Drug Trials Snapshots: KRAZATI
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the key clinical trials that supported the original FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, age, and ethnic groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Some of the information in this Snapshot is for presentation purposes and does not represent the approved conditions of use of this drug. Refer to the KRAZATI Prescribing Information for all of the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable).
KRAZATI (adagrasib)
krah zah' tee
Mirati Therapeutics, Inc.
December 12, 2022
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
KRAZATI is a prescription medicine used to treat adult patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has an abnormal KRAS G12C gene mutation, is locally advanced or has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic), and has progressed on or after one prior treatment.
How is this drug used?
KRAZATI is a tablet that is taken twice daily by mouth. KRAZATI may be taken with or without food.
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved KRAZATI based on evidence from a clinical trial of patients with KRAS G12C mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who received prior platinum-based chemotherapy and an immune checkpoint inhibitor. All patients were enrolled and treated at sites in the United States. The same trial was used to assess the efficacy of KRAZATI in 112 patients and the safety of KRAZATI in 366 patients.
Who participated in the trials?
Table 4. Baseline Demographics and Disease Characteristics in the Efficacy and Safety Populations of Patients in KRYSTAL-1
|
Characteristic |
KRAZATI 600 mg BID |
|
|
Efficacy |
Safety |
|
|
Sex, n (%) |
|
|
|
Male |
50 (45) |
156 (43) |
|
Female |
62 (55) |
210 (57) |
|
Race, n (%) |
|
|
|
White |
93 (83) |
301 (82) |
|
Black or African American |
9 (8) |
33 (9) |
|
Asian |
5 (4.5) |
14 (3.8) |
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
1 (0.9) |
2 (0.5) |
|
Other |
4 (3.6) |
16 (4.4) |
|
|
|
|
|
Hispanic or Latino |
3 (2.7) |
22 (6) |
|
Not Hispanic or Latino |
103 (92) |
334 (91) |
|
Missing |
6 (5) |
10 (2.7) |
|
Age, years |
|
|
|
Mean (SD) |
64.1 (9.7) |
63.0 (11.2) |
|
Median |
64.0 |
64.0 |
|
Q1, Q3 |
59.8, 70.0 |
57.0, 70.0 |
|
Min, max |
25, 89 |
21, 89 |
|
Age group, years |
|
|
|
<65 |
59 (51) |
197 (54) |
|
≥65 to <75 |
42 (36) |
120 (33) |
|
≥75 |
15 (13) |
49 (13) |
|
ECOG performance status |
|
|
|
0 |
18 (16) |
106 (29) |
|
1 |
93 (83) |
259 (71) |
|
Missing |
1 (0.9) |
1 (0.3) |
|
Smoking history |
|
|
|
Lifetime non-smoker |
5 (4.5) |
75 (20) |
|
Current smoker |
11 (10) |
46 (13) |
|
Former smoker |
96 (86) |
245 (67) |
Source: FDA Review
Abbreviations: BID, twice daily; ECOG, Easter Cooperative Oncology Group; Q1, first quartile; Q3, third quartile; SD, standard deviation
How were the trials designed?
KRAZATI was evaluated in a multicenter, open-label, single arm, multicohort clinical trial (KRYSTAL-1) including 112 patients with measurable disease at baseline with KRAS G12C mutated metastatic or locally advanced NSCLC whose disease had progressed on or after platinum-based chemotherapy and an immune checkpoint inhibitor. Patients received KRAZATI at a dose of 600 mg twice daily until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measure was confirmed objective response rate (ORR) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST v1.1) as evaluated by blinded independent central review, and duration of response.
How were the trials designed?
KRYSTAL-1 clinical trial was a multicenter, open-label, single arm, dose escalation and dose expansion study of KRAZATI. This study included a dose escalation phase (Part 1), for selection of the recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D) of KRAZATI, followed by an expansion phase in 7 distinct disease cohorts treated at the RP2D (Part 2). In the dose escalation phase, the doses ranged from 150 mg to 1200 mg daily. The efficacy population (N=112) included patients from Cohort A with metastatic NSCLC with KRAS G12C mutated NSCLC who had previously been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and an immune checkpoint inhibitor and received KRAZATI at 600 mg twice daily.
