2023 FDA Science Forum
Using Alamar Blue assay to measure proliferation inhibition of Trastuzumab biosimilars
- Authors:
- Center:
-
Contributing OfficeCenter for Drug Evaluation and Research
Abstract
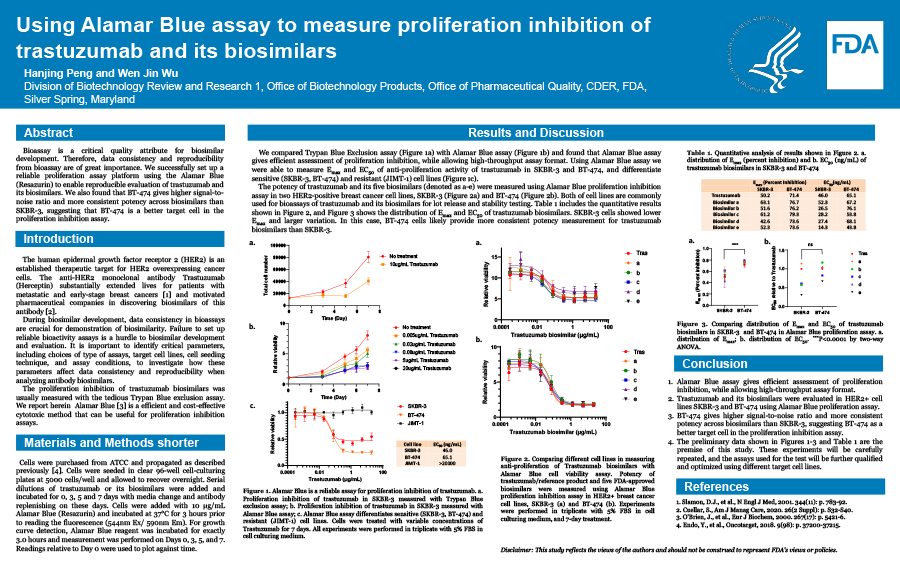
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers in women in the U.S., contributing ~30% of all new female cancers each year.[1] The human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) protein is an established therapeutic target for HER2 overexpressing cancer cells, including but not limited to breast cancers. The anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody Trastuzumab (Herceptin) substantially extended lives for patients with metastatic and early-stage breast cancers.[2, 3] On the other hand, the high potential and high cost of trastuzumab has motivated pharmaceutical companies in discovering biosimilars of this antibody. [4] During biosimilar development, data consistency, reproducibility, and similarity with the reference product in bioassays are crucial for demonstration of biosimilarity. Failure to set up reliable bioactivity assays is a hurdle to biosimilar development and evaluation. Therefore, it is important to identify critical parameters, including choices of type of assays, target cell lines, reagents, and cell seeding density, and assay incubation times, to investigate how these parameters affect data consistency and reproducibility when analyzing biological activity of antibody biosimilars. The proliferation inhibition of trastuzumab biosimilars was usually measured with the tedious Trypan Blue exclusion assay.[5] However, we found that Alamar Blue assay gives efficient assessment of proliferation inhibition, while allowing high-throughput assay format. This is especially valuable in testing multiple biosimilars at multi-concentrations, and in several different target cell lines. Then, we evaluated all 5 biosimilars together with Trastuzumab as a reference in three HER2+ cell lines, including SKBR-3, BT-474, and NCI-N87 cells. We found that different HER2+ cell lines give significantly different responses to Trastuzumab treatment. Although SKBR-3 cell line is usually used for evaluation of Trastuzumab biosimilar, BT-474 gives higher signal-to-noise ratio and more consistent potency across biosimilars, thus is a better target cell in the proliferation inhibition assay. In conclusion, we successfully set up a reliable proliferation assay platform using the Alamar Blue cell viability assay to enable reproducible evaluation of Trastuzumab biosimilars. References: 1. Key Statistics for Breast Cancer. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/about/how-common-is-breast-cancer.html. 2. Slamon, D.J., et al., Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med, 2001. 344(11): p. 783-92. 3. Romond, E.H., et al., Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med, 2005. 353(16): p. 1673-84. 4. Cuellar, S., Integrating trastuzumab biosimilars and HER2-directed therapies into HER2-positive breast cancer management. Am J Manag Care, 2020. 26(2 Suppl): p. S32-S40. 5. Nahta, R., M.C. Hung, and F.J. Esteva, The HER-2-targeting antibodies trastuzumab and pertuzumab synergistically inhibit the survival of breast cancer cells. Cancer Research, 2004. 64(7): p. 2343-2346.