2021 FDA Science Forum
Comprehensive Physico-chemical Characterization of Liposomal Doxorubicin
- Authors:
- Center:
-
Contributing OfficeNational Center for Toxicological Research
Abstract
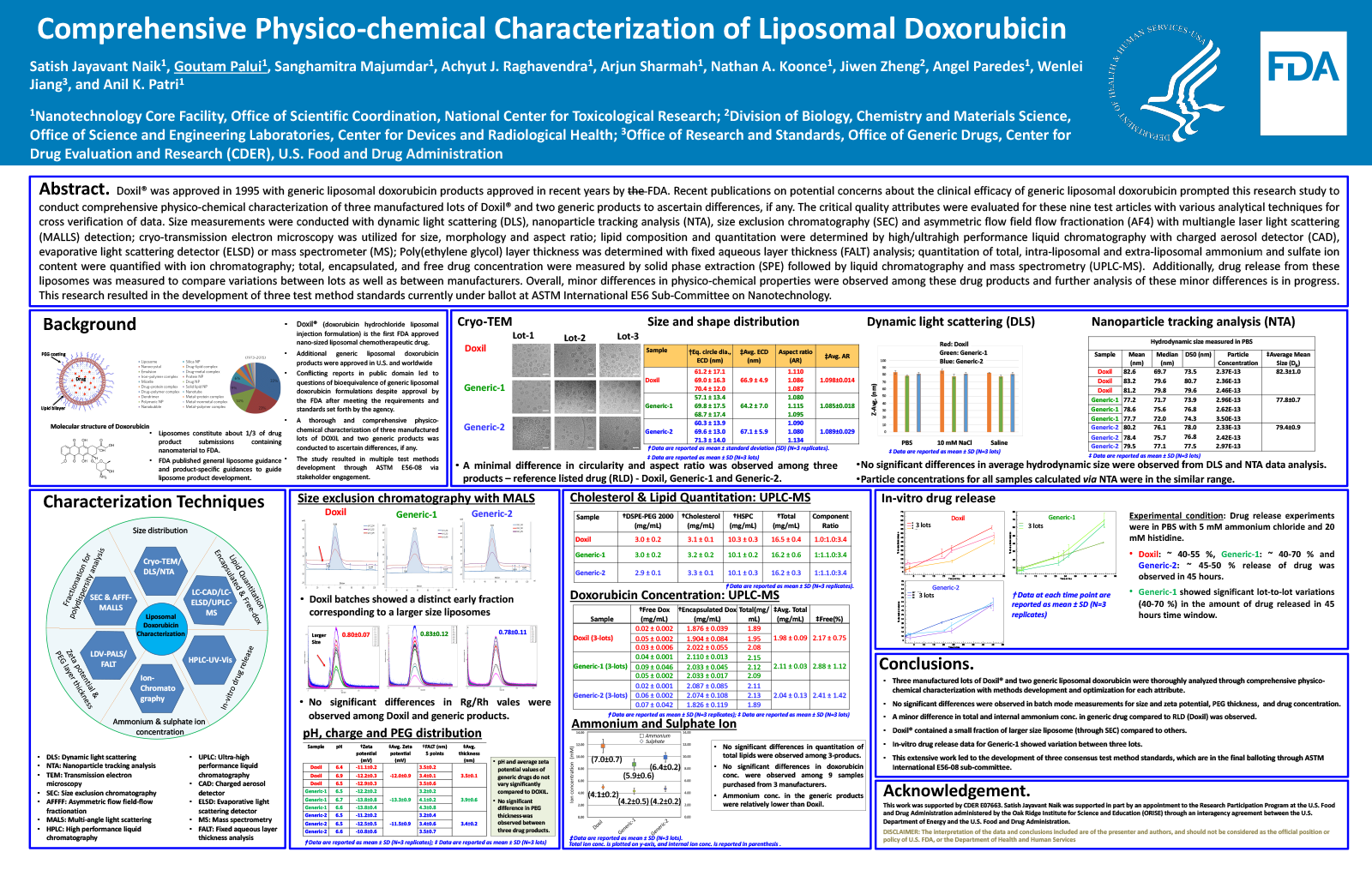
Liposomes constitute one-third of the complex drug products containing nanomaterials approved by the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER)/U.S. FDA. A series of liposomal drug products have been approved with increase in generic products submission. FDA published liposome guidance and product-specific guidances to help industry develop liposomal drug products and facilitate application review. The critical quality attributes to consider for liposomes include size distribution, morphology, composition, purity, surface properties, and drug release kinetics since variations in these attributes may influence biological interaction leading to an altered biodistribution, efficacy, and safety.
To ascertain any differences that may be present in Doxil and generic formulations of liposomal doxorubicin, we conducted research on comprehensive physico-chemical characterization. A series of advanced analytical techniques have been utilized in this study. These techniques include: size measurements utilizing dynamic light scattering (DLS), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), cryo-TEM image analysis, size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and asymmetric flow field flow fractionation (AFFFF) with multiangle laser light scattering (MALLS) detection; lipid composition analysis by high/ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography with either charged aerosol detector (CAD), evaporative light scattering detector (ELSD) or mass spectrometer (MS); Poly(ethylene glycol) layer thickness with fixed aqueous layer thickness (FALT) analysis; quantitation of ammonium and sulfate ion concentration with ion chromatography; total, encapsulated and free drug concentration was measured by solid phase extraction (SPE) column separation followed by liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Additionally, drug release from these liposomes was measured using an in vitro release assay to compare variations between lots as well as between manufacturers. Data from three manufactured lots by three different manufacturers have been compared to illustrate the utility and limitations of various analytical techniques in characterizing liposomes. Overall, a minor difference in physical characteristics was observed among these drug products, and none of these products seem to be out of specifications. This research resulted in the development of three test method standards that are currently under ballot at American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) International, E56 Sub-Committee on Nanotechnology.