Submit and Reference Tobacco Product Master Files
On this page:
- Overview of Tobacco Product Master Files (TPMF)
- Preparing and Referencing a TPMF
- TPMF Process
- TPMF Resources
Overview of TPMFs
Tobacco Product Master Files (TPMF) can be submitted by any person. TPMFs are voluntary submissions to the FDA that contain trade secret and/or confidential commercial information about a tobacco product or component that the owner does not want to share with others but may be needed for reference by other parties who are preparing tobacco product submissions. Tobacco Product Master Files are a beneficial tool for manufacturers, component and ingredient suppliers, and researchers, and can assist the tobacco product submission process. When a TPMF is established with FDA, it can be referenced by the TPMF owner and/or an authorized party:
- TPMF owners can reference their own TPMF rather than submitting the same information separately for multiple submissions.
- Authorized parties who have been granted authorization to reference a TPMF by the TPMF owner can reference TPMF data and analyses, such as extensive ingredient lists and constituent testing, in support of a tobacco product submission. The FDA can then access and review the trade secret and/or confidential information as part of the authorized party’s submission without that party seeing or accessing the TPMF owner’s confidential information.
Referencing a TPMF file rather than re-creating or submitting similar or duplicate information for each submission may allow both TPMF owners and authorized parties to reduce submission preparation costs.
Examples:
- A flavor supplier establishes a TPMF containing a full listing of ingredients and composition information of different flavors. The flavor supplier could then grant authorization to a customer to reference the TPMF to support the customer's premarket tobacco application (PMTA) for an e-cigarette that uses the supplier's flavors. When reviewing the PMTA, FDA will review the confidential TPMF ingredient and composition information, without that information being shared to the customer.
- A laboratory establishes a TPMF containing protocols and methods to determine the quantities of Harmful and Potentially Harmful Constituents (HPHCs) for new and predicate tobacco products. The laboratory could then grant authorization to a manufacturer to reference the TPMF to support the manufacturer’s substantial equivalence (SE) application. When reviewing the SE Report, FDA will review the confidential TPMF protocols and HPHC methods, without that information being shared to the manufacturer.
- A cigarette manufacturer establishes a TPMF containing all of the design parameters for one of their predicate tobacco products. The TPMF also contains evidence to demonstrate that the product was on the market as of February 15, 2007. The TPMF owner may reference its own TPMF in 50 SE applications, rather than submitting the predicate tobacco product information multiple times. When reviewing the SE Report FDA will review the TPMF to adequately characterize the predicate product and make a determination of predicate eligibility.
Common submissions that may reference TPMFs include but are not limited to:
- Premarket Tobacco Applications (PMTA)
- Substantial Equivalence (SE)
- Modified Risk Tobacco Product Applications (MRTPA)
- Exemption from SE Requirements (EX REQ)
- Pre-Existing Tobacco Products
- Use of Investigational Tobacco Products
- Listing of Ingredients in Tobacco Products
Preparing and Referencing a TPMF
- A TPMF should include:
- Cover letter that contains:
- A statement that the information is being submitted as TPMF
- A brief description of the TPMF content
- Name and contact information for the TPMF owner
- If submitted by an authorized representative, the name and contact information for the authorized representative
- Signature of the TPMF owner or authorized representative, who resides in or has a place of business in the U.S.
- If submitted by a non-attorney representative, include the TPMF owner’s authorization (e.g., on TPMF owner’s letterhead);
- If submitted by an attorney, include attorney declaration and authorization (e.g., “I am submitting on behalf of…”)
- If the TPMF owner or authorized representative does not reside in or have a place of business in the United States, the name and contact information for a U.S. agent
- Table of contents
- The information that will be included in the TPMF (e.g. tobacco product information, manufacturing and processing data, research findings)
- List of each person currently authorized to reference the TPMF including name and contact information
- Identification of any limitations on each authorization (e.g., if the TPMF owner is authorizing others to use only certain sections and, if so, identification of those sections).
- We recommend the following structure:
- Cover letter and Administrative Information
- Table of contents
- Summaries
- Product Description and Manufacturing (if applicable)
- Nonclinical (if applicable)
- Clinical – Product Impact on Individual Health (if applicable)
- Clinical – Product Impact on Population Health (if applicable)
- Environmental Impact (if applicable)
- How to Submit a TPMF
- Online:
- Request an Industry Account Manager (IAM) account to establish a CTP Portal Next Generation account, if your company does not already have an IAM.
- Prepare your submission electronically using FDA's eSubmitter software and the eSubmitter template “CTP Transmittal Form.”
- Submit online via the CTP Portal Next Generation
Note: CTP recommends using the CTP Portal Next Generation. However, if you already have a Unified Submission Portal (USP) account, you may use it to submit documents to CTP.
- Submit by Mail: If you are unable to submit online, mail submissions to CTP's Document Control Center.
- Online:
- Amendments to a TPMF Amendments can be submitted using the above instructions. The amendment should include a cover letter that includes the STN(s) of the TPMF in the subject line. If responding to a deficiency (including requests), follow the instructions as outlined in your deficiency letter.
- Grant Authorization to Reference a TPMF The TPMF owners or authorized representatives may grant parties the right to reference a TPMF through a letter of authorization (LOA). An LOA is submitted to FDA on the TPMF owner’s letterhead and includes the following:
- TPMF submission tracking number
- Limitations to the authorized party’s authorization
- Location within the TPMF of the section being authorized as right of reference
- Signature of the TPMF owner or authorized representative
FDA recommends the TPMF owner also provide a copy of the LOA to the authorized party for inclusion in their submission.
- Reference a TPMF
FDA recommends that the authorized party include the following when referencing a TPMF:- A notation in the cover letter of the TPMF STN being referenced
- If possible, where the information being referenced is located in the TPMF
- A copy of the LOA
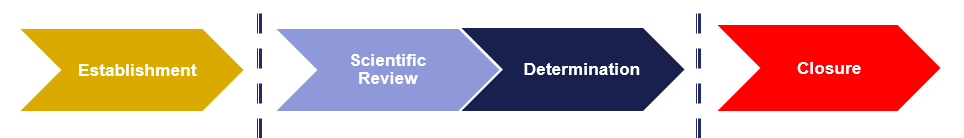
TPMF Process
- Establishment: When a request to establish a TPMF is submitted to CTP. Establishing a TPMF with FDA does not mean the data contained within has been validated by FDA and does not equate to any conclusion regarding its contents.
- Output
- Acknowledgement letter, or
- General correspondence letter: provides information if information does not allow for a TPMF to be established
- Output
- Scientific Review: When a submission appropriately references a TPMF, FDA intends to conduct scientific review of the information referenced.
- Output
- None required
- Output
- Determination: During review, FDA determines the information referenced in the TPMF is adequate or inadequate for the submission that is referencing it.
- Output
- Deficiency letter: Additional information is needed or will be helpful in making a decision on a submission which references a TPMF. Depending on the type of application referencing the TPMF, TPMF owners have between 30-180 days to respond to this type of letter.
- Output
- Closure: When FDA initiates closure of a TPMF if it has not been active or referenced in a three-year period.
- Output
- Notification letter: Notifies the TPMF owner of the intent to close and provides a timeframe for response.
- Closure letter: Letter closing the TPMF. Once a TPMF is closed, authorized parties are unable to reference the TPMF in support of its submissions. FDA will not review the TPMF in support of a submission.
- Output
TPMF Resources
- Guidance
- Webinar
- Reference Tools
- Tobacco Product Master Files (TPMFs): Presentation from 2018 Tobacco Product Application Review Public Meeting
- Q&A: Tobacco Product Review and Evaluation—Pathways to Market
- Tobacco Product Marketing Orders
- Information and Resources on Application Review Programs: Presentation from 2018 Tobacco Product Application Review Public Meeting
- CTP Electronic Submissions Standards and Activities: Presentation from 2018 Tobacco Product Application Review Public Meeting