DEMOGRAPHICS SNAPSHOT
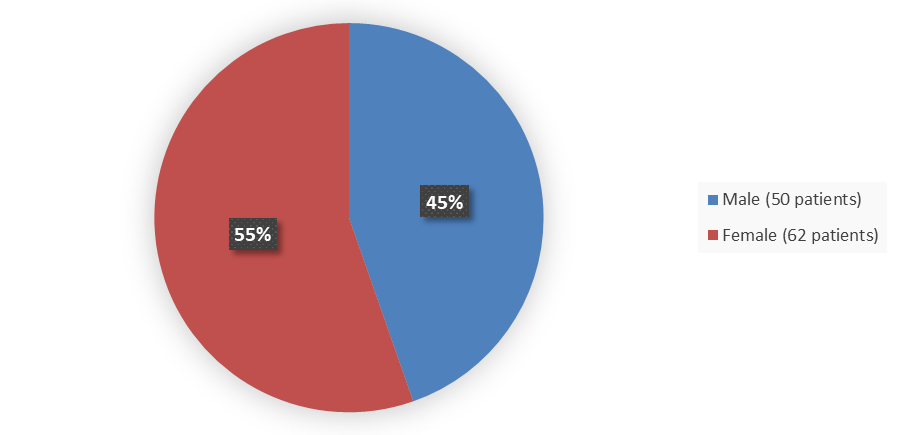
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex – Efficacy Population
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Alt-Tag: Pie chart summarizing how many male and female patients were in the clinical trial. In total, 50 (45%) male patients and 62 (55%) female patients participated in the clinical trial.
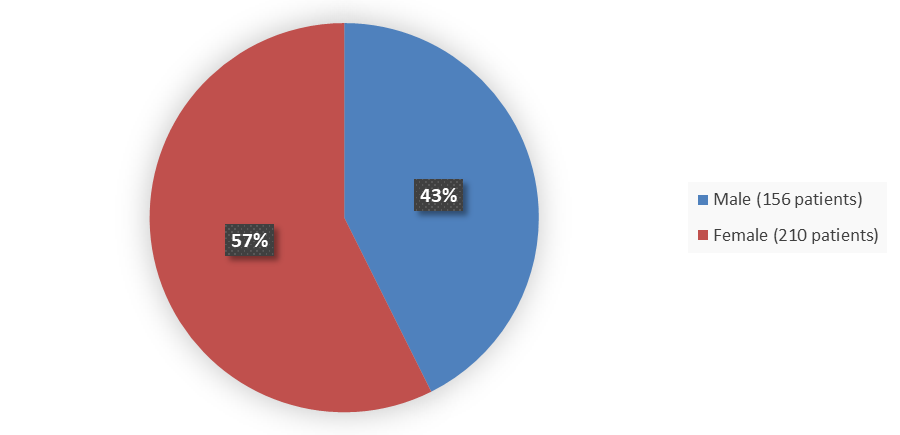
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Sex – Safety Population
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Alt-Tag: Pie chart summarizing how many male and female patients were in the clinical trial. In total, 156 (43%) male patients and 210 (57%) female patients participated in the clinical trial.
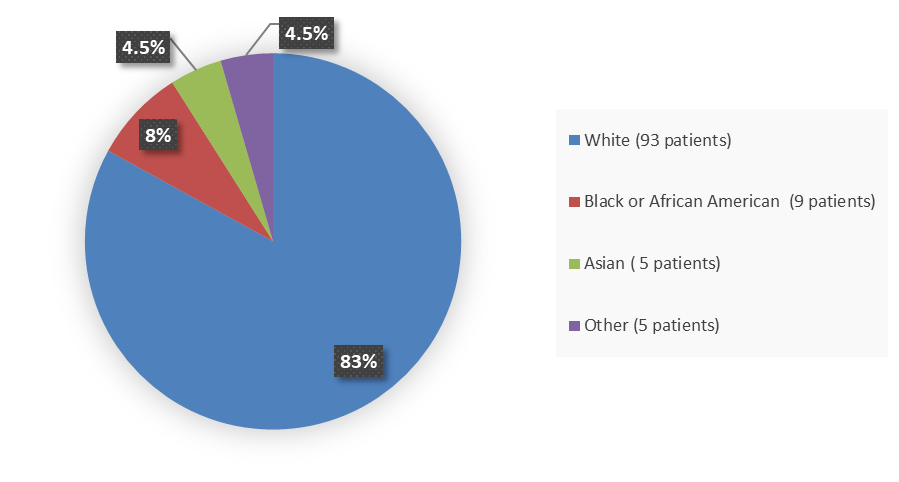
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Race - Efficacy Population
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Alt-Tag: Pie chart summarizing how many White, Black or African American, Asian, and other patients were in the clinical trial. In total, 93 (83%) White patients, 9 (8%) Black or African American patients, 5 (4.5%) Asian patients, and 5 (4.5%) Other patients participated in the clinical trial.
What are the benefits of this drug?
Approximately 43% of patients (48 of 112 patients) treated with KRAZATI in the clinical study 849-001 had shrinkage of their cancer. Shrinkage lasted more than 6 months for 58% of patients who had a response to KRAZATI.
KRAZATI was approved under FDA’s accelerated approval program, which provides earlier patient access to a promising new drug while the company continues to conduct clinical trials to confirm that the drug works well.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
Table 1 summarizes the results of the major efficacy outcome measures, ORR according to RECIST v1.1 as evaluated by blinded independent central review and duration of response.
