Drug Trials Snapshots: KENGREAL
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the KENGREAL Prescribing Information for complete information.
KENGREAL (cangrelor)
(KEN-greal)
The Medicines Company
Approval date: June 22, 2015
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
KENGREAL is a drug known as a “blood thinner” that prevents the formation of blood clots in the blood vessels of the heart (coronary arteries) in patients undergoing a procedure called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). This procedure, also known as coronary angioplasty, is used to open a blocked or narrowed heart artery to improve blood flow to the heart muscle.
During PCI, the arteries are opened by inflating a balloon at the site of the narrowing, usually followed by placement of a small tube called a stent to keep the artery open.
How is this drug used?
KENGREAL is given by a health care professional directly into the bloodstream through a needle in the vein. This is known as an intravenous, or IV, infusion.
What are the benefits of this drug?
KENGREAL reduces the risk of serious blood clotting complications related to PCI, including heart attack, blockage of the stent, and a need for further procedures to reopen an artery.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The table below summarizes the primary endpoint, which was occurrence of one or more of the following: death from any cause, myocardial infarction (MI), ischemia-driven revascularization (IDR) and stent thrombosis (ST) in the 48 hour interval after PCI. IDR is defined as being required to go back for another procedure because of reoccurrence of signs or symptoms of coronary artery disease. ST is defined as a blood clot occurring where the stent has been placed in an artery.
If a patient had more than one event at 48 hours, then the worst outcome counted, with death being worse than MI, MI being worse than IDR, and IDR being worse than ST.
Table 2. Primary Endpoint and Its Component Events at 48 hours (Efficacy Populationa)
| KENGREAL N=5470 n (%) |
Clopidogrel N=5469 n (%) |
KENGREAL vs. Clopidogrel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-value | |||
| Primary Endpoint Death/MI/IDR/ST |
257(4.7) | 322 (5.9) | 0.78 (0.66,0.93)b | 0.005 |
| Death | 18 (0.3) | 18 (0.3) | ||
| MI | 202 (3.7) | 254 (4.6) | ||
| IDR | 10 (0.2) | 14 (0.3) | ||
| ST | 27 (0.5) | 36 (0.7) | ||
a efficacy population=all randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study drug, underwent the index PCI procedure and completed assessment at 48 hours
b p-value based on logistic model adjusted for loading dose and baseline patient status for primary endpoint
Source: KENGREAL Prescribing Information, Section 14, Table 2
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
Subgroup analyses were conducted for sex, race, and age.
- Sex: KENGREAL was similarly effective in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients in the trial were white. Differences in response to KENGREAL among races could not be determined.
- Age: KENGREAL was similarly effective in all age groups studied.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes the primary endpoint results by subgroup. The odds ratio is the odds of composite events on KENGREAL compared to the odds of composite events on clopidogrel. The 95% confidence interval (CI), which is the interval that covers the true value 95% of the time, is expressed as lower (LL) and upper (UL) boundaries in the table. There is no evidence of inconsistent treatment effect in any specific subgroups in this trial.
Table 3. Subgroup Analysis of Primary Endpoint *
| KENGREAL (N=5472) |
Clopidogrel (N=5470) |
Odds Ratio | 95% CI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | x(%) | Total n | x(%) | Total n | LL | UL | |||
| Overall Response/All patients** | 257 (5) | 5470 | 322 (6) | 5469 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.93 | ||
| Sex | |||||||||
| Male | 183 (5) | 3913 | 219 (6) | 3976 | 0.84 | 0.69 | 1.03 | ||
| Female | 74 (5) | 1557 | 103 (7) | 1493 | 0.67 | 0.5 | 0.92 | ||
| Age Group | |||||||||
| >=17-65 years | 121 (4) | 2827 | 151 (5) | 2855 | 0.8 | 0.63 | 1.02 | ||
| >=65 years | 136 (5) | 2643 | 171 (7) | 2614 | 0.78 | 0.61 | 0.98 | ||
| >=75 years | 55 (5) | 1021 | 73 (7) | 987 | 0.71 | 0.5 | 1.02 | ||
| Race | |||||||||
| White | 243 (5) | 5130 | 300 (6) | 5119 | 0.8 | 0.67 | 0.95 | ||
| Black or African American |
5 (3) | 149 | 9 (6) | 146 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 1.62 | ||
| Asian | 7 (4) | 171 | 8 (5) | 175 | 0.89 | 0.32 | 2.51 | ||
| American Indian or Alaskan Native |
1 (20) | 5 | 3 (50) | 6 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 3.77 | ||
| Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander |
1 (8) | 12 | 0 | 16 | - | - | - | ||
| Unknown | 0 | 3 | 2 (29) | 7 | - | - | - | ||
*all randomized patients who received at least one dose of study drug and who underwent the PCI procedure.
