Drug Trial Snapshot: PALYNZIQ
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the PALYNZIQ Package Insert for complete information.
PALYNZIQ (pegvaliase-pqpz)
pal-lin-zeek
BioMarin Pharmaceutical, Inc.
Approval date:May 24, 2018
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
PALYNZIQ is a drug used to lower blood levels of phenylalanine in adults with phenylketonuria (PKU), who have high phenylalanine blood levels on current treatment.
Phenylketonuria is a rare inherited disorder that, if left untreated, causes brain damage and disability because of buildup of phenylalanine in the body.
How is this drug used?
PALYNZIQ is injected under the skin (subcutaneous). The initial dose is injected once weekly for four weeks. Afterwards, the dose is adjusted following a special schedule.
What are the benefits of this drug?
Patients treated with PALYNZIQ had lower levels of blood phenylalanine concentrations and were able to maintain low concentrations in comparison to patients who received placebo treatment.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The table below summarizes efficacy results for Trial 2 based on the Intent-to-Treat (ITT) population. Demographics of that population is presented in Table 7 under MORE INFO.
Table 2. Primary Endpoint: LS Mean Change in Blood Phenylalanine Concentration from Randomized Withdrawal Baseline to Week 8 in Adult Patients with PKU- Efficacy Assessment in Trial 2
Randomized Study Arm | Blood Phenylalanine Concentration (micromol/L) | LS Mean Change from | Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Pre-treatment | Trial 2 | Trial 2 | |||
PALYNZIQ 20 mg once daily | 1450.2 (310.5) | 596.8 (582.8) | 553.0 (582.4) | -23.3 | -973.0 |
Placebo 20 mg once daily | 1459.1 (354.7) | 563.9 (504.6) n = 14 | 1509.0 (372.6) | 949.8 | |
PALYNZIQ 40 mg once daily | 1185.8 (344.0) | 410.9 (440.0) | 566.3 (567.5) | 76.3 | -588.5 |
Placebo 40 mg once daily | 1108.9 (266.8) | 508.2 (363.7) n = 14 | 1164.4 (343.3) n = 10† | 664.8 | |
† Patients who did not complete phenylalanine assessment within the window for Week 8 (Day 43 to 56) were excluded.
PALYNZIQ Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: PALYNZIQ worked similarly in males and females.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The majority of patients were adults 18-65 years of age; therefore, differences in response among different age groups could not be determined.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
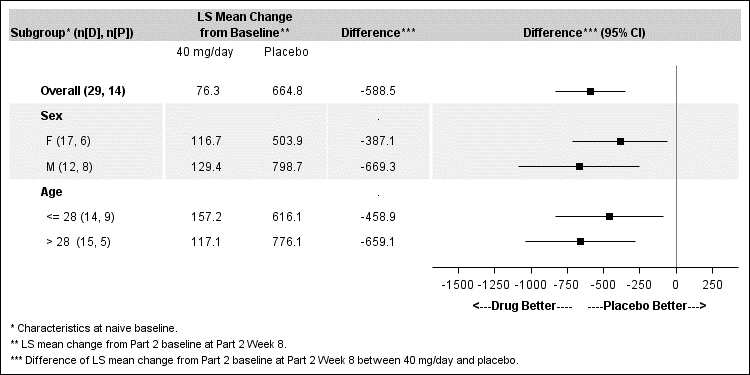
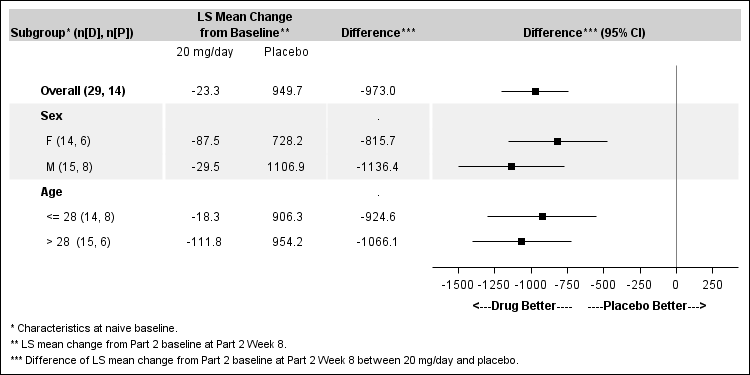
Figures 4 and 5 below summarize the results for the primary efficacy endpoint, change in blood phenylalanine concentration from baseline to Week 8 of the randomized withdrawal period, by sex and age.
