Drug Trials Snapshot: LYTGOBI
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the key clinical trials that supported the original FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, age, and ethnic groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Some of the information in this Snapshot is for presentation purposes and does not represent the approved conditions of use of this drug. Refer to the LYTGOBI Prescribing Information for all of the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable).
LYTGOBI (futibatinib)
(light-GOH-bee)
Taiho Oncology Inc
Original Approval date: September 30, 2022
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
LYTGOBI is a drug used for the treatment of adults with a type of bile duct cancer (intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma) that has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic) or cannot not be removed by surgery (unresectable). It should be used in patients who have been previously treated with chemotherapy and whose cancer has a certain type of abnormality in the FGFR2 gene.
How is this drug used?
LYTGOBI is a tablet that is taken by mouth once daily.
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved LYTGOBI based on evidence from one clinical trial (NCT02052778) consisting of 103 patients with previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic intrahepatic bile duct cancer. The trial was conducted at 48 sites in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Asia.
How were the trials designed?
There was one trial that provided data for LYTGOBI approval. The trial enrolled adult patients with intrahepatic bile duct cancer (intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma) who had been previously treated with chemotherapy for their advanced cancer and whose tumors had a certain type of abnormality in the FGFR2 gene.
Patients received LYTGOBI once daily by mouth until disease progression or the side effect became too toxic.
The trial measured the percentage of patients who achieved partial or complete shrinkage of their tumors and how long that shrinkage lasted (duration of response).
How were the trials designed?
There was one multi-center, open-label, single arm trial that provided data for approval of LYTGOBI. Enrolled patients were required to have locally advanced unresectable or metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma whose disease had progressed on or after at least one prior therapy, and an FGFR2 gene fusion or other rearrangement.
Patients received LYTGOBI 20 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The major efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate and duration of response as determined by an independent review committee according to RECIST v1.1.
DEMOGRAPHICS SNAPSHOT
Figure 1 summarizes how many male and female patients were enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LYTGOBI.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
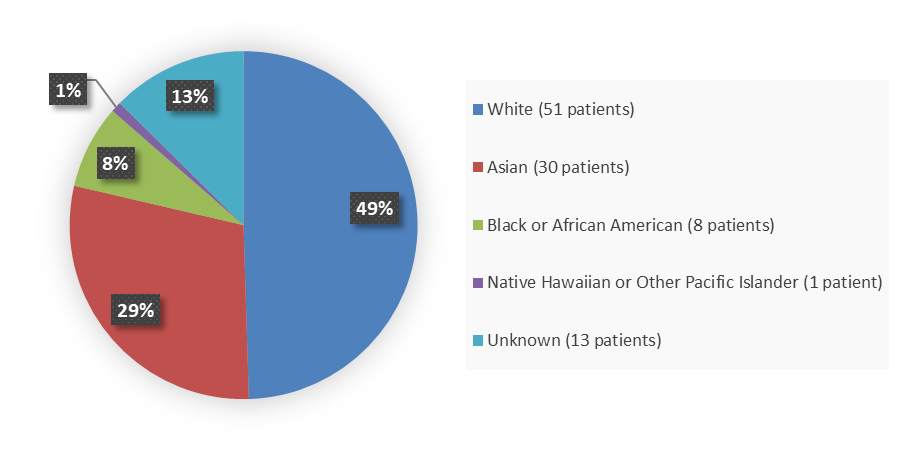
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LYTGOBI.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
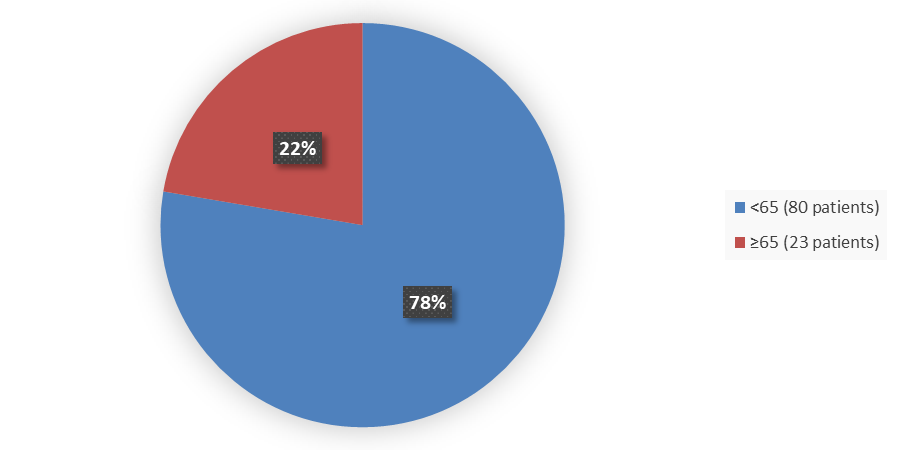
Figure 3 summarizes how many patients by age were in the trial used to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LYTGOBI.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Figure 4 summarizes how many patients by ethnicity were in the trial used to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LYTGOBI.
Figure 4. Baseline Demographics by Ethnicity
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
Demographic characteristics are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6. Demographic Characteristics
|
|
LYTGOBI |
|---|---|
|
Sex |
|
|
Male |
45 (44) |
|
Female |
58 (56) |
|
Race |
|
|
White |
51 (49) |
|
Asian |
30 (29) |
|
Black or African American |
8 (8) |
|
Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander |
1 (1) |
|
Unknown |
13 (13) |
|
Age group, years |
|
|
<65 |
80 (78) |
|
≥65 |
23 (22) |
|
Ethnicity |
|
|
Hispanic or Latino |
2 (2) |
|
Not Hispanic or Latino |
89 (86) |
|
Unknown |
12 (12) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
What are the benefits of this drug?
In the trial, 42% (43 of 103) of patients treated with LYTGOBI experienced partial shrinkage of their tumors, also known as the overall response rate. Of these patients, 72% had tumor shrinkage lasting 6 months or longer and 14% had tumor shrinkage lasting 12 months or longer.
LYTGOBI was approved under FDA’s accelerated approval program, which provides earlier patient access to a promising new drug while the company continues to conduct clinical trials to confirm that the drug works well.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
Table 1 summarizes the efficacy results based on the overall response rate and duration of response as determined by an independent review committee (IRC) according to guidelines for determining tumor shrinkage known as Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1.
Table 1. Efficacy Results
|
|
LYTGOBI |
|---|---|
|
Overall response rate (95% CI)a |
42% (32, 52) |
|
Partial response, n (%) |
43 (42) |
|
Median duration of response, months (95% CI)b |
9.7 (7.6, 17.1) |
|
Duration of response ≥6 months, n (%) |
31 (72) |
|
Duration of response ≥12 months, n (%) |
6 (14) |
Source: LYTGOBI Prescribing Information
a The 95% CI was calculated using Clopper–Pearson method.
b The 95% CI was constructed based on a log-log transformed CI for the survival function.
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: LYTGOBI worked similarly in females and males.
- Race: LYTGOBI worked similarly in White, Asian, and Black/African American participants.
- Age: The majority (78%) of patients were younger than 65 years of age and 22% of patients were 65 years of age and older. The observed response rate was larger for those age 65 years or older than for those younger than 65 years old.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 2 summarizes efficacy results by relevant demographic subgroups.
Table 2. Overall Response Rate as Assessed by IRC for Subgroups
|
Characteristics |
N |
Overall Response Rate (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
|
Sex |
||
|
Male |
45 |
38 (24, 54) |
|
Female |
58 |
45 (32, 59) |
|
Race |
||
|
White |
51 |
41 (28, 56) |
|
Asian |
30 |
43 (26, 63) |
|
Black or African American |
8 |
50 (16, 84) |
|
Other or unknown |
14 |
36 (13, 65) |
|
Age group, years |
||
|
<65 |
80 |
35 (25, 47) |
|
≥65 |
23 |
65 (43, 84) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; IRC, Independent review committee
What are the possible side effects?
LYTGOBI may cause serious side effects including detachment of retina (inner layer of the eye), increased phosphate levels in the blood, and harm to an unborn baby.
The most common side effects of LYTGOBI are nail toxicity, muscle and/or bone pain, constipation, and diarrhea.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
Table 3 summarizes adverse reactions that occurred in ≥15% of patients treated with LYTGOBI.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions (≥15%) in Patients Receiving LYTGOBI
|
Adverse Reaction |
LYTGOBI |
|
|---|---|---|
|
All Gradesa (%) |
Grade 3 (%) |
|
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
||
|
Nail toxicityb |
47 |
1.9 |
|
Alopecia |
34 |
0 |
|
Dry skin |
29 |
0 |
|
Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome |
21 |
4.9 |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
||
|
Constipation |
39 |
0 |
|
Diarrheac |
39 |
1 |
|
Dry mouth |
35 |
0 |
|
Stomatitisd |
30 |
6 |
|
Abdominal paine |
30 |
2.9 |
|
Nausea |
24 |
1.9 |
|
Vomitingf |
20 |
1 |
|
General disorders |
||
|
Fatigueg |
37 |
8 |
|
Metabolism and nutrition disorders |
||
|
Decreased appetite |
23 |
2.9 |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorder |
||
|
Musculoskeletal painh |
43 |
3.9 |
|
Arthralgiai |
25 |
0 |
|
Eye disorders |
||
|
Dry eyej |
25 |
1 |
|
Nervous system disorders |
||
|
Dysgeusiak |
25 |
0 |
|
Infections |
||
|
Urinary tract infectionl |
23 |
2.9 |
|
Investigations |
||
|
Weight decreased |
18 |
3.9 |
Source: LYTGOBI Prescribing Information
a Graded per NCI CTCAE 4.03.
b Includes nail toxicity, nail disorder, nail discoloration, nail dystrophy, nail hypertrophy, nail infection, nail pigmentation, onychalgia, onychoclasis, onycholysis, onychomadesis, onychomycosis, and paronychia.
c Includes diarrhea, colitis, and gastroenteritis.
d Includes stomatitis, glossitis, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation, pharyngeal inflammation, and tongue ulceration.
e Includes abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain upper, gastrointestinal pain, and hepatic pain.
f Includes vomiting and hematemesis.
g Includes fatigue and asthenia.
h Includes back pain, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in extremity, and spinal pain.
i Includes arthralgia and arthritis.
j Includes dry eye, keratitis, lacrimation increased, photokeratitis, punctate keratitis, and ulcerative keratitis.
k Includes dysgeusia, ageusia, and taste disorder.
l Includes urinary tract infection, cystitis, and dysuria.
Abbreviations: NCI CTCAE, National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events
Table 4. Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥15%) Worsening From Baseline in Patients Receiving LYTGOBI
|
|
LYTGOBI |
|
|---|---|---|
|
All Gradesb (%) |
Grades 3 or 4 (%) |
|
|
Hematology |
||
|
Decreased hemoglobin |
52 |
6 |
|
Decreased lymphocytes |
46 |
10 |
|
Decreased platelets |
42 |
1 |
|
Decreased leukocytes |
33 |
1.1 |
|
Decreased neutrophils |
31 |
1.6 |
|
Chemistry |
||
|
Increased phosphatec |
97 |
39 |
|
Increased creatinined |
58 |
0 |
|
Increased glucose |
52 |
4.9 |
|
Increased calcium |
51 |
1.2 |
|
Decreased sodium |
51 |
15 |
|
Decreased phosphate |
50 |
20 |
|
Increased alanine aminotransferase |
50 |
7 |
|
Increased alkaline phosphatase |
47 |
4.9 |
|
Increased aspartate aminotransferase |
46 |
13 |
|
Decreased albumin |
31 |
2.4 |
|
Increased creatine kinase |
31 |
5 |
|
Increased bilirubin |
28 |
0 |
|
Decreased glucose |
25 |
0 |
|
Decreased potassium |
22 |
2.1 |
|
Increased potassium |
16 |
2 |
|
Coagulation |
||
|
Increased activated partial thromboplastin time |
36 |
8 |
|
Increased prothrombin international normalized ratio |
25 |
0 |
Source: LYTGOBI Prescribing Information
a Graded per NCI CTCAE 4.03.
b Percentages are based on patients with data at both baseline and at least one post-baseline data value.
c NCI CTCAE 4.03 does not define grades for increased phosphate. Laboratory value shift table categories were used to assess increased phosphorus levels (Grades ≥3 defined as >7 mg/dL).
d Graded based on comparison to upper limit of normal.
Abbreviations: NCI CTCAE, National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in both the male and female patients.
- Race: All participants experienced side effects. The occurrence of grade 3 or 4 adverse events was similar in White and Asian participants. All Black or African American participants experienced a grade 3 or 4 adverse event.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar in patients below and above 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 5 summarizes adverse reactions (side effects) by sex, race, and age.
Table 5. Summary of Adverse Events by Subgroup
|
|
N |
All Grades |
Grade 3 or 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sex |
|||
|
Male |
45 |
45 (100) |
33 (73) |
|
Female |
58 |
58 (100) |
46 (79) |
|
Race |
|||
|
White |
51 |
51 (100) |
37 (73) |
|
Asian |
30 |
30 (100) |
24 (80) |
|
Black or African American |
8 |
8 (100) |
8 (100) |
|
Other or unknown |
14 |
14 (100) |
10 (71) |
|
Age group, years |
|||
|
<65 |
80 |
80 (100) |
63 (79) |
|
≥65 |
23 |
23 (100) |
16 (70) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.