2021 FDA Science Forum
Updated Safety Assessment of Tris(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) Phosphite (Irgafos 168) Used in Food Contact Applications
- Authors:
- Center:
-
Contributing OfficeCenter for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition
Abstract
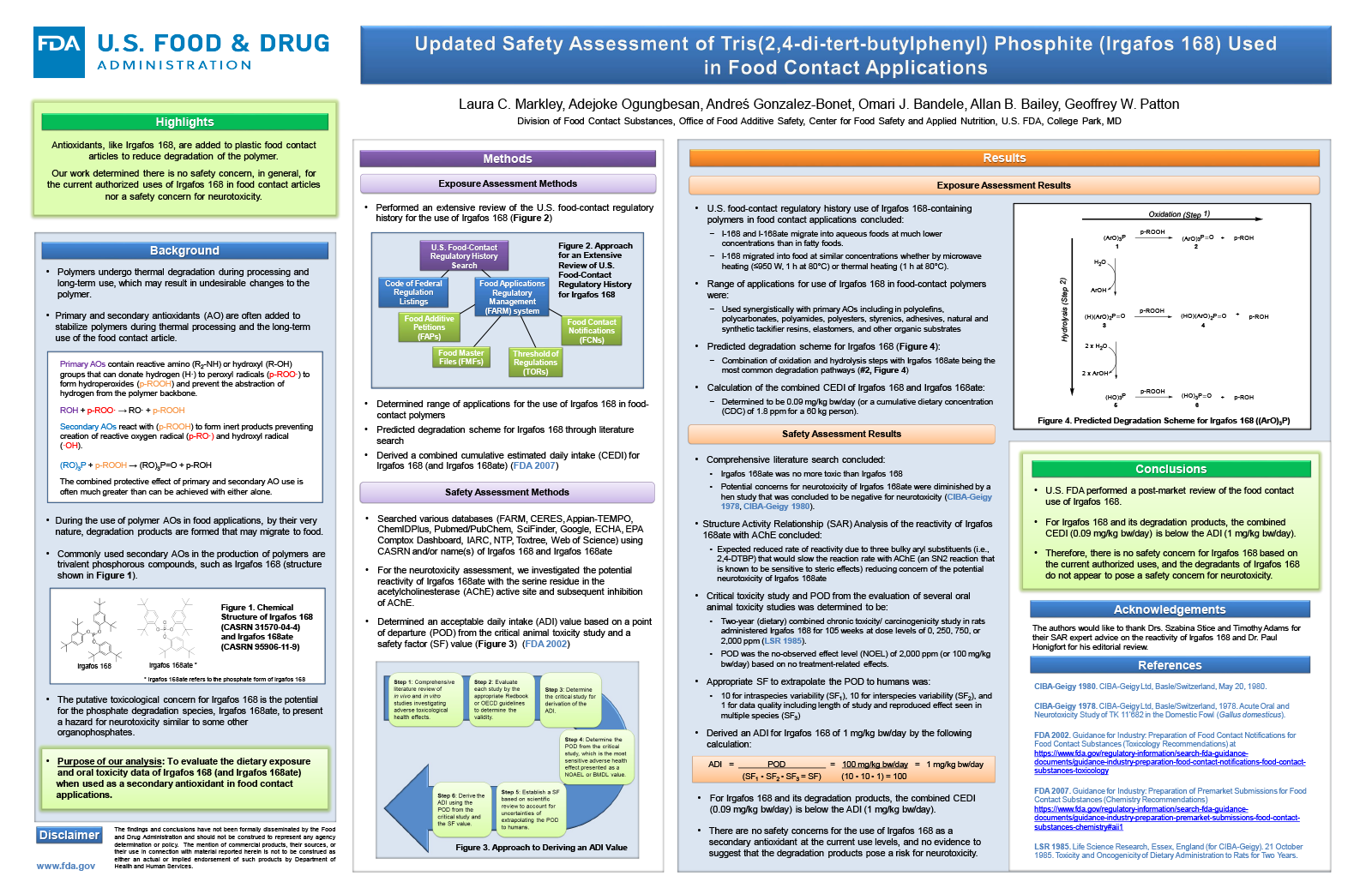
Some food contact articles are produced from polymers via several processing steps, which promote thermo-oxidative and thermo-mechanical degradation of the polymers. These steps include chemical reactions initiated by oxygen, heat, light, shear, or catalyst residues. Primary and secondary antioxidants (AO) are often added to reduce degradation of the polymers during thermal processing and provide long-term AO properties to the food contact article. Trivalent phosphorous compounds, such as Irgafos 168 (I-168), are commonly used secondary AOs in the production of polymers. However, there are possible safety concerns for the use of I-168 in plastics intended for food contact use due to the potential for the phosphate degradation species, I-168ate, to present a hazard for neurotoxicity similar to some other organophosphates. The purpose of our assessment was to evaluate the dietary exposure and oral toxicity data of I-168 and I-168ate when used as an AO in food contact applications. Our exposure assessment included an extensive review of the U.S. food-contact regulatory history for I-168, which resulted in a combined cumulative estimated daily intake (CEDI) of 0.09 mg/kg bw/day (or 1.8 ppb for a 60 kg person) for I-168 and I-168ate. Our comprehensive literature review of toxicological data for I-168 determined that I-168 and its degradants, including I-168ate, were not of toxicological concern. The potential concern for neurotoxicity was diminished by the finding of no neurotoxicity in a study performed in hens combined with our determination that steric hindrance inhibits the interaction between I-168ate and the serine residue in the acetylcholinesterase active site, which plays a key role in facilitating neurotransmission. An acceptable daily intake (ADI) value of 1 mg/kg bw/day (20 ppm) was derived for Irgafos 168 and its degradants, based on a safety factor of 100 and a no-observed-effect-level (NOEL) of 2,000 ppm from a two-year combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity study in rats. In conclusion, the combined CEDI for I-168 and its degradation products (0.09 mg/kg bw/day) is below the ADI (1 mg/kg bw/day). Therefore, there is no safety concern for its current authorized use levels, and the degradants of I-168 do not appear to pose a safety concern for neurotoxicity.