2023 FDA Science Forum
LC-MS/MS Determination of Antibiotic Residues in Distillers Grains: Method Upgrade
- Authors:
- Center:
-
Contributing OfficeCenter for Veterinary Medicine
Abstract
Background:
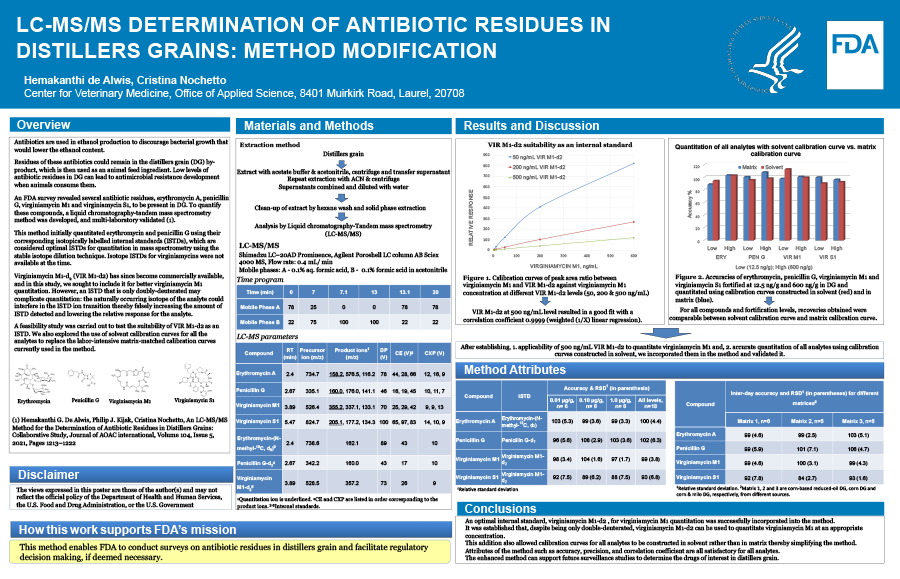
Antibiotics are used in ethanol production to discourage bacterial growth that would lower the ethanol content. Residues of these antibiotics can remain in the distillers grain (DG) by-product, which is used an animal feed ingredient. Low levels of antibiotic residues in DG can lead to antimicrobial resistance when animals consume them. An FDA survey revealed several residues, erythromycin A, penicillin G, virginiamycin M1 and virginiamycin S1, to be present in DG. To quantify these compounds, a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method was developed, and multi-laboratory validated.
Purpose:
The method initially quantitated erythromycin and penicillin G using their corresponding isotopically labelled internal standards (ISTDs). However, isotope ISTDs for virginiamycins were not available at the time. Virginiamycin M1-d2 has since become commercially available, and in this study, efforts were made to include it for better virginiamycin M1 quantitation. However, because virginiamycin M1-d2 was only doubly deuterated, there could be potential interference to its ion transition from the naturally occurring isotope of the analyte. Therefore, its viability as an ISTD needed to be first established.
Methodology:
Antibiotic residues were solvent-extracted from DG, the extract was cleaned up by a hexane wash and solid phase extraction, and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Virginiamycin M1 calibration curves were created with differing concentrations of virginiamycin M1-d2 to establish a suitable ISTD concentration.
Results:
At a concentration of 500 ng/mL, virginiamycin M1-d2 resulted in a linear calibration curve for virginiamycin M1 in the range 2.5–600 ng/mL. Encompassing all analytes, accuracy and precision ranged 90 to 102% and 3.8 to 6.8, respectively. In addition to improving virginiamycin M1 quantitation, the addition of virginiamycin M1-d2 allowed elimination of the tedious matrix-extracted calibration curve for all four analytes and use of a calibration curve in solvent instead, rendering analysis of investigational samples more efficient.
Conclusion:
A previously developed LC-MS/MS method was successfully modified to use virginiamycin M1-d2 as an ISTD after establishing its suitability despite its low deuterium substitution level. The method could support surveillance studies to determine drugs of interest in DG.