Drug Trials Snapshots: VELSIPITY
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the key clinical trials that supported the original FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, age, and ethnic groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Some of the information in this Snapshot is for presentation purposes and does not represent the approved conditions of use of this drug. Refer to the VELSIPITY Prescribing Information for all the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable).
VELSIPITY (etrasimod)
(vel si’ pi tee)
Pfizer Inc.
Approval date: October 12, 2023
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
VELSIPITY is a drug that reduces the number of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) in the blood by binding to human sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors that is used to treat adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC).
How is this drug used?
VELSIPITY is a tablet taken by mouth once daily.
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved VELSIPITY based on evidence from two clinical trials, UC-1 and UC-2, of 741 patients with moderately to severely active UC. UC-1 and UC-2 were conducted at 205 sites in 37 countries and 185 sites in 29 countries, respectively, in Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, Croatia, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, France, Georgia, Germany, Hungary, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Latvia, Lebanon, Lithuania, Mexico, Moldova, Republic of Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, South Africa, Spain, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, Ukraine, United Kingdom, and the United States.
For UC-1, approximately 18% (75) of the patients were from the United States. In addition, 70% (286) were from Europe, 19% (76) from North America that included patients from the United States and Canada, and 11% (46) from the rest of the world.
For UC-2, approximately 9% (29) of the patients were from the United States. In addition, 62% (207) were from Europe, 9% (29) from North America that included patients from the United States and Canada, and 29% (97) from the rest of the world.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of VELSIPITY were evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials that enrolled patients with moderately to severely active UC. Patients received VELSIPITY 2 mg once daily or placebo for up to 52 weeks in UC-1 and for up to 12 weeks in UC-2. The benefit of VELSIPITY was evaluated based on the percentage of patients who achieved clinical remission at Week 52 for UC-1 and at Week 12 for UC-2.
A third randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, UC-3, contributed to the safety assessment of VELSIPITY.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of VELSIPITY were established in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies, UC-1 and UC-2. Both trials included patients with moderately to severely active UC who had an inadequate response, loss of response, or intolerance to at least one of the following treatment options: oral aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, thiopurines, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, or biologic therapies (e.g., TNF blocker, anti-integrin, anti-IL12/23). In both studies, subjects were randomized to receive either VELSIPITY 2 mg once daily or placebo. Patients in UC-1 were treated for up to 52 weeks and patients in UC-2 were treated for up to 12 weeks.
In UC-1, a total of 408 patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive VELSIPITY 2 mg once daily or placebo. The coprimary endpoints were the proportion of patients achieving clinical remission at Week 12 and at Week 52.
In UC-2, a total of 333 patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive VESLIPITY 2 mg once daily or placebo. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving clinical remission at Week 12.
The safety of VELSIPITY was also evaluated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, UC-3, that enrolled patients with moderately to severely active UC who were treated for up to 12 weeks.
DEMOGRAPHICS SNAPSHOT
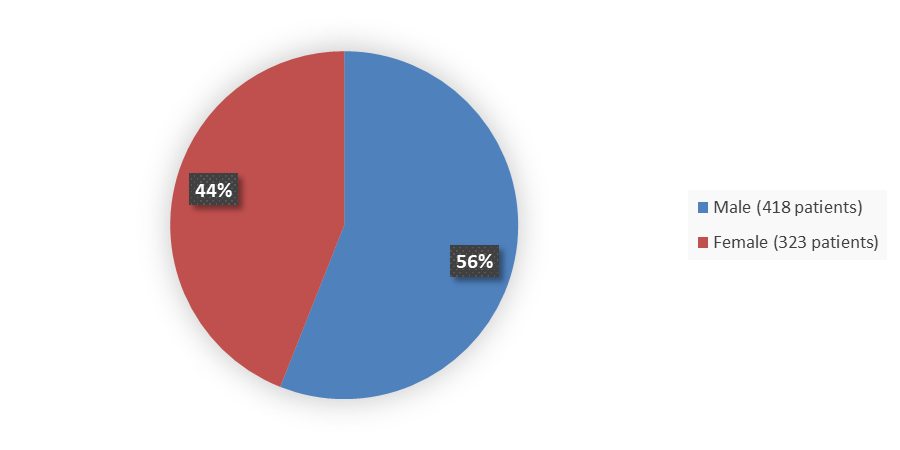
Figure 1 summarizes the percentage of male and female patients enrolled in the clinical trials that evaluated the efficacy of VELSIPITY.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
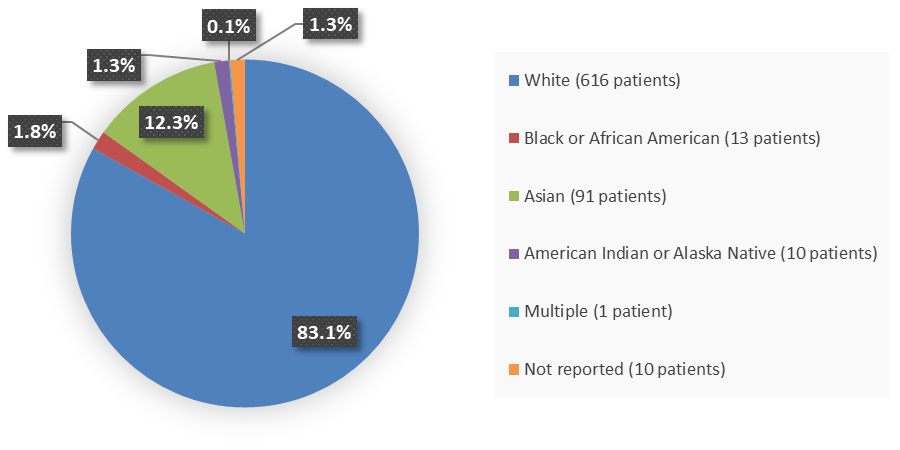
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trials that evaluated the efficacy of VELSIPITY.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
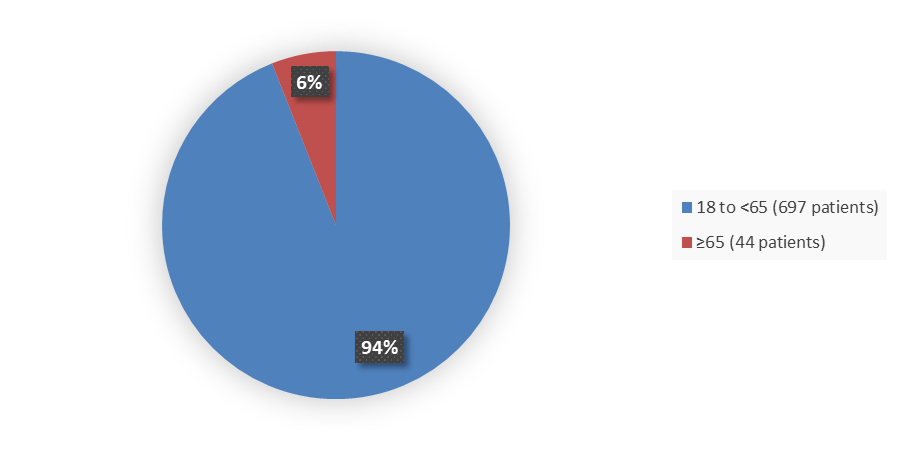
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age enrolled in the clinical trials that evaluated the efficacy of VELSIPITY.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
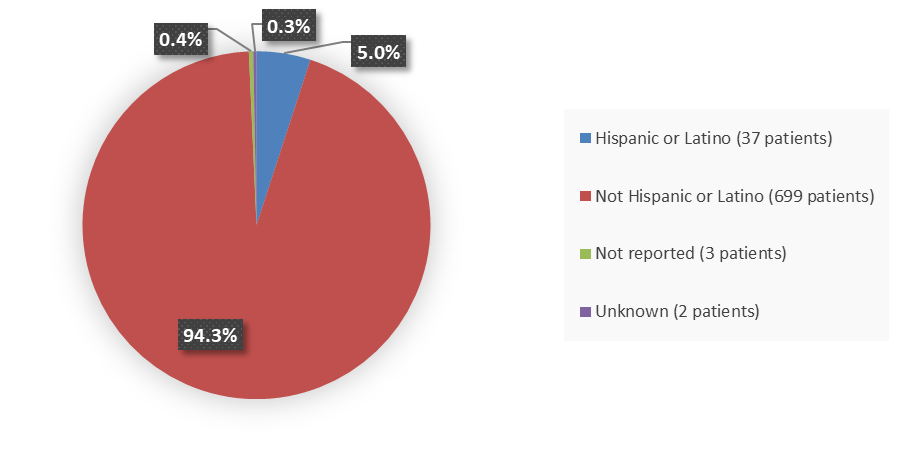
Figure 4 summarizes the percentage of patients by ethnicity enrolled in the clinical trials that evaluated the efficacy of VELSIPITY.
Figure 4. Baseline Demographics by Ethnicity
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
Table 1. Demographics Table (Studies UC1 and UC2)
| Demographic | UC1 N=408 n (%) |
UC2 N=333 n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | ||
| 18 to <65 | 381 (93) | 316 (95) |
| ≥65 | 27 (7) | 17 (5) |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 185 (45) | 138 (41) |
| Male | 223 (55) | 195 (59) |
| Race | ||
| White | 363 (89) | 253 (76) |
| Black or African American | 9 (2) | 4 (1) |
| Asian American Indian or Alaska Native Multiple Not Reported |
28 (7) 4 (1) N/A 4 (1) |
63 (19) 6 (2) 1 (<1) 6 (2) |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Hispanic or Latino | 19 (4) | 18 (5) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino Not Reported Unknown |
386 (95) 2 (<1) 1 (<1) |
313 (94) 1 (<1) 1 (<1) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
What are the benefits of this drug?
VELSIPITY was better than placebo at helping to get UC under control (induce clinical remission) and keep UC under control (maintain clinical remission). It may help reduce or stop the need to take corticosteroid medicines. It also may help improve the way the lining of the large intestine looks to a healthcare provider during a colonoscopy procedure.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
Efficacy results for the primary analysis of clinical remission are presented in Table 2 (UC-1 at Week 12 and Week 52) and Table 3 (UC-2 at Week 12). In UC-1, for the coprimary endpoints of clinical remission at Week 12 and Week 52, patients who received VELSIPITY had a statistically significant higher rate of clinical remission than patients who received placebo.
In UC-2, for the primary endpoint of clinical remission at Week 12, patients who received VELSIPITY had a statistically significant higher rate of clinical remission than patients who received placebo.
Table 2. Clinical Remission at Weeks 12 and 52, UC-1
Parameter |
VELSIPITY N=274 |
Placebo N=134 |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical remission at Week 12, n (%) | 75 (27.4) | 10 (7.5) |
| Treatment difference, (95% CI) | 20.1 (13.2, 27.0) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | |
| Clinical remission at Week 52, n (%) | 89 (32.5) | 9 (6.7) |
| Treatment difference, (95% CI) | 25.7 (18.7, 32.7) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval
Table 3. Clinical Remission at Week 12, UC-2
| Parameter | VELSIPITY N=221 |
Placebo N=112 |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical remission at Week 12, n (%) | 58(26.2) | 17 (15.2) |
| Treatment difference, (95% CI) | 11.2 (2.7, 19.8) | |
| p-value | 0.010 | |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age?
- Sex: The observed effect of VELSIPITY was similar for males and females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in how VELSIPITY worked among races could not be determined.
- Age: The number of patients who were older than 65 years of age was small; therefore, whether VELSIPITY worked differently in older adults could not be determined.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Subgroup analyses were conducted to assess the potential for differences in the treatment effect for various demographic groups. For the development program, the treatment effect of VELSIPITY compared to placebo appeared consistent across the demographic subgroup of sex. However, there was an insufficient number of patients of races other than White and an insufficient number of patients older than 65 years of age to determine whether VELSIPTY worked differently in different races or in older adults.
Table 4. Clinical Remission at Week 12 by Sex, Race, and Age, UC-1
Group |
VELSIPITY n/N (%) |
Placebo n/N (%) |
Treatment Difference (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 28/144 (19.4) | 7/79 (8.9) | 10.6 (1.6, 19.6) |
| Female | 47/130 (36.2) | 3/55 (5.5) | 30.7 (20.5, 40.9) |
| Race | |||
| White | 67/244 (27.5) | 10/119 (8.4) | 19.1 (11.6, 26.6) |
| Asian | 4/19 (1.1) | 0/9 (0) | 21.1 (2.7, 39.4) |
| Black or African American | 2/6 (33.3) | 0/3 (0) | 33.3 (-4.4, 71.0) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 1/1 (100) | 0/3 (0) | NA |
| Age, years | |||
| <65 | 73/257 (28.4) | 10/124 (8.1) | 20.3 (13.0, 27.6) |
| ≥65 | 2/17 (11.8) | 0/10 (0) | 11.8 (-3.5, 27.1) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; NA, not applicable
Table 5. Clinical Remission at Week 52 by Sex, Race, and Age, UC-1
Group |
VELSIPITY n/N (%) |
Placebo n/N (%) |
Treatment Difference (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 42/144 (29.2) | 5/79 (6.3) | 22.8 (13.7, 32.0) |
| Female | 47/130 (36.2) | 4/55 (7.3) | 28.9 (18.1, 39.6) |
| Race | |||
| White | 80/244 (32.8) | 7/119 (5.9) | 26.9 (19.6, 34.1) |
| Asian | 6/19 (31.6) | 1/9 (11.1) | 20.5 (-8.8, 49.8) |
| Black or African American | 2/6 (33.3) | 1/3 (33.3) | 0 (-65.3, 65.3) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 0/1 (0) | 0/3 (0) | NA |
| Age, years | |||
| <65 | 79/257 (30.7) | 9/124 (7.3) | 23.5 (16.2, 30.7) |
| ≥65 | 10/17 (58.5) | 0/10 (0) | 58.8 (35.4, 82.2) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; NA, not applicable
Table 6. Clinical Remission at Week 12 by Sex, Race, and Age, UC-2
Group |
VELSIPITY n/N (%) |
Placebo n/N (%) |
Treatment Difference (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 32/125 (25.6) | 8/70 (11.4) | 14.2 (3.5, 24.9) |
| Female | 26/96 (27.1) | 9/42 (21.4) | 5.7 (-9.6, 20.9) |
| Race | |||
| White | 46/166 (27.7) | 16/87 (18.4) | 9.3 (-1.3, 19.9) |
| Asian | 7/41 (17.1) | 1/22 (4.5) | 12.5 (-1.9, 27.0) |
| Black or African American | 1/2 (50.0) | 0/2 (0) | 50.0 (-19.3, 119.3) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 3/5 (60.0) | 0/1 (0) | 60.0 (17.1, 102.9) |
| Multiple | 0/1 (0) | 0 (NA) | NA |
| Age, years | |||
| <65 | 56/210 (26.7) | 17/106 (16.0) | 10.6 (1.4, 19.8) |
| ≥65 | 2/11 (18.2) | 0/6 (0) | 18.2 (-4.6, 41.0) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; NA, not applicable
What are the possible side effects?
VELSIPITY may cause serious side effects including:
- Increased risk of serious infections
- Slow heart rate, especially after first dose
- Increased liver enzymes
- Increased blood pressure
- Macular edema, which can lead to permanent visual loss
- Skin cancer
- Swelling and narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain (Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome [PRES])
- Shortness of breath
- Harm to an unborn baby. Effective birth control should be used during treatment with VELSIPITY and for seven days after stopping VELSIPITY.
The most common side effects (≥5%) in patients treated with VELSIPITY include headache, elevated liver tests, and dizziness.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
Table 7 shows adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of subjects and at a higher rate than placebo in patients treated with VELSIPITY in UC-1. Table 8 shows adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of subjects and at a higher rate than placebo in patients treated with VELSIPITY in UC-2 and UC-3.
Table 7. Adverse Reactions by Week 52, UC-1
Adverse Reaction |
VELSIPITY N=289 % |
Placebo N=144 % |
|---|---|---|
| Headache1 | 9 | 5 |
| Elevated liver tests2 | 6 | 5 |
| Dizziness3 | 5 | 2 |
| Arthralgia | 4 | 2 |
| Hypertension4 | 3 | 1 |
| Urinary tract infection5 | 3 | 2 |
| Nausea | 3 | 1 |
| Hypercholesterolemia6 | 3 | 0 |
| Herpes viral infection7 | 2 | 1 |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
1 Headache includes related terms headache, migraine, and tension headache
‡ Elevated liver tests includes related terms ALT increased, AST increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, cholestasis, GGT increased, hepatic enzyme increased, hyperbilirubinemia, liver function test increased, and transaminases increased
3 Dizziness includes related terms dizziness, dizziness exertional, and dizziness postural
4 Hypertension includes related terms hypertension, and blood pressure increased
5 Urinary tract infection includes related terms urinary tract infection and cystitis
6 Hypercholesterolemia includes related terms hypercholesterolemia and blood cholesterol increased
7 Herpes viral infection includes related terms herpes zoster, oral herpes, and herpes simplex
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase
Table 8. Adverse Reactions by Week 12, UC-2 and UC-3
Adverse Reaction |
VELSIPITY N=288 % |
Placebo N=170 % |
|---|---|---|
| Headache1 | 6 | 4 |
| Elevated liver tests2 | 4 | 1 |
| Nausea | 4 | 2 |
| Bradycardia3 | 3 | 0 |
| Urinary tract infection4 | 3 | 0 |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
1 Headache includes related terms headache, migraine, and sinus headache.
2 Elevated liver tests includes related terms ALT increased, AST increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, blood bilirubin increased, cholestasis, GGT increased, hepatic enzyme increased, hepatic function abnormal, liver function test abnormal, and transaminases increased.
3 Bradycardia includes related terms bradycardia, sinus bradycardia, and heart rate decreased.
4 Urinary tract infection includes related terms urinary tract infection, cystitis, and genitourinary tract infection.
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in males and females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The number of patients of 65 years of age and older was small; therefore, it could not be determined whether there were any differences in side effects among patients 65 years of age or older.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Subgroup analyses were conducted to assess the potential for differences in the side effects for various demographics. Overall, the reported side effects of VELSIPITY compared to placebo appeared consistent across the demographic subgroup of sex. However, there was an insufficient number of patients of races other than White and an insufficient number of patients older than 65 years of age to determine any differences in side effects among different races or in older adults.
Table 9. Adverse Events by Week 52 by Sex, Age, Race, and Ethnicity, UC-1
Characteristic |
VELSIPITY N=289 n/Ns (%) |
Placebo N=144 n/Ns (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Female | 101/137 (73.7) | 34/56 (60.7) |
| Male | 105/152 (69.1) | 47/88 (53.4) |
| Age group, years | ||
| <65 | 194/272 (71.3) | 78/134 (58.2) |
| ≥65 | 12/17 (70.6) | 3/10 (30.0) |
| Race | ||
| White | 183/256 (71.5) | 70/129 (54.3) |
| Asian | 15/22 (68.2) | 7/9 (77.8) |
| Black or African American | 5/6 (83.3) | 2/3 (66.7) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 0/1 (0) | 2/3 (66.7) |
| Not reported | 3/4 (75) | 0/0 (0) |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Hispanic or Latino | 7/12 (58.3) | 7/7 (100) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 205/275 (74.5) | 76/136 (55.9) |
| Not reported | 0/2 (0) | 1/1 (100) |
Source: Adapted from FDA review
Abbreviations: N, number of subjects in treatment arm; n, number of subjects with adverse event; Ns, total number of subjects for each specific subgroup and were assigned to that specific arm
Table 10. Adverse Events by Week 12 by Sex, Age, Race, and Ethnicity, UC-2 and UC-3
Characteristic |
VELSIPITY N=288 n/Ns (%) |
Placebo N=170 n/Ns (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Female | 67/126 (53.5) | 30/65 (46.3) |
| Male | 73/162 (46.1) | 51/105 (48.2) |
| Age group, years | ||
| <65 | 134/275 (49.5) | 75/159 (46.7) |
| ≥65 | 6/13 (37.5) | 6/11 (67.5) |
| Race | ||
| White | 105/225 (47.0) | 64/139 (45.1) |
| Asian | 26/48 (64.9) | 13/27 (39.0) |
| Black or African American | 2/2 (75.0) | 3/3 (100.0) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 3/6 (37.5) | 1/1 (75) |
| Multiple | 1/1 (75) | 0/0 (0) |
| Not reported | 3/6 (37.5) | 0/0 (0) |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Hispanic or Latino | 8/11 (77.5) | 5/12 (41.7) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 138/275 (50.6) | 81/158 (51.7) |
| Not reported or Unknown | 1/2 (75.0) | 0/0 (0) |
Source: Adapted from FDA review
Proportions are adjusted for different randomization ratios of 302 and 003 by Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel weights.
Abbreviations: N, number of subjects in treatment arm; n, number of subjects with adverse event; Ns, total number of subjects for each specific subgroup and were assigned to that specific arm
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.