Figure 4. Mean Change from Part 2 Baseline at Week 8 in the ITT Population (20 mg/day versus Placebo)
FDA Review
Figure 5. Mean Change from Part 2 Baseline at Week 8 in the ITT Population (40 mg/day versus Placebo)
FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
PALYNZIQ may cause serious side effects including life threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis.
The most common side effects of PALYNZIQ are injection site reactions, joint pain, hypersensitivity reactions, headache, and various skin reactions.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes adverse reactions, in patients with phenylketonuria, who received at least one dose of PALYNZIQ.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions* Reported in at Least 15% of PKU Patients Treated with PALYNZIQ in an Induction/Titration/Maintenance Regimen in Clinical Trials- Incidence and Exposure-Adjusted Rates
Treatment Phase
Induction/Titration Phase (N = 285)
Maintenance Phase (N = 223)
Treatment Duration
135 person-years
Mean: 178 days
Median: 116 days
Range: 1 to 1607 days444 person-years
Mean: 739 days
Median: 697 days
Range: 5 to 1561 daysAdverse Reaction
N (%)†
Episodes (Rate)†
N (%)†
Episodes (Rate)†
Injection site reactions‡
252 (88%)
2964 (21.9)
161 (72%)
1754 (4)
Arthralgia§
210 (74%)
1035 (7.6)
137 (61%)
661 (1.5)
Hypersensitivity reactions¶
152 (53%)
633 (4.7)
135 (61%)
663 (1.5)
Headache#
100 (35%)
211 (1.6)
111 (50%)
778 (1.8)
Generalized skin reaction lasting at least 14 daysÞ
61 (21%)
95 (0.7)
82 (37%)
133 (0.3)
Pruritus
58 (20%)
100 (0.7)
53 (24%)
402 (0.9)
Nausea
51 (18%)
66 (0.5)
57 (26%)
106 (0.2)
Dizziness
46 (16%)
64 (0.5)
38 (17%)
72 (0.2)
Abdominal painß
39 (14%)
53 (0.4)
55 (25%)
128 (0.3)
Oropharyngeal pain
38 (13%)
43 (0.3)
51 (23%)
70 (0.2)
Fatigue
37 (13%)
81 (0.6)
48 (22%)
86 (0.2)
Vomiting
36 (13%)
53 (0.4)
58 (26%)
100 (0.2)
Cough
27 (9%)
33 (0.2)
50 (22%)
65 (0.2)
Diarrhea
25 (9%)
31 (0.2)
50 (22%)
91 (0.2)
Anxiety
14 (5%)
23 (0.2)
41 (18%)
79 (0.2)
Alopecia
13 (5%)
14 (0.1)
39 (17%)
50 (0.1)
Nasal congestion
12 (4%)
15 (0.1)
41 (18%)
50 (0.1)
* ≥ 15% incidence in either treatment phase
† N (%) = Number of patients with at least 1 Adverse Reaction (%); Rate = Exposure-Adjusted Rate of Adverse Reactions (Adverse Reactions/Person Years)
‡ Includes Injection site: reaction, erythema, pruritus, pain, bruising, rash, swelling, urticaria, induration, hemorrhage, edema, mass, inflammation, nodule, discoloration, warmth, hematoma, irritation, vesicles, hypersensitivity, papule, discomfort, scar, paresthesia, hypertrophy, extravasation, and dryness
§ Includes arthralgia, pain in extremity, back pain, musculoskeletal pain, neck pain
¶ Includes rash, urticaria, anaphylaxis, rash generalized, hypersensitivity, rash erythematous, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, serum sickness, swelling face, dermatitis contact, swollen tongue, lip swelling, rash macular, pharyngeal edema, injection site hypersensitivity, eczema, drug eruption, dermatitis allergic, dermatitis, tongue edema, palatal edema, edema mouth, multiple allergies, lip edema, eye edema, exfoliative rash, drug hypersensitivity, dermatitis atopic, dermatitis acneiform, pruritus allergic, mouth swelling, implant site rash, gingival swelling, face edema, eyelid edema, eye swelling, dermatitis psoriasiform, dermatitis infected, conjunctivitis allergic, bronchospasm, angioedema, allergic sinusitis, allergic cough
# Includes headache, migraine, sinus headache
Þ Includes pruritus, rash, urticaria, dry skin, rash erythematous, erythema, cellulitis, rash macular, pruritus generalized, petechiae, dermatitis allergic, skin infection, skin induration, rash maculo-papular, rash generalized, pharyngeal edema, macule, granulomatous dermatitis, exfoliative rash, drug eruption, dermatitis atopic, dermatitis, xanthogranuloma, skin plaque, skin mass, skin lesion, skin hypopigmentation, skin hypertrophy, skin hyperpigmentation, skin exfoliation, septal panniculitis, scleroderma, scar, rash pruritic, rash papular, psoriatic arthropathy, pruritus allergic, papule, necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum, furuncle, eczema, ecchymosis, dermatitis psoriasiform, dermatitis infected, blister
ß Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort
PALYNZIQ Prescribing InformationWere there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of certain hypersensitivy side effects was higher in females than males.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The majority of patients were adults 18-65 years of age; therefore, differences in side effects among different age groups could not be determined.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes three most frequent adverse reactions by sex using number of events (exposure-adjusted event rate). Race and age subgroups are not presented because the trial population consisted of predominantly White patients 18-65 years of age.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions by Sex (safety population)
Male (N=142)
Events (Event Rate)Female (N=143)
Events (Event Rate)Total treatment exposure (person-years)
248
225.4
Injection site reactions
115 (0.46)
224 (0.99)
Arthralgia
385 (1.55)
799 (3.54)
Hypersensitivity
1237 (4.99)
2281 (10.12)
FDA Review
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIAL?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved PALYNZIQ based on evidence from 2 clinical trials, Trial 1 (NCT01819727) and Trial 2 (NCT01889862) which included 285 adult patients with phenylketonuria. The trials were conducted at 60 sites in the United States.
Figure 1 summarizes how many males and females were enrolled in the clinical trials used to evaluate safety.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex (safety population)
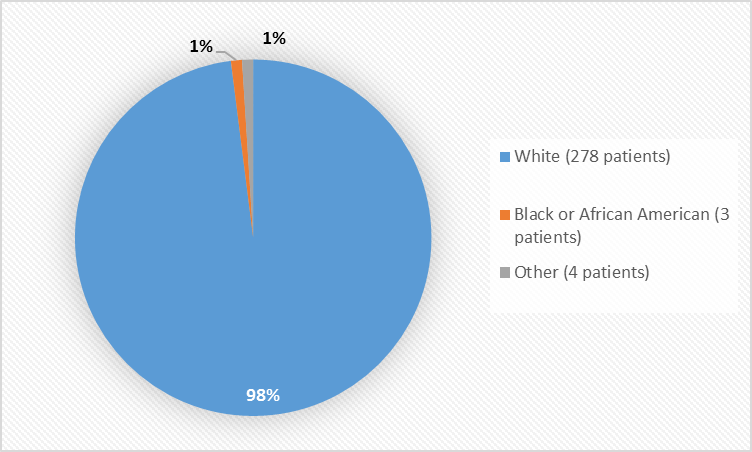
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race (safety population)
FDA Review
Table 1. Baseline Demographics by Race (safety population)
Race
Number of Patients
Percentage
White
278
98%
Black or African American
3
1%
American Indian or Alaska Native
1
less than 1%
Other
2
less than 1%
Missing
1
less than 1%
FDA Review
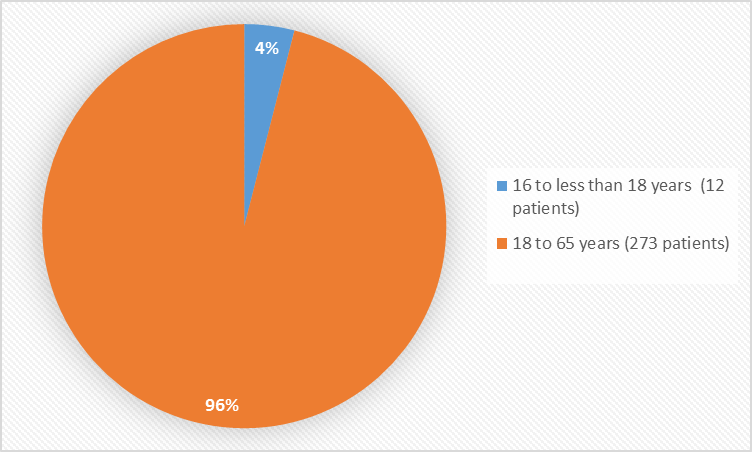
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age based on the safety population.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
FDA Review
Who participated in the Trials
The table blow summarizes demographics of all patients in the safety population.
Table 5. Demographic Characteristics of Safety Population
Demographic Parameters
All Patients
N=285
n (%)Sex
Male
142 (49.8%)
Female
143 (50.2%)
Race
White
278 (97.5%)
Black or African American
3 (1.1%)
American Indian or Native Alaskan
1 (>
Other
2 (>
Missing
1 (1>
Age
16 to 18="" years="" of="">
12 (4.2%)
18 to 65="" years="" of="">
273 (95.8%)
Ethnicity
Hispanic
7 (2.5%)
Not Hispanic
277 (97.2%)
Missing
1 (>
Region
United States
285 (100.0%)
FDA Review
The table below summarizes demographics of intent to treat population from the Trial 2 used to assess the efficacy.
Table 6. Demographic Characterisitics of the Intent-to-Treat Population (ITT)
Naive Demographic or Baseline Characteristic
PALYNZIQ
20 mg/day
(N=29)PALYNZIQ
40 mg/day
(N=29)Placebo
20 mg/day
(n = 14)Placebo
40 mg/day
(n = 14)Sex
Female
14 (48.3%)
17 (58.6%)
6 (42.9%)
6 (42.9%)
Male
15 (51.7%)
12 (41.4%)
8 (57.1%)
8 (57.1%)
Race
White
29 (100.0%)
29 (100.0%)
13 (92.9%)
14 (100.0%)
Black/African American
0
0
1 (7.1%)
0
Age, years
Mean (SD)
30.72 (9.1)
28.59 (7.6)
30.50 (10.9)
30.00 (10.2)
Median
29.0
29.0
27.5
25.5
Min, Max
19, 50
16, 40
19, 51
18, 50
16 to 18="" years="">
0
3 (10.3%)
0
0
18 to 65="" years="">
29 (100.0%)
26 (89.7%)
14 (100.0%)
14 (100.0%)
Region
United States
29 (100%)
29 (100%)
14 (100%)
14 (100%
FDA Review
How were the trials designed?
The benefit and side effects of PALYNZQ were evaluated in two clinical trials of adult patients with phenylketonuria (PKU). Each trial had a different design and treatment duration.
Trial 1: Trial evaluated patients with high phenylalanine blood concentrations who had never been treated before with PALYNZIQ. All patients received PALYNZIQ for up to 36 weeks, starting with low doses given once weekly up to the maximum dose given once daily. The trial data were used to assess the side effects of PALYNZIQ.
Trial 2: Patients, who were previously treated with PALYNZIQ, received up to an additional 13 weeks of PALYNZIQ. After that, if patients achieved at least a 20% decrease in blood phenylalanine concentration from their pre-treatment levels, they were randomly assigned to continue PALYNZIQ or to switch to placebo for 8 weeks. The benefit of PALYNZIQ was assessed by measuring the level of phenylalanine in the blood at the end of 8 weeks.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of PALINZIQ was evaluated in two clinical trials of adult patients with phenylketonuria (PKU).
Trial 1 (NCT01819727) evaluated PALYNZIQ, in adult patients with PKU , who had inadequate phenylalanine blood concentrations on existing management. This trial was an open-label, randomized, multi-center clinical trial. Patients were treated with PALYNZQ with an induction/titration/maintenance regimen, gradually increasing from weekly low doses to daily higher doses. Patients were randomized to receive PALYNZIQ target maintenance doses at 20 mg or 40 mg once daily for up to 36 weeks. The primary objective of this trial was to assess PALYNZIQ safety.
Trial 2 (NCT01889862) evaluated PALYNZIQ in adult patients with PKU previously-treated with PALYNZIQ. Enrolled patients included patients from Trial 1 and other PAYNZIQ trials. Patients received PALYNZIQ treatment up to an additional 13 weeks. If patients achieved > 20% reduction in blood phenylalanine concentration from their pre-treatment baseline concentration (in previous trials), they were enrolled into the efficacy assessment period (randomized withdrawal period). In the randomized withdrawal period, patients were randomized to continue PALYNZIQ or receive placebo for 8 weeks. The efficacy endpoint was the change in blood phenylalanine concentration from baseline to Week 8 of the randomized withdrawal period.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION