Medical Device Reporting
Medical Device Reporting
Medical Device Reporting
Inspectional Objectives
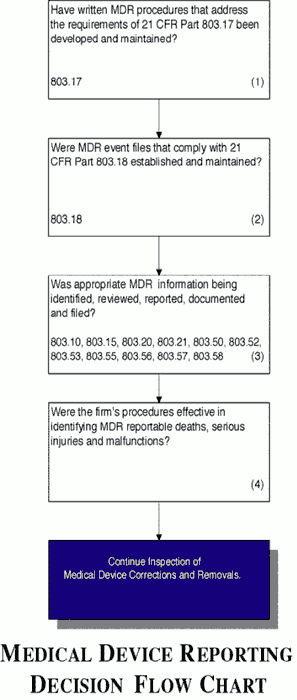
- Verify that the firm has MDR procedures that address the requirements in 21 CFR Part 803.17.
- Verify that the firm has established and maintains MDR event files that comply with 21 CFR Part 803.18.
- Confirm that the appropriate MDR information is being identified, reviewed, reported, documented and filed.
- Confirm that the firm follows their procedures and they are effective in identifying MDR reportable deaths, serious injuries and malfunctions.
Medical Device Reporting
Narrative
Purpose/Importance
The Medical Device Reporting (MDR) Regulation requires medical device manufacturers, device user facilities and importers to establish a system that ensures the prompt identification, timely investigation, reporting, documentation, and filing of device-related death, serious injury, and malfunction information.
The events described in Medical Device Reports (MDR's) may require the FDA to initiate corrective actions to protect the public health. Therefore, compliance with Medical Device Reporting must be verified to ensure that CDRH's Surveillance Program receives both timely and accurate information.

- Verify that the firm has MDR procedures that address the requirements in 21 CFR Part 803.17.
Review and confirm that the firm's written MDR procedures address:
- Internal systems that provide for the timely and effective identification, communication, and evaluation of events that may be subject to medical device reporting.
- A standard review process/procedure for determining when an event meets the criteria for MDR reporting and ensuring the timely transmission of complete device reports to FDA.
- Documentation and recordkeeping regarding: information evaluated to determine if an event is reportable; all MDR reports and other information submitted to the FDA; and systems that ensure access to information that facilitates timely follow-up and inspection by FDA.

-
Verify that the firm has established and maintains MDR event files that comply with 21 CFR Part 803.18
Using the sampling tables, select a number of MDR event files. Review and verify that the MDR event files (hard copy or electronic) are prominently identified and easy to access. MDR files may be maintained as part of the 820.198 complaint file IF the two aforementioned criteria are met.
Confirm that the MDR event files contain: information from any source that describes a device-related death, serious injury or malfunction; the firm's evaluation of this information including decisions to submit or not to submit an MDR report; and copies or references to supporting documentation (e.g., failure analysis, lab reports, etc.).
Decisions not to submit an MDR report for a device-related death, serious injury or malfunction must be documented in the MDR file.
When applicable, the files will also contain copies of MDR death, serious injury, malfunction and five-day reports submitted on FDA form 3500A, Supplemental Reports (3500A), Baseline Reports (3417) and MDR-related correspondence.

-
Confirm that the appropriate MDR information is being identified, reviewed, reported, documented and filed.
Using the sampling tables, select a number of MDR reports that were submitted to the FDA.
Compare the firm's written procedures to the way it identified, processed, evaluated, reported and filed the reports. Note any discrepancies between the firm's practice/written procedures and any failure to follow or obtain information required by the regulation and form 3500A (e.g., timely reporting, complete investigation, consistency, etc.)

-
Confirm that the firm follows their procedures and they are effective in identifying MDR reportable deaths, serious injuries and malfunctions.
Using the sampling tables, select a number of unreported complaints and records from one additional source of quality data (service reports, repair reports, returned goods files, etc.).
Review these records and confirm that they do not contain information relating to MDR reportable events (device-related deaths, serious injuries or malfunctions).
If unreported events are identified, determine the firm's rationale for not submitting MDR reports. If the firm has failed to identify these events, or does not provide an adequate rationale for not submitting an MDR report (an adequate rationale may be that the firm's investigation determined that it was in fact another manufacturer's device involved in the event), then this may be a significant MDR related observation.

