Drug Trials Snapshots: IBTROZI
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the key clinical trials that supported the original FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, age, and ethnic groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Some of the information in this Snapshot is for presentation purposes and does not represent the approved conditions of use of this drug. Refer to the IBTROZI Prescribing Information for all the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable).
IBTROZI (taletrectinib)
(ib TRO zee)
Nuvation Bio, Inc.
Approval date: June 11, 2025
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
IBTROZI is a prescription medicine used to treat adult patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) caused by an abnormal ROS1 gene that is locally advanced or has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic). IBTROZI is an inhibitor of proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS1.
How is this drug used?
IBTROZI is a 200 mg capsule taken by mouth at 600 mg once daily on an empty stomach (no food intake at least two hours before and two hours after taking IBTROZI).
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved IBTROZI based on evidence from 270 patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC that had spread beyond the lungs who received IBTROZI 600 mg orally once daily, enrolled in two clinical trials: TRUST-I (NCT04395677) or TRUST-II (NCT04919811). The TRUST-I trial was conducted exclusively in China and the TRUST-II trial was conducted globally in North America (United States and Canada), Europe (France, Italy, Spain, and Poland), and Asia (China, Japan, and South Korea).
The efficacy of IBTROZI was evaluated in two subgroups of patients:
- Patients for whom IBTROZI was their first ROS1-targeted drug (tyrosine kinase inhibitor [TKI]-naïve subgroup). In TRUST-I among 103 patients, the median age was 56 years (range: 26 to 78); 55% were female; and 100% were Asian. In TRUST-II, among 54 patients, the median age was 57 years (range: 27 to 82); 56% were female; 65% were Asian; 22% were White; 1.9% were Black or African American; 11% were of unknown race; and 1.9% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
- Patients who had received one prior ROS1-targeted therapy before receiving IBTROZI (TKI-pretreated subgroup). In TRUST-I among 66 patients, the median age was 51 years (range: 31 to 77); 61% were female; and 100% were Asian. In TRUST-II among 47 patients the median age was 55 years (range: 27 to 79); 57% were female; 47% were Asian; 34% were White; 2.1% were Black or African American, 17% were of unknown or other races; and 2.1% were Hispanic or Latino.
The safety of IBTROZI was evaluated in 352 patients (337 with NSCLC and 15 with other solid tumors) who received at least one 600 mg dose of IBTROZI. In the 337 patients with NSCLC, the median age was 56 years (range: 26 to 83); 56% female; 76% Asian, 15% White, 0.6% Black or African American, 8% unknown or other races; and 1.8% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The number of patients representing efficacy findings differs from the number of patients representing safety findings due to different groups of study participants analyzed for efficacy and safety.
How were the trials designed?
The efficacy and safety of IBTROZI were evaluated in 270 patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC that had spread beyond the lungs from two multicenter single-arm open label clinical trials, TRUST-I which was conducted in a single region and TRUST-II which was a global trial with multiple cohorts. Each trial included patients for whom IBTROZI was their first ROS1-targeted drug (TKI-naïve subgroup), or patients who had received one prior ROS1-targeted therapy before receiving IBTROZI (TKI-pretreated subgroup). All patients received IBTROZI 600 mg once a day until either the cancer progressed, or intolerable side effects developed.
The efficacy of IBTROZI was evaluated by measuring the percentage of patients who had a complete or partial reduction of their tumors (overall response rate or ORR) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST v1.1) as evaluated by blinded independent central review (BICR) and by measuring the duration of that benefit before the cancer started to grow again (duration of response or DOR).
How were the trials designed?
TRUST-I and TRUST-II were two multicenter, single-arm, open-label clinical trials of IBTORZI. In both trials, patients were required to have histologically confirmed, locally advanced or metastatic, ROS1-positive NSCLC, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1, and measurable disease per RECIST v1.1. Patient received IBTROZI at a dose of 600 mg orally once daily.
