2021 FDA Science Forum
Temporal Trends in Medication Utilization Among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in the United States
- Authors:
- Center:
-
Contributing OfficeCenter for Drug Evaluation and Research
Abstract
Background
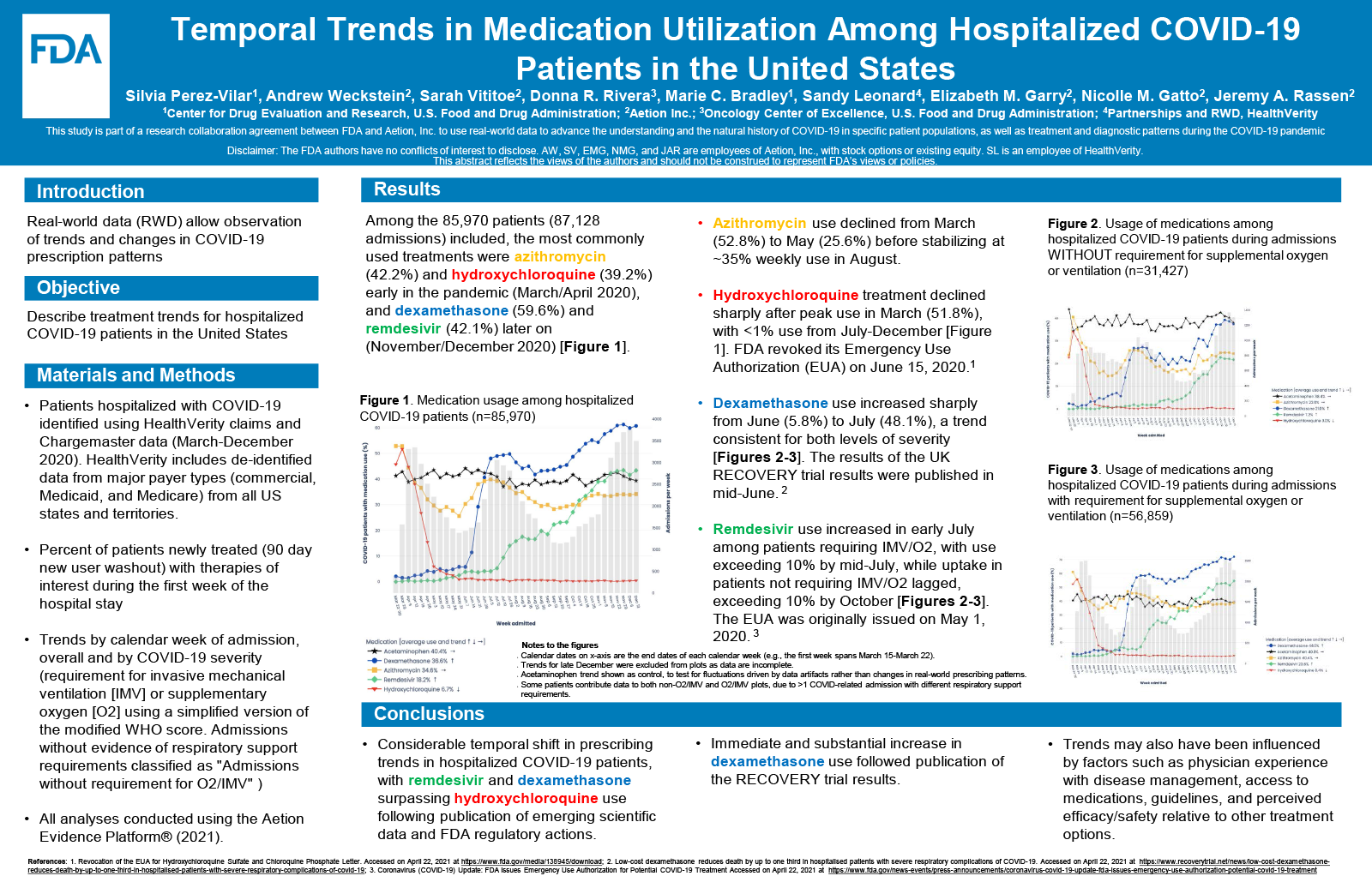
Real-world data allow observation of trends and changes in COVID-19 prescription patterns.
Objective
Describe treatment trends for hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the United States.
Methods
Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 were identified using HealthVerity claims (March-December 2020). Percent of patients newly treated with hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, remdesivir, and dexamethasone, during the first week of the hospital stay, were reported. Trends by calendar week of admission, overall, by COVID-19 severity (requirement for invasive mechanical ventilation [IMV] or supplementary oxygen [O2]), and, for dexamethasone, before and after publication of the UK RECOVERY trial results in mid-June, were examined.
Results
Among the 85,970 patients included, the most commonly used treatments were azithromycin (42.2%) and hydroxychloroquine (39.2%) early in the pandemic (March/April 2020), and dexamethasone (59.6%) and remdesivir (42.1%) later on (November/December 2020). Hydroxychloroquine treatment declined sharply after peak use in March (51.8%), with <1% use from July-December. Azithromycin use declined from March (52.8%) to May (25.6%) before stabilizing at ~35% weekly use in August. Dexamethasone use increased sharply from June (5.8%) to July (48.1%), a trend consistent for both levels of severity. Remdesivir use increased in early July among patients requiring IMV/O2, with use exceeding 10% by mid-July, while uptake in patients not requiring IMV/O2 lagged, exceeding 10% by October.
Conclusion
A considerable temporal shift in prescribing trends in hospitalized COVID-19 patients was observed, with remdesivir and dexamethasone surpassing hydroxychloroquine use following publication of emerging scientific data and FDA regulatory actions. An immediate and substantial increase in dexamethasone use followed publication of the RECOVERY trial results. Trends may also have been influenced by factors such as physician experience with disease management, access to medications, guidelines, and perceived efficacy/safety relative to other treatment options.