Table 1. Efficacy Results for KRYSTAL-1
|
Efficacy Parameter |
KRAZATI |
|
Objective response rate (95% CI) |
43 (34, 53) |
|
Complete response rate, % |
0.9 |
|
Partial response rate, % |
42 |
|
Duration of responsea |
|
|
Medianb in months (95% CI) |
8.5 (6.2, 13.8) |
|
Patients with duration ≥6 monthsc, % |
58 |
Source: KRAZATI Prescribing Information
a Assessed by BICR
b Estimate using Kaplan-Meier method
c Observed proportion of patients with duration of response beyond landmark time
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age?
- Sex: KRAZATI worked similarly in males and females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in how KRAZATI worked among races could not be determined.
- Age: KRAZATI worked similarly in patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 2. Subgroup Analysis of Objective Response Rate (Cohort A)
|
Subgroup |
N |
ORR % (95% CI) |
|
Overall |
112 |
43 (34, 53) |
|
Age, years |
|
|
|
<65 |
59 |
49 (36, 63) |
|
≥65 |
53 |
36 (23, 50) |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
Female |
62 |
42 (30, 55) |
|
Male |
50 |
44 (30, 59) |
|
Race |
|
|
|
White |
93 |
41 (31, 52) |
|
Asian |
5 |
80 (28, 99) |
|
Black or African American |
9 |
44 (14, 79) |
|
Other and American Indian or Alaska Native |
5 |
40 (5, 85) |
Source: FDA Review
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; ORR, objective response rate
What are the possible side effects?
KRAZATI can cause serious side effects including stomach and intestinal (gastrointestinal) problems, changes in the electrical activity of your heart (QTc prolongation), liver problems (liver toxicity), and inflammation of the lung (interstitial lung disease or pneumonitis).
The most common side effects observed with KRAZATI include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, tiredness, muscle and bone pain, kidney problems, swelling, breathing trouble, and decreased appetite.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
Table 3. Adverse Reactions (≥20%) in Patients With KRAS G12C-Mutated NSCLC Who Received KRAZATI in KRYSTAL-1
|
Adverse Reactions |
KRAZATI 600 mg BID N=116 |
|
|
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
|
|
|
Diarrhea* |
70 |
0.9 |
|
Nausea |
69 |
4.3 |
|
Vomiting* |
56 |
0.9 |
|
Constipation |
22 |
0 |
|
Abdominal pain* |
21 |
0 |
|
General disorders and administration site conditions |
|
|
|
Fatigue* |
59 |
7 |
|
Edema* |
32 |
0 |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders |
|
|
|
Musculoskeletal pain* |
41 |
7 |
|
Hepatobiliary disorders |
|
|
|
Hepatotoxicity*,1 |
37 |
10 |
|
Renal and urinary disorders |
|
|
|
Renal impairment*,2 |
36 |
6 |
|
Respiratory |
|
|
|
Dyspnea* |
35 |
10 |
|
Cough* |
24 |
0.9 |
|
Metabolism and nutrition disorders |
|
|
|
Decreased appetite |
30 |
4.3 |
|
Infections and infestations |
|
|
|
Pneumonia* |
24 |
17 |
|
Nervous system disorders |
|
|
|
Dizziness* |
23 |
0.9 |
|
Cardiac disorders |
|
|
|
Electrocardiogram QT prolonged |
20 |
6 |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
* Grouped term
1 Hepatotoxicity includes mixed liver injury, blook alkaline phosphatase increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, liver function test increased, blood bilirubin increased, and bilirubin conjugated increased.
2 Renal impairment includes acute kidney injury and increased blood creatinine.
Abbreviations: BID, twice daily; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in males and females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of serious and high-grade side effects was similar in patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 4. Overview of Side Effects by Sex, Race, and Age in Trial 849-001 Cohort A, Safety Population
|
|
KRAZATI 600mg BID N=116 |
||
|
Demographic Variable |
All Patients n (%) |
All Grades n/Ns (%) |
Grades 3 or 4 n/Ns (%) |
|
Sex, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
Female |
65 (56.0) |
65/65 (100) |
52/65 (80.0) |
|
Male |
51 (44.0) |
51/51 (100) |
39/51 (76.5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Race, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
White |
97 (83.6) |
97/97 (100) |
76/97 (78.4) |
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
1 (0.9) |
1/1 (100) |
1/1 (100) |
|
Asian |
5 (4.3) |
5/5 (100) |
4/5 (80.0) |
|
Black or African American |
9 (7.8) |
9/9 (100) |
7/9 (77.8) |
|
Other |
4 (3.4) |
4/4 (100) |
3/4 (75.0) |
|
Age group, years, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
< 65 years |
59 (50.9) |
59/59 (100) |
47/59 (79.7) |
|
≥ 65 years |
57 (49.1) |
57/57 (100) |
44/57 (77.2) |
Source: FDA reviewer's analysis
Abbreviation: N, number of patients in the safety population; n, number of patients with given characteristic; Ns, total number of patients in each category
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.