The major efficacy outcome measures were confirmed ORR and DOR according to RECIST v1.1 as assessed by a BICR. Intracranial response according to modified RECIST v1.1 was assessed by BICR. Tumor assessments with imaging were performed every 6 weeks for the first 24 weeks, every 9 weeks for the following year, and every 12 weeks thereafter. The efficacy populations included 157 patients naïve to treatment with a ROS1 TKI and 113 patients who received one prior ROS1 TKI. Patients could be chemotherapy-naïve or have received prior chemotherapy for locally advanced disease.
DEMOGRAPHICS SNAPSHOT
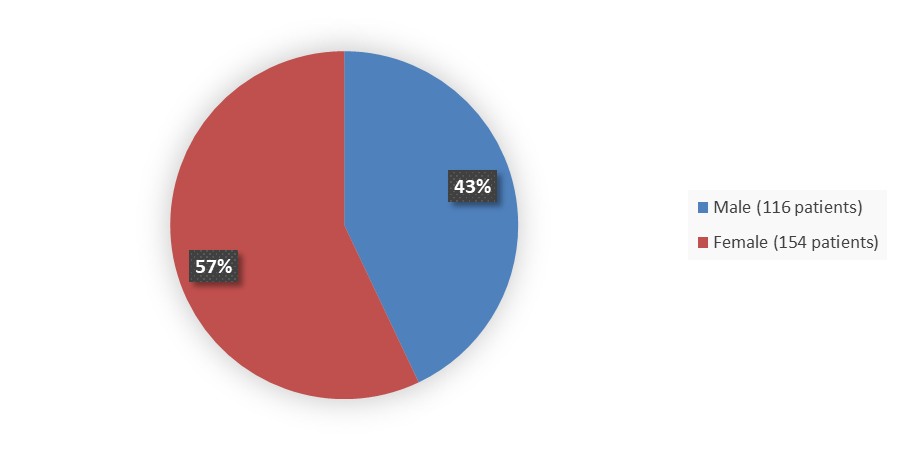
Figure 1 summarizes male and female patients enrolled in the TRUST-I and TRUST-II of 270 patients with ROS1-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex, Efficacy Population
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
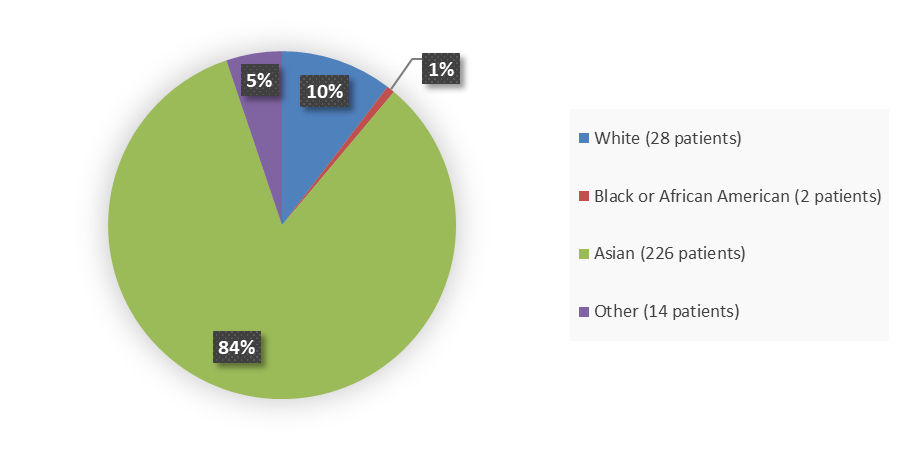
Figure 2 summarizes baseline demographics by race in TRUST-I and TRUST-II.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race, Efficacy Population
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Note: "Other" including Unknown.
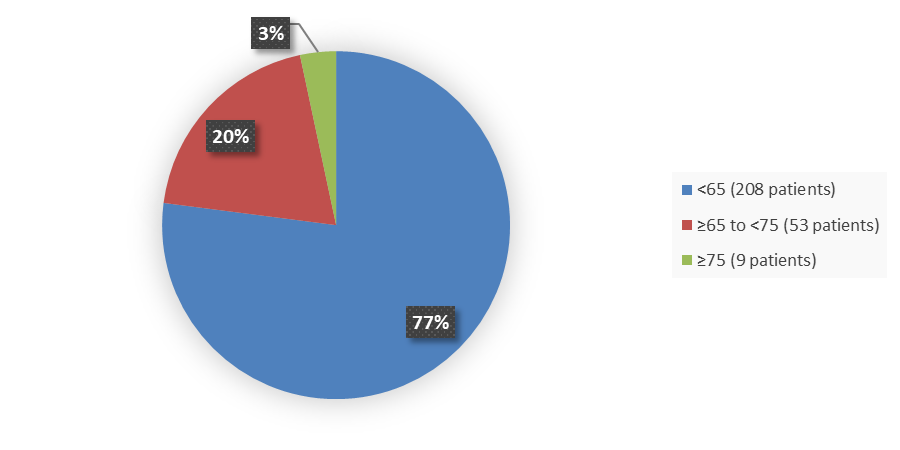
Figure 3 summarizes baseline demographics by age in TRUST-I and TRUST-II.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age, Efficacy Population
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
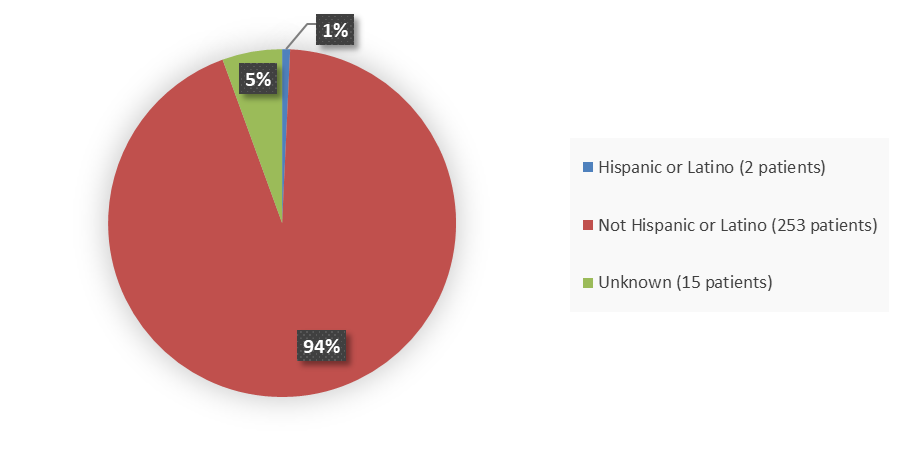
Figure 4 summarizes baseline demographics by ethnicity enrolled in TRUST-I and TRUST-II.
Figure 4. Baseline Demographics by Ethnicity, Efficacy Population
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Note: All patients who are Asian in TRUST-I study were assigned as “not Hispanic or Latino” because CRF didn’t collect ethnicity data. In TRUST-II, 1 patient in the United States, 1 patient in Spain, and 13 patients in France are with unknown ethnicity due to reporting restriction.
Who participated in the trials?
Table 1. Baseline Demographics of Efficacy Trials by Age, Race, Sex, and Ethnicity
| Category | ROS1 TKI-Naive N=157 | ROS1 TKI-Pretreated N=113 | Overall N=270 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 70 (44.6) | 46 (40.7) | 116 (43.0) |
| Female | 87 (55.4) | 67 (59.3) | 154 (57.0) |
| Age category, years, n (%) | |||
| <65 | 119 (75.8) | 89 (78.8) | 208 (77.0) |
| ≥65 to <75 | 33 (21.0) | 20 (17.7) | 53 (19.6) |
| ≥75 | 5 (3.2) | 4 (3.5) | 9 (3.3) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 12 (7.6) | 16 (14.2) | 28 (10.4) |
| Asian | 138 (87.9) | 88 (77.9) | 226 (83.7) |
| Black or African American | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (0.7) |
| Other1 | 6 (3.8) | 8 (7.1) | 14 (5.2) |
| Ethnicity, n (%)2 | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (0.7) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 149 (94.9) | 104 (92.0) | 253 (93.7) |
| Unknown or Not reported2 | 7 (4.5) | 8 (7.1) | 15 (5.6) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
1"Other" including: Unknown.
