Drug Trials Snapshots: SUNOSI
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to the SUNOSI Package Insert for complete information.
SUNOSI (solriamfetol)
suh-NOH-see
Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc
Approval date: March 20, 2018
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
SUNOSI is a drug used to improve wakefulness in adults with narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder with excessive daytime drowsiness and sudden attacks of sleep. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a sleep disorder with frequent sleep disruptions because of the blocked the airway. This leads to poor sleep and daytime drowsiness.
How is this drug used?
SUNOSI is a tablet that is taken by mouth once a day. The dose may be adjusted, and the dose range depends on whether the drug is taken for narcolepsy or OSA.
Patients who have OSA should continue modalities to treat airway obstruction while taking SUNOSI.
What are the benefits of this drug?
Patients treated with SUNOSI remained awake longer and had decreased daytime sleepiness compared with patients treated with placebo.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The tables below summarize efficacy results for the evaluated patients in clinical trials 1 and 2. The co-primary endpoints were the change from baseline in MWT and ESS score at Week 12.
Table 2. Maintenance of Wakefulness Test (minutes) in Patients with Narcolepsy (Trial 1) and OSA (Trial 2)
| Indication/Trial | Treatment Group (N) | Mean Baseline Score (SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline at Week 12 (SE) | Difference from Placebo (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narcolepsy Trial 1 |
Placebo (58) | 6.2 (5.7) | 2.1 (1.3) | - |
| SUNOSI 75 mg (59) | 7.5 (5.4) | 4.7 (1.3) | 2.6 (-1.0, 6.3) | |
| SUNOSI 150 mg* (55) | 7.9 (5.7) | 9.8 (1.3) | 7.7 (4.0, 11.3) | |
| OSA Trial 2 |
Placebo (114) | 12.6 (7.1) | 0.2 (1.0) | - |
| SUNOSI 37.5 mg* (56) | 13.6 (8.1) | 4.7 (1.4) | 4.5 (1.2, 7.9) | |
| SUNOSI 75 mg* (58) | 12.4 (6.9) | 9.1 (1.4) | 8.9 (5.6, 12.4) | |
| SUNOSI 150 mg* (116) | 12.5 (7.2) | 11.0 (1.0) | 10.7 (8.1, 13.4) |
SD = standard deviation; SE = standard error; LS Mean = least square mean; CI = confidence interval
Maximum possible MWT score is 40 minutes. A positive change represents improvement
Difference from Placebo = LS Mean Difference between change from baseline between active drug and placebo.
* Dose that was statistically significantly superior to placebo after adjusting for multiplicity.
SUNOSI Prescribing Information
Table 3. Epworth Sleepiness Scale in Patients with Narcolepsy (Trial 1) and OSA (Trial 2)
| Indication/Trial | Treatment Groups (N) | Mean Baseline Score (SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline at Week 12 (SE) | Difference from Placebo (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narcolepsy Trial 1 |
Placebo (58) | 17.3 (2.9) | -1.6 (0.7) | - |
| SUNOSI 75 mg (59) | 17.3 (3.5) | -3.8 (0.7) | -2.2 (-4.0, -0.3) | |
| SUNOSI 150 mg* (55) | 17.0 (3.6) | -5.4 (0.7) | -3.8 (-5.6, -2.0) | |
| OSA Trial 2 |
Placebo (114) | 15.6 (3.3) | -3.3 (0. 5) | - |
| SUNOSI 37.5 mg* (56) SUNOSI 75 mg* (58) |
15.1 (3.5) 15.0 (3.5) |
-5.1 (0.6) -5.0 (0.6) |
-1.9 (-3.4, -0.3) -1.7 (-3.2, -0.2) |
|
| SUNOSI 150 mg* (116) | 15.1 (3.4) | -7.7 (0.4) | -4.5 (-5.7, -3.2) |
SD = standard deviation; SE = standard error; LS Mean = least square mean; CI = confidence interval
Scores range from 0 to 24 with higher scores indicating more severe sleepiness. A negative change represents improvement.
Difference from placebo = LS mean difference between change from baseline between SUNOSI and placebo.
* Dose that was statistically significantly superior to placebo after adjusting for multiplicity.
SUNOSI Prescribing Information
Maintenance of effect was assessed in Trials 3 and 4.The results are presented below.
Table 4. Efficacy Results from Randomized Withdrawal Trials in Patients with Narcolepsy and OSA in Trials 3 and 4
| Indication/Trial | Endpoint | Treatment Groups (N) | Beginning of Randomized Withdrawal Period (Baseline) Mean (SD) |
LS Mean Change from Baseline (SE) | Difference from Placebo (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSA Trial 3 |
MWT (minutes) | Placebo (62) SUNOSI* (60) |
29.0 (9.9) 31.7 (9.2) |
-12.1 (1.3) -1.0 (1.4) |
11.2 (7.8, 14.6) |
| ESS Score | Placebo (62) SUNOSI* (60) |
5.9 (3.8) 6.4 (4.4) |
4.5 (0.7) -0.1 (0.7) |
-4.6 (-6.4, -2.8) | |
| OSA and Narcolepsy Trial 4 |
ESS Score | Placebo (141) SUNOSI* (139) |
7.8 (5.0) 7.3 (5.3) |
5.3 (0.4) 1.6 (0.4) |
-3.7 (-4.8, -2.7) |
SD = standard deviation; SE = standard error; LS Mean = least square mean; CI = confidence interval
For MWT, maximum possible score is 40 minutes; positive changes indicate improvement.
For ESS, scores range from 0 to 24; negative changes indicate improvement.
* Statistically significantly superior to placebo after adjusting for multiplicity
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: SUNOSI worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in how well the drug worked among other races could not be determined.
- Age: SUNOSI worked similarly in patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below summarize efficacy results by sex, race and age in individual Trials 1 and 2.
Table 5. Subgroup Analysis Results on MWT - Trial 1
| Dose(mg) | Subgroup | SUNOSI LS Mean (SE) (n) |
Placebo LS Mean (SE) (n) |
LS Mean Difference (SE) SUNOSI-Placebo | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 75 | Sex | |||||
| Men | 3.7 (2.12) (20) | 4.3 (2.01) (22) | -0.6 (2.93) | |||
| Women | 5.2 (1.73) (34) | 0.6 (1.69) (34) | 4.6 (2.42) | |||
| Race | ||||||
| White | 4.9 (1.54) (42) | 2.0 (1.47) (44) | 2.9 (2.13) | |||
| Other | 4.3 (2.80) (12) | 2.1 (2.80) (12) | 2.2 (3.93) | |||
| 150 | Sex | |||||
| Men | 7.3 (2.33) (15) | 4.3 (2.01) (22) | 3.0 (3.08) | |||
| Women | 11.0 (1.63) (37) | 0.6 (1.69) (34) | 10.3 (2.36) | |||
| Race | ||||||
| White | 10.0 (1.52) (41) | 2.0 (1.47) (44) | 8.1 (2.13) | |||
| Other | 9.1 (2.85) (11) | 2.1 (2.80) (12) | 7.0 (3.94) | |||
FDA Review
Table 6. Subgroup Analysis Results on ESS - Trial 1
| Dose (mg) | Subgroup | SUNOSI LS Mean (SE) (n) |
Placebo LS Mean (SE) (n) |
LS Mean Difference (SE) SUNOSI-Placebo |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 75 | Sex | ||||
| Men | -3.1 (1.00) (22) | -3.2 (0.96) 24 | 0.1 (1.39) | ||
| Women | -4.2 (0.86) (37) | -0.7 (0.85) (34) | -3.6 (1.21) | ||
| Race | |||||
| White | -3.5 (0.69) (46) | -2.1 (0.66) (46) | -1.4 (0.95) | ||
| Other | -5.1 (1.94) (13) | 0.3 (2.03) (12) | -5.4 (2.80) | ||
| 150 | Sex | ||||
| Men | -2.9 (1.11) (16) | -3.2 (0.96) (24) | 0.3 (1.48) | ||
| Women | -6.5 (0.81) (39) | -0.7 (0.85) (34) | -5.8 (1.18) | ||
| Race | |||||
| White | -5.6 (0.68) (44) | -2.1 (0.66) (46) | -3.5 (0.95) | ||
| Other | -4.9. (1.99) (11) | 0.3 (2.03) (12) | -5.2 (2.82) | ||
FDA Review
Table 7. Subgroup Analysis Results on MWT - Trial 2
| Dose (mg) | Subgroup | SUNOSI LS Mean (SE) (n) |
Placebo LS Mean (SE) (n) |