** result was based on unadjusted logistic regression model
Source: Company Clinical Trial Data
What are the possible side effects?
The most common side effect of KENGREAL during clinical trials was bleeding, which can be serious. This is because KENGREAL is a medicine that interferes with the process of blood clotting in the body, making bleeding more likely.
What are the possible side effects?
The table below summarizes major bleeding results for subjects treated with KENGREAL and clopidogrel. The population includes every patient who received at least one dose of study drug.
Table 4. Major Bleeding Results (Non CABG related bleeding)
| KENGREAL (N=5529) |
Clopidogrel (N=5527) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Any GUSTO* bleeding, n (%) | 857 (16) | 602 (11) |
| Severe/life-threatening a | 11 (<> | 6 (<> |
| Moderate b | 21 (<> | 14 (<> |
| Mild c | 825 (15) | 582 (11) |
| Any TIMI** bleeding, n (%) | 45 (1) | 17 (<> |
| Major d | 12 (<> | 6 (<> |
| Minor e | 33 (1) | 11 (<> |
*GUSTO=Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Arteries
**TIMI=Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction
a intracranial hemorrhage or bleeding resulting in substantial hemodynamic compromise requiring treatment
b requiring blood transfusion but not resulting in hemodynamic compromise
c all other bleeding not included in severe or moderate
d any intracranial hemorrhage, or any overt bleeding associated with a reduction in hemoglobin of ≥5 g/dL (or, when hemoglobin is not available, an absolute reduction in hematocrit ≥15%)
e any overt sign of bleeding (including observation by imaging techniques) that is associated with a reduction in hemoglobin of ≥3 g/dL and <5 g/dl="" (or,="" when="" hemoglobin="" is="" not="" available,="" an="" absolute="" reduction="" in="" hematocrit="" of="" ≥9%="" and=""><>
Source: KENGREAL Prescribing Information, Section 6, Table 1
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
Subgroup analyses were conducted for sex, race, and age.
- Sex: More bleeding was seen in women taking KANGREAL compared to men taking KANGREAL. In the trial, all patients (men and women) treated with KANGREAL had more bleeding compared to patients given another blood thinner called clopidogrel.
- Race: The majority of patients in the trial were white. Differences in bleeding among races could not be determined.
- Age: More bleeding was observed in patients 65 and older treated with KANGREAL compared to younger patients taking KANGREAL. In the trial, all patients (in every age group) treated with KANGREAL had more bleeding compared to patients given another blood thinner called clopidogrel.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes all non-CABG bleeds by subgroup.
Table 5. Subgroup Analysis of all non-CABG Bleeds in Safety Population*
| KENGREAL (N=5529) |
Clopidogrel (N=5527) |
95% CI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | x (%) | Total, n | x (%) | Total, n | Odds Ratio | LL | UL | ||
| Any GUSTO bleed | 857 (16) | 5529 | 602 (11) | 5527 | 1.5 | 1.34 | 1.68 | ||
| Sex | |||||||||
| Male | 517 (13) | 3946 | 394 (10) | 4018 | 1.39 | 1.21 | 1.59 | ||
| Female | 340 (22) | 1583 | 208 (14) | 1509 | 1.71 | 1.42 | 2.07 | ||
| Age Group | |||||||||
| >=17-64 years | 366 (13) | 2863 | 254 (9) | 2885 | 1.52 | 1.28 | 1.8 | ||
| >=65 years | 491 (18) | 2666 | 348 (13) | 2642 | 1.49 | 1.28 | 1.73 | ||
| >=75 years | 204 (20) | 1025 | 162 (16) | 996 | 1.28 | 1.02 | 1.61 | ||
| Race | |||||||||
| White | 810 (16) | 5188 | 564 (11) | 5175 | 1.51 | 1.35 | 1.7 | ||
| Black or African American |
15 (10) | 149 | 19 (13) | 147 | 0.75 | 0.37 | 1.55 | ||
| Asian | 27 (16) | 172 | 16 (9) | 176 | 1.86 | 0.96 | 3.6 | ||
| American Indian or Alaskan Native |
2 (40) | 5 | 0 | 6 | . | . | . | ||
| Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander |
2 (17) | 12 | 3 (19) | 16 | 0.87 | 0.12 | 6.21 | ||
| Unknown | 1 (33) | 3 | 0 | 7 | . | . | . | ||
*Safety population defined as any patient who received at least one dose of study drug.
Source: Company Clinical Trial Data
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved KENGREAL based on evidence from a clinical trial that enrolled 11,145 patients with blockages in the arteries of the heart (known as coronary artery disease) and who were to undergo PCI. The trial was conducted in the United States, Canada, South America, Asia, and New Zealand. The same trial was used to assess the benefit and the side effects of the drug.
The figure below summarizes how many men and women were enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Source: Company Clinical Trial Data
The figure and table below summarize how many patients by race were enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
*Other=Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, American Indian or Alaskan Native and Unknown combined
Source: Company Clinical Trial Data
Table 1b. Baseline Demographics by Race
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 10437 | 94 |
| Black or African American | 308 | 3 |
| Asian | 350 | 3 |
| Other* | 50 | <> |
*Other=Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, American Indian or Alaskan Native and Unknown combined
Source: Company Clinical Trial Data
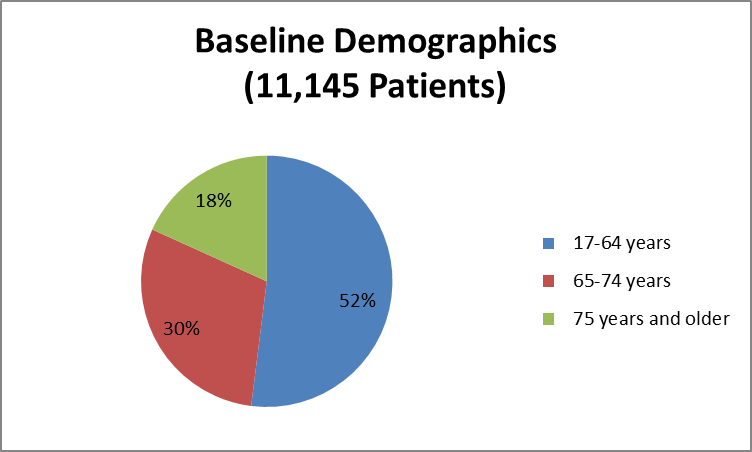
The figure below summarizes how many patients by age were enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Source: Company Clinical Trial Data
Who participated in the trial?
The table below summarizes baseline demographics for the trial.
Table 6. Baseline Demographics for the Trial (Randomized Population)
| Treatment Groups | Overall (N=11,145) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Parameters | KENGREAL (N=5581) |
Clopidogrel (N=5564) |
|
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 3982 (71) | 4042 (73) | 8024 (72) |
| Female | 1599 (29) | 1522 (27) | 3121 (28) |
| Age (years) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 64.0 (11.0) | 63.8 (11.0) | 63.9 (11.0) |
| Median | 64 | 64 | 64 |
| (Min, Max) | 26, 94 | 26, 95 | 26, 95 |
| Age group, n (%) | |||
| 17-64 years | 2892 (52) | 2902 (52) | 5794 (52) |
| 65-74 years | 1656 (29) | 1662 (30) | 3318 (30) |
| >=75 | 1033 (19) | 1000 (18) | 2033 (18) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 5231 (94) | 5206 (94) | 10437 (94) |
| Black or African American |
156 (3) | 152 (3) | 308 (3) |
| Asian | 173 (3) | 177 (3) | 350 (3) |
| Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander |
13 (<> | 16 (<> | 29 (<> |
| American Indian or Alaskan Native |
5 (<> | 6 (<> | 11 (<> |
| Unknown | 3 (<> | 7 (<> | 10 (<> |
Source: Company Clinical Trial Data
How was the trial designed?
There was one trial that evaluated the benefit and side effects of KENGREAL. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either KENGREAL for 2 hours or until the PCI was completed, or an approved drug called clopidogrel given around the time of PCI. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed. When the KANGREAL infusion was stopped after 2 hours or completion of the PCI, clopidogrel was given.
The trial was designed to compare the numbers of patients in the two groups who had one or more of the following events: death, heart attack, clogged stents, and repeated heart procedure that occurred in the first 48 hours after PCI.
How was the trial designed?
A randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active-control, parallel-group trial was conducted in patients who required percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The efficacy of KENGREAL in comparison to clopidogrel was measured by the first occurrence of any of the composite endpoint of all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), ischemia-driven revascularization (IDR) and stent thrombosis (ST). Safety assessments included comparisons in non CABG related bleeding.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.