2 All patients who are Asian in TRUST-I study were assigned as “not Hispanic or Latino” because CRF didn’t collect ethnicity data.
3 In TRUST-II, 1 patient in the United States, 1 patient in Spain, and 13 patients in France are with unknown ethnicity due to reporting restriction.
Abbreviations: TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor
What are the benefits of this drug?
In the TRUST-I trial, 90% of the 103 patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC who were ROS1 inhibitor naïve experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors; 72% of these patients had complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than twelve months. In the TRUST-II trial, 85% of the 54 patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC who were ROS1 inhibitor naïve experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors; 63% of these patients had complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than twelve months.
In the TRUST-I trial, 52% of the 66 patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC who were pretreated with an ROS1 inhibitor experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than six months for 74% of patients. In the TRUST-II trial, 62% of the 47 patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC who were pretreated with an ROS1 inhibitor experienced complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors which lasted more than six months for 83% of patients.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
Table 2 and Table 3 summarize efficacy results for ROS1-positive NSCLC in TKI-naive and TKI-pretreated patients. Outcomes presented include confirmed ORR and DOR according to RECIST v1.1 as assessed by BICR.
Table 2. Efficacy Results in ROS1-Positive TKI-Naïve NSCLC Patients per BICR Assessment
| Efficacy Parameters | ROS1 TKI-Naïve, N=157 | |
|---|---|---|
| TRUST-I n=103 | TRUST-II n=54 | |
| Response rate, % (95% CI) | 90 (83, 95) | 85 (73, 93) |
| Complete response, % | 5 | 7 |
| Partial response, % | 85 | 78 |
| Duration of response (DOR) | n=93 | n=46 |
| Median DOR (95% CI) | NR (30.4, NR) | NAa |
| Range (months) | 1.1, 46.9+ | 1.4+, 30.4+ |
| % with DORb ≥12 months | 72 | 63 |
Source: Adapted from IBTROZI Prescribing Information a Median DOR not included for TRUST-II given the shorter duration of follow-up b Based on observed duration of response Abbreviations: BICR, blinded independent central review; CI, confidence interval; NA, not applicable; NR, not reached; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; “+” indicating ongoing response
Table 3. Efficacy Results in ROS1-Positive TKI-Pretreated NSCLC Patients per BICR Assessment
| Efficacy Parameters | ROS1 TKI-Pretreated, N=113 | |
|---|---|---|
| TRUST-I n=66 | TRUST-II n=47 | |
| Response rate, % (95% CI) | 52 (39, 64) | 62 (46, 75) |
| Complete response, % | 0 | 11 |
| Partial response, % | 52 | 51 |
| Duration of response (DOR) | n=34 | n=29 |
| Median DOR (95% CI) | 13.2 (7.7, 24.9) | NAa |
| Range (months) | 1.4, 38.7+ | 1.7+, 30.4+ |
| % with DORb ≥6 months | 74 | 83 |
| % with DORb ≥12 months | 44 | 45 |
Source: Adapted from IBTROZI Prescribing Information
a Median DOR not included for TRUST-II given the shorter duration of follow-up
b Based on observed duration of response
Abbreviations: BICR, blinded independent central review; CI, confidence interval; NA, not applicable; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; “+” indicating ongoing response
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age?
- Sex: The effect of IBTROZI was similar for females and males.
- Race: IBTROZI worked similarly in Asian, White, and patients of other races. The number of patients of other races was small; therefore, differences in how the drug worked in other races could not be determined.
- Age: IBTROZI appears to work similarly in patients younger and older than 65 years of age; however, the number of enrolled patients older than 65 years old is limited.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 4 and Table 5 summarize ORR by sex, race, ethnicity, and age subgroups.
Table 4. Efficacy Results by Subgroup for ROS1 TKI-Naïve Patients
| Subgroup | Responders n/N | Confirmed ORR % (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 62/70 | 88.6 (78.7, 94.9) |
| Female | 77/87 | 88.5 (79.9, 94.4) |
| Age, years | ||
| 65 | 108/119 | 90.8 (84.1, 95.3) |
| ≥65 | 31/38 | 81.6 (65.7, 92.3) |
| Race | ||
| Asian | 123/138 | 89.1 (82.7, 93.8) |
| White | 10/12 | 83.3 (51.6, 97.9) |
| Black or African American | 1/1 | 100 (2.5, 100) |
| Other1 | 5/6 | 83.3 (35.9, 99.6) |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Hispanic or Latino | 0/1 | 0 (NA, NA) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 133/149 | 89.3 (83.2, 93.7) |
| Unknown or Not reported | 6/7 | 85.7 [42.1, 99.6] |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
1"Other" including Unknown
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; NA, not applicable; ORR, overall response rate; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Table 5. Efficacy Results by Subgroup for ROS1 TKI-Pretreated Patients
| Subgroup | Responders n/N | Confirmed ORR % (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 25/46 | 54.3 (39.0, 69.1) |
| Female | 38/67 | 56.7 (44.0, 68.8) |
| Age, years | ||
| <65 | 48/89 | 53.9 (43.0, 64.6) |
| ≥65 | 15/24 | 62.5 (40.6, 81.2-) |
| Race | ||
| Asian | 47/88 | 53.4 (42.5, 64.1) |
| White | 10/16 | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) |
| Black or African American | 1/1 | 100 (2.5 100.0) |
| Other1 | 6/8 | 75.0 (34.9, 96.8) |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Hispanic or Latino | 1/1 | 100 (2.5, 100.0) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 56/104 | 53.8 (43.8, 63.7) |
| Unknown or Not reported | 6/8 | 75.0 (34.9, 96.8) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
1“Other" including Unknown
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; ORR, overall response rate; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor
What are the possible side effects?
IBTROZI may cause serious side effects including liver problems; lung problems; changes in the electrical activity of your heart called QTc interval prolongation; increased uric acid level in your blood (hyperuricemia); muscle pain, tenderness, and weakness (myalgia); bone fractures, and harm to an unborn baby (if taken while pregnant).
The most common side effects of IBTROZI include:
- diarrhea
- nausea
- vomiting
- dizziness
- rash constipation
- tiredness
- changes in your liver function tests
- decreased white blood cell levels
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
Table 6 and Table 7 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities that occurred in patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC.
Table 6. Adverse Reactions (≥15%) in Patients With ROS1-Positive NSCLC Who Received IBTROZI in TRUST-I and TRUST-II
| Adverse Reaction1 | IBTROZI, N=337 | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrheaa | 64 | 2.1 |
| Nausea | 47 | 1.5 |
| Vomiting | 43 | 1.5 |
| Constipation | 21 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Dizzinessb | 22 | 0.3 |
| Peripheral neuropathyc | 17 | 0.3 |
| Dysgeusiad | 15 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||
| Rashe | 22 | 1.8 |
| General disorders | ||
| Fatiguef | 20 | 0.9 |
| Cardiac | ||
| Electrocardiogram QT prolonged | 19 | 3.6 |
| Metabolism and nutritional | ||
| Decreased appetite | 16 | 0.3 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Coughg | 16 | 0 |
Source: IBTROZI Prescribing information
1Based on NCI CTCAE version 5.0
aIncludes enterocolitis
bIncludes vertigo and vertigo positional
cIncludes dysesthesia, hypoesthesia, neuralgia, paresthesia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy
dIncludes ageusia
eIncludes dermatitis, dermatitis acneiform, drug eruption, eczema, eyelid rash, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, rash, maculo-papular, rash papular, skin exfoliation, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
fIncludes asthenia
gIncludes productive cough
Abbreviations: NCI CTCAE, National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer
Table 7. Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥20%) That Worsened From Baseline in Patients With ROS1-Positive NSCLC Who Received IBTROZI in TRUST-I and TRUST-II
| Laboratory Abnormality1 | IBTROZI2 | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | |
| Hematology | ||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 48 | 3.6 |
| Lymphocytes decreased | 38 | 4.8 |
| Neutrophils decreased | 25 | 5 |
| Chemistry | ||
| AST increased | 87 | 10 |
| ALT increased | 85 | 13 |
| Creatine phosphokinase increased | 53 | 5 |
| Cholesterol increased | 41 | 0 |
| Triglycerides increased | 41 | 2.5 |
| Creatinine increased | 39 | 0.3 |
| Uric acid increased | 38 | 0 |
| Gamma glutamyl transferase increased | 36 | 1.8 |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 30 | 0 |
| Calcium decreased | 28 | 1.8 |
| Albumin decreased | 25 | 0.9 |
| Bilirubin increased | 24 | 0.6 |
| Potassium increased | 21 | 1.2 |
| Sodium increased | 20 | 0.9 |
Source: IBTROZI Prescribing information
1 Based on NCI CTCAE version 5.0
2 The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 149 to 336 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; NCI CTCAE, National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in males and females.
- Race: The occurrence of side effects was similar across races.
- Age: The occurrences of grade 3 or higher adverse reactions, severe adverse reactions, and adverse reactions leading to treatment interruptions were higher in patients who were 65 years old and older compared to patients younger than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 8. Side Effects by Sex for Patients Who Received IBTROZI 600 mg QD
| Parameter | Male N=155 n (%) | Female N=197 n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| All-grade TEAEs | 154 (99) | 197(100) |
| Grade ≥3 TEAEs | 74 (48) | 107 (54) |
| Serious TEAEs | 49 (32.0) | 58 (29) |
| TEAEs leading to drug interruption | 58 (37) | 85 (43) |
| TEAEs leading to dose reduction | 34 (22) | 68 (35) |
| TEAEs leading to drug withdrawal | 12 (8) | 11 (6) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; QD, once daily
Table 9. Side Effects by Race for Patients Who Received IBTROZI 600 mg QD
| Parameter | Asian N=272 n (%) | White N=52 n (%) | Other or Unknown N=28 n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| All-grade TEAEs | 272 (100) | 51 (98) | 28 (100) |
| Grade ≥3 TEAEs | 138 (51.0) | 25 (48) | 18(64) |
| Serious TEAEs | 86 (32) | 12 (23) | 9 (32) |
| TEAEs leading to drug interruption | 109 (40) | 25 (48) | 9 (32) |
| TEAEs leading to dose reduction | 71 (26) | 20 (38) | 11 (39) |
| TEAEs leading to drug withdrawal | 18 (7) | 2 (3.8) | 3 (11) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; QD, once daily
Table 10. Side Effects by Age for Patients Who Received IBTROZI 600 mg QD
| Parameter | <65 Years N=264 n (%) | ≥65 to <75 Years N=74 n (%) | ≥75 Years N=14 n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| All-grade TEAEs | 263 (100) | 74 (100) | 14 (100) |
| Grade ≥3 TEAEs | 124 (47) | 49 (66) | 8 (57) |
| Serious TEAEs | 72 (27) | 30 (41) | 5 (36) |
| TEAEs leading to drug interruption | 102 (39) | 34 (46) | 7 (50) |
| TEAEs leading to dose reduction | 71 (27) | 23 (31) | 8 (57) |
| TEAEs leading to drug withdrawal | 18 (7) | 3 (4.1) | 2 (14) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; QD, once daily
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.