LS Mean Difference (SE) SUNOSI-Placebo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37.5 | Sex | ||||
| Men | 3.9 (1.78) (33) | 0.5 (1.28) 70 | 3.4 (2.16) | ||
| Women | 6.3 (2.35) (19) | -0.3 (1.61) (39) | 6.5 (2.83) | ||
| Race | |||||
| White | 3.1 (1.57) (41) | -0.2 (1.16) (79) | 3.3 (1.93) | ||
| Other | 10.1 (3.22) (11) | 1.0 (1.96) (30) | 9.1 (3.75) | ||
| Age Group (years) | |||||
| < 65 | 5.0 (1.62) (39) | 0.1 (1.13) (86) | 4.9 (1.96) | ||
| > 65 | 3.3 (2.97) (13) | 0.1 (2.18) (23) | 3.2 (3.60) | ||
| 75 | Sex | ||||
| Men | 7.1 (1.84) (30) | 0.5 (1.28) (70) | 6.6 (2.21) | ||
| Women | 11.5 (2.00) (25) | -0.3 (1.61) (34) | 11.8 (2.55) | ||
| Race | |||||
| White | 8.5 (1.57) (40) | -0.2 (1.16) (79) | 8.7 (1.92) | ||
| Other | 10.2 (2.77) (15) | 1.0 (1.96) (39) | 9.1 (3.37) | ||
| Age Group (years) | |||||
| < 65 | 9.3 (1.52) (44) | 0.1 (1.13) (86) | 9.1 (1.88) | ||
| > 65 | 7.3 (3.12) (11) | 0.1 (2.18) (23) | 7.2 (3.68) | ||
| 150 | Sex | ||||
| Men | 9.8 (1.23) (69) | 0.5 (1.28) (70) | 9.3 (1.74) | ||
| Women | 13.0 (1.58) (42) | -0.3 (1.61) (39) | 13.3 (2.24) | ||
| Race | |||||
| White | 11.0 (1.07) (89) | -0.2 (1.16) (79) | 11.2 (1.54) | ||
| Other | 10.2 (2.40) (22) | 1.0 (1.96) (30) | 9.2 (3.11) | ||
| Age Group (years) | |||||
| < 65 | 11.4 (1.03) (100) | 0.1 (1.13) (86) | 11.3 (1.51) | ||
| > 65 | 7.1 (3.02) (11) | 0.1 (2.18) (23) | 7.0 (3.65) | ||
FDA Review
Table 8. Subgroup Analysis Results on ESS - Trial 2
| Dose (mg) | Subgroup | SUNOSI LS Mean (SE) (n) |
Placebo LS Mean (SE) (n) |
LS Mean Difference (SE) SUNOSI-Placebo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37.5 | Sex | ||||
| Men | -4.5 (0.80) (37) | -3.6 (0.58) (73) | -0.9 (0.97) | ||
| Women | -6.5 (1.07) (19) | -2.6 (0.72) (41) | -3.9 (1.28) | ||
| Race | |||||
| White | -4.9 (0.72) (43) | -3.1 (0.53) (82) | -1.7 (0.88) | ||
| Other | -5.8 (1.33) (13) | -3.3 (0.82) (32) | -2.4 (1.56) | ||
| Age Group (years) | |||||
| < 65 | -5.4 (0.75) (42) | -3.3 (0.52) (90) | -2.0 (0.90) | ||
| > 65 | -4.5 (1.17) (14) | -2.9 (0.87) (24) | -1.5 (1.42) | ||
| 75 | Sex | ||||
| Men | -4.5 (0.84) (33) | -3.6 (0.58) (73) | -0.8 (1.00) | ||
| Women | -5.7 (0.91) (25) | -2.6 (0.72) (41) | -3.1 (1.15) | ||
| Race | |||||
| White | -5.3 (0.72) (43) | -3.1 (0.53) (82) | -2.2 (0.88) | ||
| Other | -3.8 (1.16) (15) | -3.3 (0.82) (32) | -0.5 (1.42) | ||
| Age Group (years) | |||||
| < 65 | -4.7 (0.71) (46) | -3.3 (0.52) (90) | -1.4 (0.87) | ||
| > 65 | -5.7 (1.26) (12) | -2.9 (0.87) (24) | -2.8 (1.47) | ||
| 150 | Sex | ||||
| Men | -7.8 (0.56) (72) | -3.6 (0.58) (73) | -4.1 (0.79) | ||
| Women | -7.7 (0.70) (44) | -2.6 (0.72) (41) | -5.1 (1.00) | ||
| Race | |||||
| White | -7.4 (0.49) (93) | -3.1 (0.53) (82) | -4.2 (0.70) | ||
| Other | -8.1 (0.98) (23) | -3.3 (0.82) (32) | -4.8 (1.28) | ||
| Age Group (years) | |||||
| < 65 | -7.7 (0.48) (105) | -3.3 (0.52) (90) | -4.4 (0.69) | ||
| > 65 | -7.5 (1.23) (11) | -2.9 (0.87) (24) | -4.6 (1.48) | ||
FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
SUNOSI can cause serious side effects including increases in blood pressure and heart rate that may increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. SUNOSI may worsen symptoms of psychiatric diseases.
The most common side effects of SUNOSI are headache, nausea, decreased appetite, difficulty sleeping and anxiety.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The tables below summarize adverse reactions in patients with narcolepsy and OSA in the combined three trials (safety population).
Table 9. Adverse Reactions ≥ 2% in Patients Treated with SUNOSI and Greater than Placebo in Pooled 12 Week Placebo Controlled Clinical Trials in Narcolepsy (75 mg and 150 mg)
| Narcolepsy | ||
|---|---|---|
| System Organ Class |
Placebo N = 108 (%) |
SUNOSI N = 161 (%) |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 1 | 9 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Insomnia* | 4 | 5 |
| Anxiety* | 1 | 6 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Headache* | 7 | 16 |
| Cardiac Disorders | ||
| Palpitations | 1 | 2 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Nausea* | 4 | 7 |
| Dry mouth | 2 | 4 |
| Constipation | 1 | 3 |
Table 10. Adverse Reactions ≥ 2% in Patients Treated with SUNOSI and Greater than Placebo in Pooled 12 Week Placebo Controlled Clinical Trials in OSA (37.5 mg, 75 mg, and 150 mg)
| OSA | ||
|---|---|---|
| System Organ Class | Placebo N = 118 (%) |
SUNOSI N = 235 (%) |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 1 | 6 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Anxiety* | 1 | 4 |
| Irritability | 0 | 3 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Dizziness | 1 | 2 |
| Cardiac Disorders | ||
| Palpitations | 0 | 3 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Nausea* | 6 | 8 |
| Diarrhea | 1 | 4 |
| Abdominal pain* | 2 | 3 |
| Dry mouth | 2 | 3 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||
| Feeling jittery | 0 | 3 |
| Chest discomfort | 0 | 2 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||
| Hyperhidrosis | 0 | 2 |
*“Anxiety” includes anxiety, nervousness, and panic attack; “Nausea” includes nausea and vomiting; “Abdominal pain” includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, and abdominal discomfort.
SUNOSI Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar between men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The occurrence of side effects was similar among White and Black or African American patients. The number of patients in other races was limited; therefore, differences in the occurrence of side effects among other races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar between patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes the occurrence of the most common adverse reaction, headache, by subgroup.
Table 11. Subgroup Analysis of Headache (safety population)
| Demographic Characteristics | SUNOSI n/N (%) |
Placebo n/N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Men | 12/197 (6.1) | 7/119 (5.9) |
| Women | 33/199 (16.6) | 13/107 (12.1) |
| Race, n (%) | ||
| White | 32/307 (10.4) | 17/173 (9.8) |
| Black or African American | 9/69 (13.0) | 3/45 (6.7) |
| Asian | 2/11 (18.1) | 0/4 (0) |
| Age Group, n (%) | ||
| < 65 years | 42/351 (12.0) | 19/197 (9.6) |
| > 65 years | 3/45 (6.7) | 1/29 (3.4) |
Clinical Trial Data
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved SUNOSI based primarily on evidence from five clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT02348593, Trial 2/NCT02348606, Trial 3/NCT02348619, Trial 4/NCT02348632, Trial 5 NCT01681121) of 622 patients with narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). The trials were conducted in Canada, Europe, and the United States.
The population that provided data for side effects of SUNOSI (safety population) is presented below.
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were in the clinical trials.
Figure 1. Demographics by Sex
FDA Review
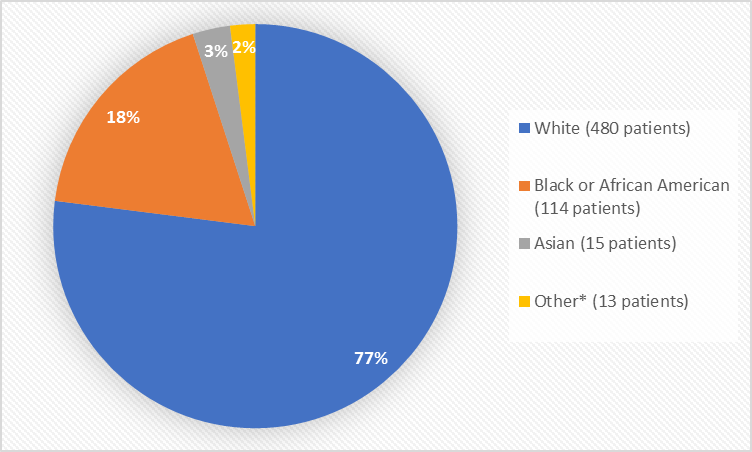
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trials.
Figure 2. Demographics by Race
*Other includes American Indian or Alaska Native and Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander
FDA Review
Table 1. Demographics of Trials by Race
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage of Patients |
|---|---|---|
| White | 480 | 77% |
| Black or African American | 114 | 18% |
| Asian | 15 | 3% |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 2 | less than 1% |
| Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander | 3 | less than 1% |
| Other | 8 | 1% |
FDA Review
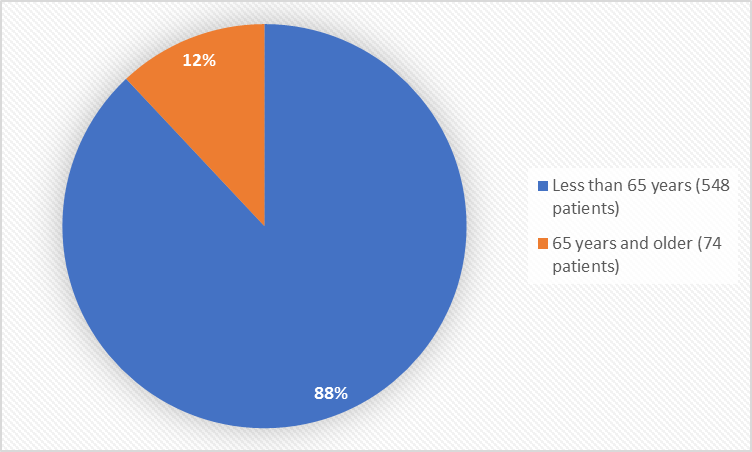
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age in the clinical trials.
Figure 3. Demographics by Age
FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes the demographics of the patients in the clinical trials. The safety population from Trials 1, 2 and 5 is presented.
Table 12. Demographics of Patients in the Clinical Trials (Safety Population)
| Demographic Characteristics | SUNOSI N=396 |
Placebo N=226 |
Total N=622 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Men | 197 (49.7) | 119 (52.7) | 316 (50.8) |
| Women | 199 (50.3) | 107 (47.4) | 306 (49.2) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 307 (77.5) | 173 (76.6) | 480 (77.2) |
| Black or African American | 69 (17.4) | 45 (19.9) | 114 (18.3) |
| Asian | 11 (2.8) | 4 (1.8) | 15 (2.4) |
| American Indian or Alaskan Native | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.4) | 2 (0.3) |
| Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander | 2 (0.5) | 1 (0.4) | 3 (0.4) |
| Other | 6 (1.5) | 2 (0.9) | 8 (1.3) |
| Age Group (years), n (%) | |||
| < 65 years | 351 (88.6) | 197 (87.2) | 548 (88.1) |
| > 65 years | 45 (11.4) | 29 (12.8) | 74 (11.9) |
| Age (years) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 49.7 (12.9) | 45.6 (15.4) | 47.6 (14.1) |
| Median | 51.0 | 48.0 | 49.0 |
| Range | 18, 75 | 18, 74 | 18, 75 |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic | 33 (8.3) | 17 (7.5) | 50 (8.0) |
| Not Hispanic | 363 (91.7) | 209 (92.5) | 572 (92.0) |
| Region, n (%) | |||
| USA | 351 (88.6) | 206 (91.2) | 557 (89.5) |
| Europe | 31 (7.8) | 11 (4.8) | 42 (6.8) |
| Canada | 14 (3.5) | 9 (4.0) | 23 (3.7) |
Clinical Trial Data
How were the trials designed?
The benefits and side effects of SUNOSI were evaluated in five clinical trials. All trials enrolled adults 18 to 75 years old with narcolepsy or OSA who had excessive daytime sleepiness or trouble maintaining wakefulness.
Trial 1 enrolled patients with narcolepsy. Patients were randomized to receive one of two doses of SUNOSI or placebo by mouth once daily for 12 weeks. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed. The benefit of SUNOSI was assessed by determining the difference in Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) and Maintenance of Wakefulness Test (MWT) before and during treatment. The ESS is an 8-item questionnaire where patients rate their perceived likelihood of falling asleep during usual daily life activities. The MWT measures the number of minutes an individual can remain awake during the daytime in a darkened, quiet environment.
Trial 2 enrolled patients with OSA. Patients were randomized to receive one of three doses of SUNOSI or placebo by mouth once daily for 12 weeks. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed. The benefit of SUNOSI was assessed by determining the difference in ESS scores and MWT times before and during treatment.
Trial 3 was a 6-week trial that enrolled patients with OSA. Patients were randomized to receive SUNOSI or placebo. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed. The data were used to assess continuation of SUNOSI benefit.
Trial 4 was a 52-week trial that included patients with either OSA or narcolepsy who completed prior trials. All patients received SUNOSI for up to 50 weeks. After 6 months of treatment, some patients were randomized to continue SUNOSI or switch to placebo. The data were used to assess continuation of SUNOSI benefit.
Trial 5 was a 12-week trial that enrolled patients with narcolepsy. Patients were randomized to receive SUNOSI or placebo for 12 weeks. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed. The data were primarily used to assess side effects in addition to data on side effects from Trial 1 and Trial 2.
How were the trials designed?
Five trials were used to assess SUNOSI in adults 18 to 75 years with narcolepsy or OSA and excessive daytime sleepiness. Primary efficacy was evaluated in 2 trials (Trial 1 and Trial 2). Maintenance of effect was assessed in 2 trials (Trial 3 and Trial 4), and safety was primarily assessed in three trials (Trial 1, Trial 2, and Trial 5).
Trial 1 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that enrolled patients with narcolepsy who met the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders criteria (DSM-V) for narcolepsy. Patients had excessive daytime sleepiness based on the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) with a score > 10 and trouble maintaining wakefulness (mean sleep latency < 10 minutes). Patients in Trial 1 were randomized to receive SUNOSI 75 mg, 150 mg, or placebo by mouth once daily for 12 weeks. The co-primary endpoints were change from baseline in the Maintenance of Wakefulness Test (MWT) and ESS score at Week 12.
Trial 2 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that enrolled patients with OSA who met the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3), had excessive daytime sleepiness (ESS Score > 10) and trouble maintaining wakefulness (mean sleep latency < 25 minutes). Patients were randomized to receive SUNOSI 37.5 mg, 75 mg, 150 mg, or placebo by mouth. The co-primary endpoints were change from baseline in MWT and ESS score at Week 12.
Trial 3 was a 6-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized-withdrawal trial that enrolled patients with OSA. During an initial 2-week open label titration phase, patients were titrated to the maximum tolerable SUNOSI dose between 75 mg and 300 mg. Patients continued this dose for 2 weeks. After 2 weeks of stable-dose treatment, patients were randomized to continue SUNOSI or switch to placebo. The endpoints were change from the beginning to the end of the randomized withdrawal period in MWT and ESS.
Trial 4 was a 52-week, open-label clinical trial with a 2-week withdrawal period. The trial enrolled patients with OSA or narcolepsy who had completed a prior trial that assessed SUNOSI. During an initial 2-week open label titration phase, patients were titrated to the maximum tolerable SUNOSI dose between 75 mg and 300 mg. Patients continued this dose for up to 50 weeks. After 6 months of stable-dose treatment, some patients were randomized to continue SUNOSI or switch to placebo. The endpoint was change from the beginning to the end of the randomized withdrawal period in ESS.
Trial 5 was a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that enrolled patients with narcolepsy who met the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders criteria (DSM-V) for narcolepsy. Patients had excessive daytime sleepiness based on the ESS with a score > 10 and trouble maintaining wakefulness (mean sleep latency < 10 minutes). Patients in Trial 5 were randomized to receive SUNOSI 150 mg or placebo by mouth for 12 weeks. This trial was used to primarily assess side effects.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION