Drug Trials Snapshot: LUNSUMIO
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the key clinical trials that supported the original FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, age, and ethnic groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
Follicular lymphoma is a type of blood cancer.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Some of the information in this Snapshot is for presentation purposes and does not represent the approved conditions of use of this drug. Refer to the LUNSUMIO Prescribing Information for all of the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable).
LUNSUMIO (mosunetuzumab-axgb)
(lun-SUM-mee-oh)
Genentech, Inc.
Original Approval date: December 22, 2022
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
LUNSUMIO is a drug used to treat adult patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least two prior treatments that did not work or are no longer working.
Follicular lymphoma is a type of blood cancer.
How is this drug used?
LUNSUMIO is given through a vein weekly during the first cycle up to a dose of 60 mg (i.e., 1 mg, 2 mg, then 60 mg). The same dose, 60 mg, is repeated on the first day of the second cycle, then patients receive 30 mg during cycle 3 and during subsequent cycles every 21 days. LUNSUMIO is administered for a total of 8 cycles unless patients develop progressive lymphoma or unacceptable toxicity. After 8 cycles, patients with a complete response in whom all signs of cancer disappear can discontinue therapy. Patients with a partial response or stable disease in whom there is residual lymphoma can continue treatment up to 17 cycles as long as they have no evidence of progressive lymphoma or unacceptable toxicity.
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved LUNSUMIO based on evidence from a clinical trial (Study GO29781) that included 90 adults with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma who received at least two prior treatments for follicular lymphoma that did not work or was no longer working.
Trials were conducted at 40 sites in 7 countries that included Australia, Canada, Germany, South Korea, Spain, United Kingdom, and the United States.
How were the trials designed?
The benefit and side effects of LUNSUMIO were evaluated in Study GO29781, a clinical trial which enrolled 90 patients with follicular lymphoma who had received at least two prior therapies that did not work or were no longer working. Patients received increasing doses of LUNSUMIO through a vein weekly during the first cycle up to a dose of 60 mg. Patients received a single 60 mg dose of LUNSUMIO in Cycle 2, and a single 30 mg dose of LUNSUMIO 21 days later in Cycle 3 and during subsequent cycles every 21 days (i.e., 1 mg, 2 mg, 60 mg, then 30 mg dose schedule). For patients whose lymphoma disappeared by Cycle 8, treatment was stopped as long as they did not develop an unacceptable side effect. For patients with residual lymphoma whose disease did not disappear, patients continued treatment through Cycle 17 as long as they had no evidence of growing disease or unacceptable toxicity. The benefit of LUNSUMIO was evaluated by measuring how many patients had complete or partial tumor shrinkage (response) and by how long that response lasted.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of LUNSUMIO was established in the clinical trial GO29781, an open-label, multicenter, multi-cohort study of adult patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
Safety was established by reviewing the side effects of LUNSUMIO in 218 patients with B cell NHL from GO29781 who received the same dose and schedule of LUNSUMIO described above (1/2/60/30 mg). Efficacy of LUNSUMIO was established by reviewing a 90-patient cohort from GO29781 with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma who had at least two prior systemic therapies, including an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and an alkylating agent. Efficacy was established based on objective response rate and duration of response as assessed by an independent review facility according to standard criteria for NHL (Cheson 2007).
DEMOGRAPHICS SNAPSHOT
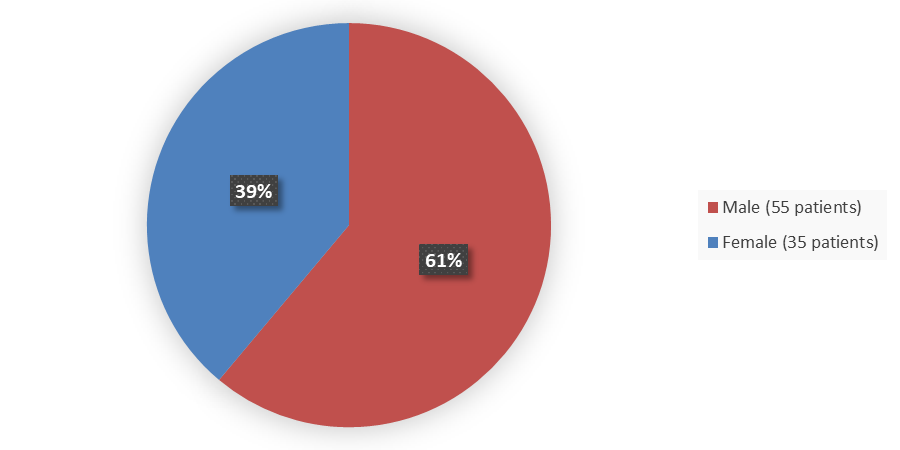
Figure 1 summarizes how many male and female patients were enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LUNSUMIO.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
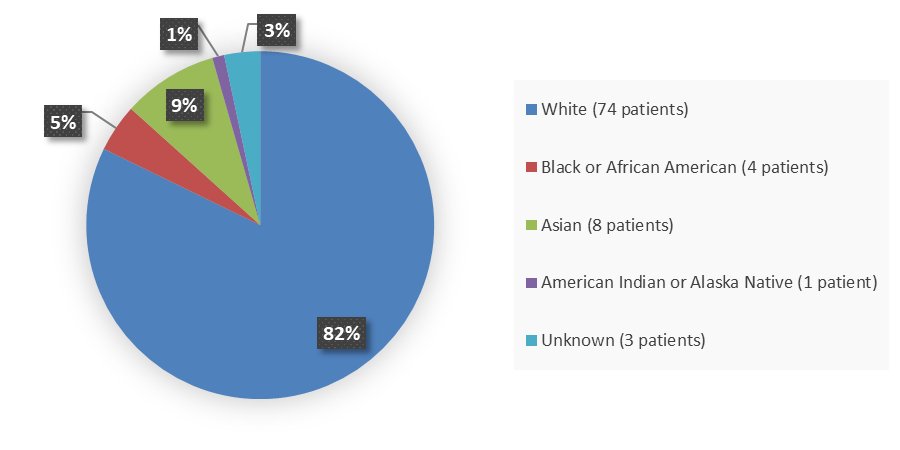
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LUNSUMIO.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
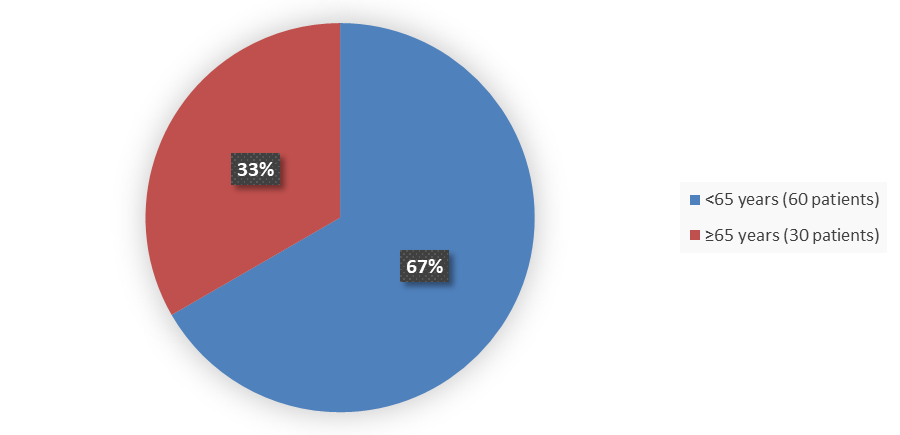
Figure 3 summarizes how many patients by age were enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LUNSUMIO.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
Table 6 and Table 7 summarize the demographics of the safety and efficacy population.
Table 6. Baseline Demographics of the Safety and Efficacy Population
|
Demographic Parameters |
LUNSUMIO |
|---|---|
|
Sex |
|
|
Male |
55 (61) |
|
Female |
35 (39) |
|
Age, years |
|
|
Median |
60 |
|
Min, max |
29, 90 |
|
Age group, years |
|
|
<65 |
60 (67) |
|
≥65 |
30 (33) |
|
≥75 |
7 (8) |
|
Race |
|
|
White |
74 (82) |
|
Black or African American |
4 (4) |
|
Asian |
8 (9) |
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
1 (1) |
|
Unknown |
3 (3) |
|
Ethnicity |
|
|
Hispanic or Latino |
7 (8) |
|
Not Hispanic or Latino |
77 (86) |
|
Not reported |
5 (6) |
|
Unknown |
1 (1) |
|
ECOG performance status |
|
|
0 |
53 (59) |
|
1 |
37 (41) |
|
Region (sites) |
|
|
United States (10) |
40 (44) |
|
Australia (7) |
17 (19) |
|
Canada (3) |
13 (14) |
|
Europe (8) |
16 (18) |
|
Asia (2) |
4 (4) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
Table 7. Baseline Disease Characteristics of the Safety and Efficacy Population
|
Baseline Disease Parameters |
LUNSUMIO |
|---|---|
|
Stage of disease at screening |
|
|
I |
5 (6) |
|
II |
16 (18) |
|
III |
25 (28) |
|
IV |
44 (49) |
|
Bulky disease (more than 6 cm) |
31 (34) |
|
FLIPI risk group at study entry |
|
|
Low (0,1) |
26 (29) |
|
Intermediate (2) |
24 (27) |
|
High (3-5) |
40 (44) |
|
Prior cancer therapy |
|
|
Anti-CD20 |
90 (100) |
|
Alkylator chemotherapy |
90 (100) |
|
Autologous-SCT |
19 (21) |
|
CAR‑T |
3 (3) |
|
PI3K inhibitor |
17 (19) |
|
Immunomodulatory imide drugs |
13 (14) |
|
Prior systemic therapy |
|
|
Median (minimum, maximum) |
3 (2,10) |
|
2 |
34 (38) |
|
3 |
28 (31) |
|
>3 |
28 (31) |
|
Not responding to: |
|
|
Last prior therapy |
62 (69) |
|
Any prior anti-CD20 |
71 (79) |
|
Prior anti-CD20 and alkylator chemotherapy |
48 (53) |
|
Progressive disease within 24 months from start of first systemic therapy |
47 (52) |
Source: Adapted from FDA Review
What are the benefits of this drug?
In a clinical trial with 90 patients with follicular lymphoma, 80% of patients had a complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors (response).
LUNSUMIO was approved under the FDA’s accelerated approval program, which provides earlier patient access to a promising new drug while the company continues to conduct clinical trials to confirm that the drug works well.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
Table 1. Overall Response Rate and Duration of Response in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma
|
Outcome Per IRC |
LUNSUMIO |
|---|---|
|
ORR, n (%)a |
72 (80) |
|
95% CI |
(70, 88) |
|
Complete response, n (%) |
54 (60) |
|
Partial response, n (%) |
18 (20) |
|
Duration of response |
|
|
Median, months (95% CI) b |
22.8 (10, Not reached) |
Source: LUNSUMIO Prescribing Information
a Per Independent Review Committee according to Cheson et al 2007 criteria.
b Based on Kaplan-Meier estimation
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; IRC, Independent Review Committee; ORR, overall response rate
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: LUNSUMIO worked similarly in males and females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in how well the drug worked among races could not be determined because of the small number of patients in other races.
- Age: LUNSUMIO worked similarly among patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 2 summarizes efficacy results by sex, age, and race. Because of the small sample sizes, these exploratory analyses should be interpreted with caution.
Table 2. Analysis of Overall Response Rate by Sex, Age, and Race
|
Subgroup |
N |
Overall Response Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
Sex |
||
|
Male |
55 |
76 |
|
Female |
35 |
86 |
|
Age, years |
||
|
<65 |
60 |
77 |
|
≥65 |
30 |
87 |
|
Race |
||
|
White |
74 |
80 |
|
Black or African American |
4 |
100 |
|
Asian |
8 |
75 |
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
1 |
100 |
|
Unknown |
3 |
67 |
Source: FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
LUNSUMIO may cause serious side effects including an acute systemic inflammatory syndrome called cytokine release syndrome (characterized by fever, nausea, headache, rash, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, low oxygen levels, and trouble breathing), neurologic problems, serious infections, low blood cell counts, and growth in your tumor or worsening of tumor-related problems (tumor flare).
The most common side effects of LUNSUMIO include cytokine release syndrome, fatigue, rash, fever, and headache.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
Table 3 summarizes adverse reactions in adult patients with follicular lymphoma who were treated with at least one dose of LUNSUMIO in a clinical trial (safety population).
Table 3. Common Adverse Reactions (>10% Incidence) in Patients With Follicular Lymphoma
|
|
LUNSUMIO, N=90 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
All Grades |
Grade 3 or 4 |
|
|
Immune system disorders |
||
|
Cytokine release syndrome |
44 |
2.2 |
|
General disorders and administration site conditions |
||
|
Fatigue2 |
42 |
0 |
|
Pyrexia |
29 |
1.1# |
|
Edema3 |
17 |
1.1 |
|
Chills |
13 |
1.1# |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
||
|
Rash4 |
39 |
4.4# |
|
Pruritis |
21 |
0 |
|
Dry skin |
16 |
0 |
|
Skin exfoliation |
10 |
0 |
|
Nervous system |
||
|
Headache5 |
32 |
1.1# |
|
Peripheral neuropathy6 |
20 |
0 |
|
Dizziness7 |
12 |
0 |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders |
||
|
Musculoskeletal pain8 |
28 |
1.1# |
|
Arthralgia |
11 |
0 |
|
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders |
||
|
Cough9 |
22 |
0 |
|
Dyspnea10 |
11 |
1.1# |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
||
|
Diarrhea |
17 |
0 |
|
Nausea |
17 |
0 |
|
Abdominal pain11 |
12 |
1.1# |
|
Infections |
||
|
Upper respiratory infection12 |
14 |
2.2# |
|
Urinary tract infection13 |
10 |
1.1# |
|
Psychiatric disorder |
||
|
Insomnia |
12 |
0 |
Source: LUNSUMIO Prescribing Information
1 Adverse reactions were graded based on CTCAE Version 4.0, with the exception of CRS, which was graded per ASTCT 2019 criteria
2 Fatigue includes fatigue, asthenia, and lethargy
3 Edema includes edema, edema peripheral, peripheral swelling, face edema, swelling face, pulmonary edema, fluid overload, and fluid retention
4 Rash includes rash, rash erythematous, exfoliative rash, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, rash pruritic, rash pustular, erythema, palmar erythema, dermatitis, and dermatitis acneiform
5 Headache includes headache and migraine
6 Peripheral neuropathy includes peripheral neuropathy, peripheral sensory neuropathy, paresthesia, dysaesthesia, hypoaesthesia, burning sensation, and neuralgia
7 Dizziness includes dizziness and vertigo
8 Musculoskeletal pain includes musculoskeletal pain, back pain, myalgia, musculoskeletal chest pain, and neck pain
9 Cough includes cough, productive cough, and upper airway cough syndrome
10 Dyspnea includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional
11 Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain, lower abdominal pain, and abdominal discomfort
12 Upper respiratory tract infection includes upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, sinusitis, and rhinovirus infection
13 Urinary tract infection includes urinary tract infection and acute pyelonephritis
# Only Grade 3 adverse reactions occurred
Table 4. Laboratory Adverse Reactions Reported (>20%) That Worsened From Baseline in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma
|
Laboratory Parameter |
LUNSUMIO1 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
All Grades |
Grade 3 or 4 |
|
|
Hematologic |
||
|
Lymphocyte count decreased |
100 |
98 |
|
Hemoglobin decreased |
68 |
12 |
|
White blood cells decreased |
60 |
13 |
|
Neutrophils decreased |
58 |
40 |
|
Platelets decreased |
46 |
10 |
|
Chemistry |
||
|
Phosphate decreased |
78 |
46 |
|
Glucose increased |
42 |
42 |
|
Aspartate aminotransferase increased |
39 |
4.4 |
|
Gamma glutamyl transferase increased |
34 |
9 |
|
Magnesium decreased |
34 |
0 |
|
Potassium decreased |
33 |
6 |
|
Alanine aminotransferase increased |
32 |
7 |
|
Uric acid increased |
22 |
22 |
Source: LUNSUMIO Prescribing Information
1 The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 72 to 90 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race, and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was generally similar in males and females. However, cytokine release syndrome was reported more frequently in males whereas fatigue, rash, and headache were reported more frequently in females.
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; Therefore, differences in the occurrence of side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was generally similar in patients younger than 65 years of age and 65 years of age and older. However, cytokine release syndrome was reported more frequently in patients younger than 65 years of age as compared to patients 65 years of age and older.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Table 5 summarizes some of the common adverse reactions by sex and age subgroups. Because of the small sample sizes, these exploratory analyses should be interpreted with caution.
Table 5. Subgroup Analysis of Common Adverse Reactions by Sex and Age
|
Adverse Reaction |
Sex |
Age, Years |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Male |
Female |
<65 |
≥65 |
|
|
Any adverse reaction |
55 (100) |
34 (97) |
60 (100) |
29 (97) |
|
Cytokine release syndrome |
27 (49) |
1 |
31 (52) |
9 (30) |
|
Fatigue |
18 (33) |
20 (57) |
25 (42) |
13 (43) |
|
Rash |
17 (31) |
18 (51) |
24 (40) |
11 (37) |
|
Headache |
16 (29) |
13 (37) |
22 (37) |
7 (23) |
Source: Adapted from FDA review
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.