcg/kg neostigmine was administered in a randomized order as a single bolus injection. The time from start of administration of BRIDION or neostigmine to recovery of the TOF (T4/T1) ratio to 0.9 was assessed. Generally, a T4/T1 ratio 0.9 correlates with recovery from neuromuscular blockade.
Trial 2 was a multicenter, randomized, parallel-group, active-controlled, safety-assessor blinded study comparing BRIDION and neostigmine. Patients were randomly assigned to the rocuronium or vecuronium group and underwent elective surgical procedures under general anesthesia that required endotracheal intubation and maintenance of neuromuscular blockade. The surgical procedures were mainly abdominal (gynecological, colorectal, urological), orthopedic, reconstructive, or neurological. At 1 to 2 PTCs, after the last dose of rocuronium or vecuronium, 4 mg/kg BRIDION or 70 mcg/kg neostigmine was administered in a randomized order as a single bolus injection. The time from start of administration of BRIDION or neostigmine to recovery of the TOF (T4/T1) ratio to 0.9 was assessed, although neostigmine was not expected to reverse neuromuscular blockade at a depth of 1 to 2 PTCs. Generally, a T4/T1 ratio 0.9 correlates with recovery from neuromuscular blockade.
Trial 3 was a multicenter, randomized, parallel-group, active-controlled, safety-assessor blinded study in which time to recovery from neuromuscular blockade induced by succinylcholine compared with recovery from neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium followed 3 minutes later with BRIDION was assessed. Patients underwent elective surgical procedures under general anesthesia that required endotracheal intubation and a short duration of neuromuscular relaxation. The laparoscopic or open surgical procedures were mainly gynecological, orthopedic, or reconstructive. Return of the first twitch in a TOF (T1) to 10% of baseline was compared between BRIDION 16 mg/kg for reversal of rocuronium 1.2 mg/kg versus spontaneous recovery from succinylcholine 1 mg/kg.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION