Drug Trials Snapshots: SCEMBLIX
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the key clinical trials that supported the original FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, age, and ethnic groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Some of the information in this Snapshot is for presentation purposes and does not represent the approved conditions of use of this drug. Refer to the SCEMBLIX Prescribing Information for all of the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable).
SCEMBLIX (asciminib)
(sem blix)
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.
Approval date: October 29, 2021
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
SCEMBLIX is a prescription drug used to treat adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase (CP) with a specific gene mutation (T315I).
CML is a form of cancer that forms in the bone marrow because of the presence of an abnormal gene and results in an increased number of white blood cells in the bone marrow and in the bloodstream.
How is this drug used?
SCEMBLIX is a tablet that is taken by mouth on an empty stomach. SCEMBLIX is taken twice a day as determined by your health care provider.
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved SCEMBLIX based on evidence from a clinical trial of 48 patients with CML with a certain type of mutation (T315I mutation). The trial was conducted at 18 sites in 10 countries (Australia, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, the Republic of Korea, Singapore, Spain, and the United States).
What are the benefits of this drug?
In the trial, approximately half of the patients who received SCEMBLIX had a reduction of abnormal cells in their blood to a very low level within 96 weeks after starting treatment.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The main efficacy outcome measures were major molecular response (MMR) at 24 and 96 weeks.
Table 1. Efficacy Results in Ph+ CML-CP Patients with the T315I Mutation (Study X2101)
| SCEMBLIX 200 mg twice daily N = 45 |
|
|---|---|
| MMR rate, % (95% CI) by 24 weeks |
42 (28, 58) |
| MMR rate, % (95% CI) by 96 weeks |
49 (34, 64) |
Abbreviations: MMR, major molecular response (BCR-ABL1IS≤ 0.1%); CI, confidence interval
SCEMBLIX Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: There were not enough females to determine whether there were differences in how SCEMBLIX worked in males and females.
- Race: Differences in how well SCEMBLIX worked among races could not be determined because of the small number of patients of races other than White.
- Age: Most patients were between 18-65 years of age. There were not enough patients 65 years or older to determine whether there was a difference in how SCEMBLIX worked in patients below and above 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below summarize the efficacy results by sex and age subgroups. Subgroup analysis for efficacy by race was not performed as only one Black or African American patient was included.
Table 2. Efficacy Results by Sex in Ph+ CML-CP Patients with the T315I mutation
| SCEMBLIX 200 mg twice daily |
||
|---|---|---|
| Men N = 36 | Women N = 9 | |
| MMR rate, % (95% CI) by 24 weeks |
44 (28, 62) | 33 (7.5, 70) |
| MMR rate, % (95% CI) by 96 weeks |
53 (36, 70) | 33 (7.5, 70) |
Abbreviations: MMR, major molecular response (BCR-ABL1IS≤ 0.1%); CI, confidence interval
Table 3. Efficacy Results by Age in Ph+ CML-CP Patients with the T315I mutation
| SCEMBLIX 200 mg twice daily |
||
|---|---|---|
| Less than 65 years N = 31 | 65 years and older N = 14 | |
| MMR rate, % (95% CI) by 24 weeks |
29 (14, 48) | 71 (42, 92) |
| MMR rate, % (95% CI) by 96 weeks |
39 (22, 58) | 71 (42, 92) |
Abbreviations: MMR, major molecular response (BCR-ABL1IS≤ 0.1%); CI, confidence interval
What are the possible side effects?
SCEMBLIX may cause serious side effects including low blood cell counts, pancreas problems, high blood pressure, allergic reactions, heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) problems, and harm to the unborn baby.
The most common side effects of SCEMBLIX include nose, throat, or sinus (upper respiratory tract) infections; muscle, bone, or joint pain; tiredness, nausea, rash, and diarrhea. The most common laboratory abnormalities of SCEMBLIX include low blood platelet, white blood cell and red blood cell counts; increased blood fat (triglycerides) levels; increased creatine kinase levels; increased liver enzyme levels; and increased pancreas enzyme (amylase and lipase) levels.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The tables below summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in the clinical trial.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions (≥10%) in Patients with Ph+ CML-CP with the T315I Mutation who Received SCEMBLIX in Study X2101
| SCEMBLIX 200 mg twice daily N = 48 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | All Grades % |
Grade 3 or 4 % |
|
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | |||
| Musculoskeletal paina | 42 | 4.2 | |
| Arthralgia | 17 | 0 | |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | |||
| Fatigueb | 31 | 2.1 | |
| Edema | 10 | 4.2 | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | |||
| Nausea | 27 | 0 | |
| Diarrhea | 21 | 2.1 | |
| Vomiting | 19 | 6 | |
| Abdominal painc | 17 | 8 | |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | |||
| Rashd | 27 | 0 | |
| Pruritus | 13 | 0 | |
| Nervous system disorders | |||
| Headachee | 19 | 2.1 | |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | |||
| Coughf | 15 | 0 | |
| Vascular disorders | |||
| Hemorrhageg | 15 | 2.1 | |
| Hypertensionh | 13 | 8 | |
| Infections and infestations | |||
| Upper respiratory tract infectioni | 13 | 0 | |
aMusculoskeletal pain includes: pain in extremity, back pain, myalgia, musculoskeletal pain, non-cardiac chest pain, bone pain, arthritis, and musculoskeletal chest pain.
bFatigue includes: fatigue and asthenia.
cAbdominal pain includes: abdominal pain and hepatic pain.
dRash includes: rash, rash maculopapular, dermatitis acneiform, eczema, rash papular, skin exfoliation, and dyshidrotic eczema.
eHeadache includes: headache and migraine.
fCough includes: cough and productive cough.
gHemorrhage includes: epistaxis, ear hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, post procedural hemorrhage, skin hemorrhage, and vaginal hemorrhage.
hHypertension includes: hypertension and hypertensive crisis.
iUpper respiratory tract infection includes: upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, rhinitis, and pharyngitis.
SCEMBLIX Prescribing Information
Table 5. Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 10%) in Patients with Ph+ CML-CP with the T315I Mutation in Study X2101
| SCEMBLIX1 200 mg twice daily |
||
|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Abnormality | All Grades % |
Grade 3-4 % |
| Hematologic parameters | ||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 44 | 4.2 |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 44 | 15 |
| Lymphocyte count decreased | 42 | 4.2 |
| Platelet count decreased | 25 | 15 |
| Biochemical parameters | ||
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) increased | 48 | 6 |
| Potassium increased | 48 | 2.1 |
| Triglycerides increased | 46 | 2.1 |
| Lipase increased | 46 | 21 |
| Phosphate decreased | 40 | 6 |
| Uric acid increased | 40 | 4.2 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased | 35 | 2.1 |
| Calcium corrected decreased | 33 | 0 |
| Creatinine increased | 31 | 0 |
| Amylase increased | 29 | 10 |
| Bilirubin increased | 23 | 0 |
| Cholesterol increased | 15 | 0 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) increased | 13 | 0 |
1The denominator used to calculate the rate was 48 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and a least one post-treatment value. CTCAE version 4.03.
SCEMBLIX Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: There were not enough women to determine whether there were differences in the occurrence of side effects between men and women.
- Race: As only one patient was not White, differences in the occurrence of side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: There were not enough patients 65 years or older to determine whether there was a difference in the occurrence of side effects between older and younger patients.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Tables 6 and 7 summarize adverse events that occurred in sex and age subgroups. Subgroup analysis for safety by race was not performed as only one Black or African American patient was included.
Table 6. Subgroup Analyses of Adverse Events by Sex in Ph+ CML-CP Patients with the T315I Mutation (Study X2101)
| SCEMBLIX 200 mg twice daily |
||
|---|---|---|
| Men N = 37 | Women N = 11 | |
| Any AE, % | 100 | 100 |
| Any AE with Grade ≥ 3, % | 60 | 64 |
| Any SAE, % | 30 | 0 |
Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; SAE, serious adverse event
Table 7. Subgroup Analyses of Adverse Events by Age in Ph+ CML-CP Patients with the T315I Mutation (Study X2101)
| SCEMBLIX 200 mg twice daily |
||
|---|---|---|
| Less than 65 years N = 32 | 65 years and older N = 16 | |
| Any AE, % | 100 | 100 |
| Any AE with Grade ≥ 3, % | 53 | 75 |
| Any SAE, % | 16 | 38 |
Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; SAE, serious adverse event
DEMOGRAPHICS SNAPSHOT
Who participated in the trials?
The FDA approved SCEMBLIX based on evidence from a clinical trial of 48 patients with CML with a certain type of mutation (T315I mutation). The trial was conducted at 18 sites in 10 countries (Australia, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, the Republic of Korea, Singapore, Spain, and the United States).
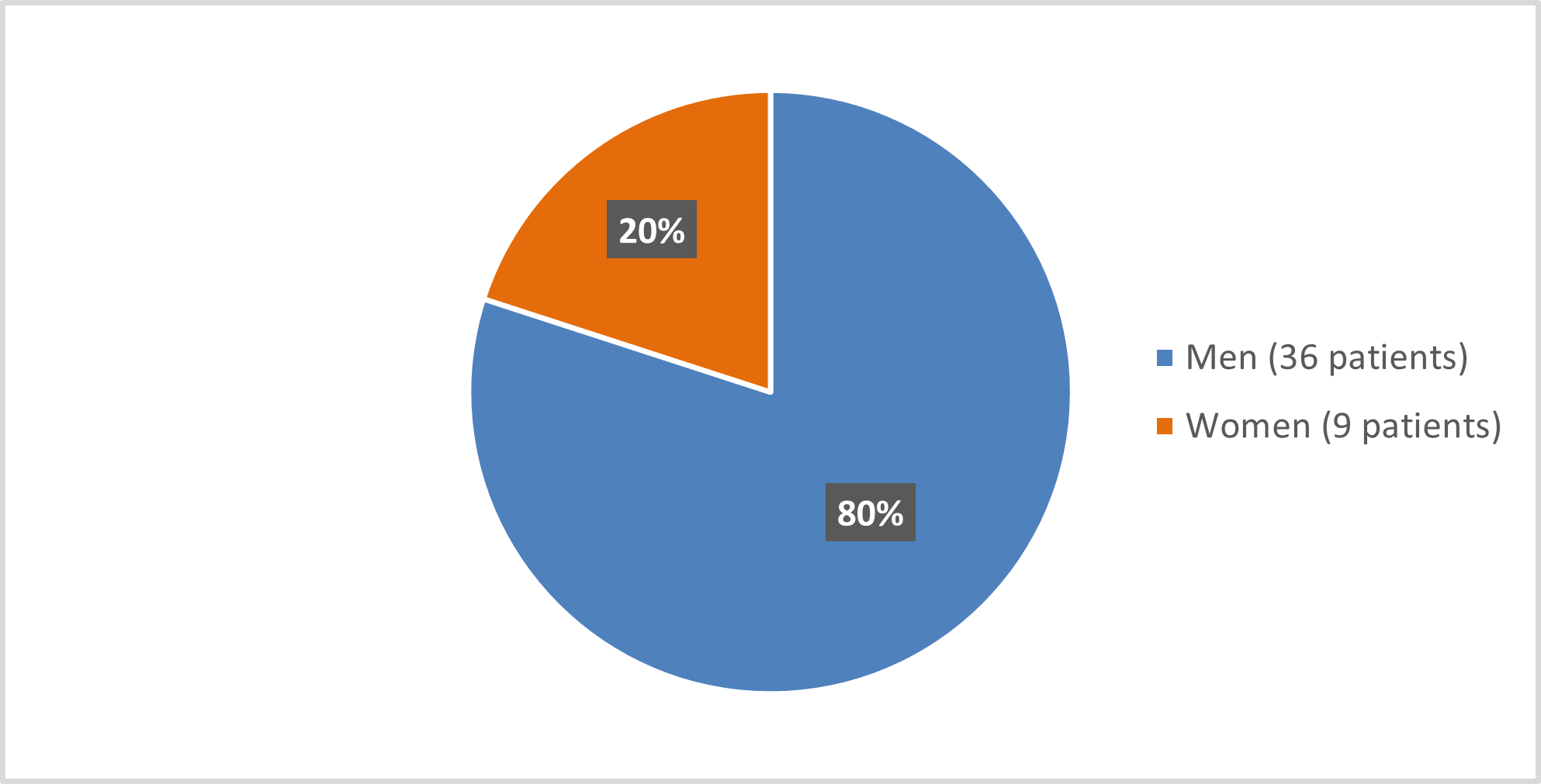
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the efficacy of SCEMBLIX.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex (efficacy population*)
*The Safety Population included one more male patient and two more female patients
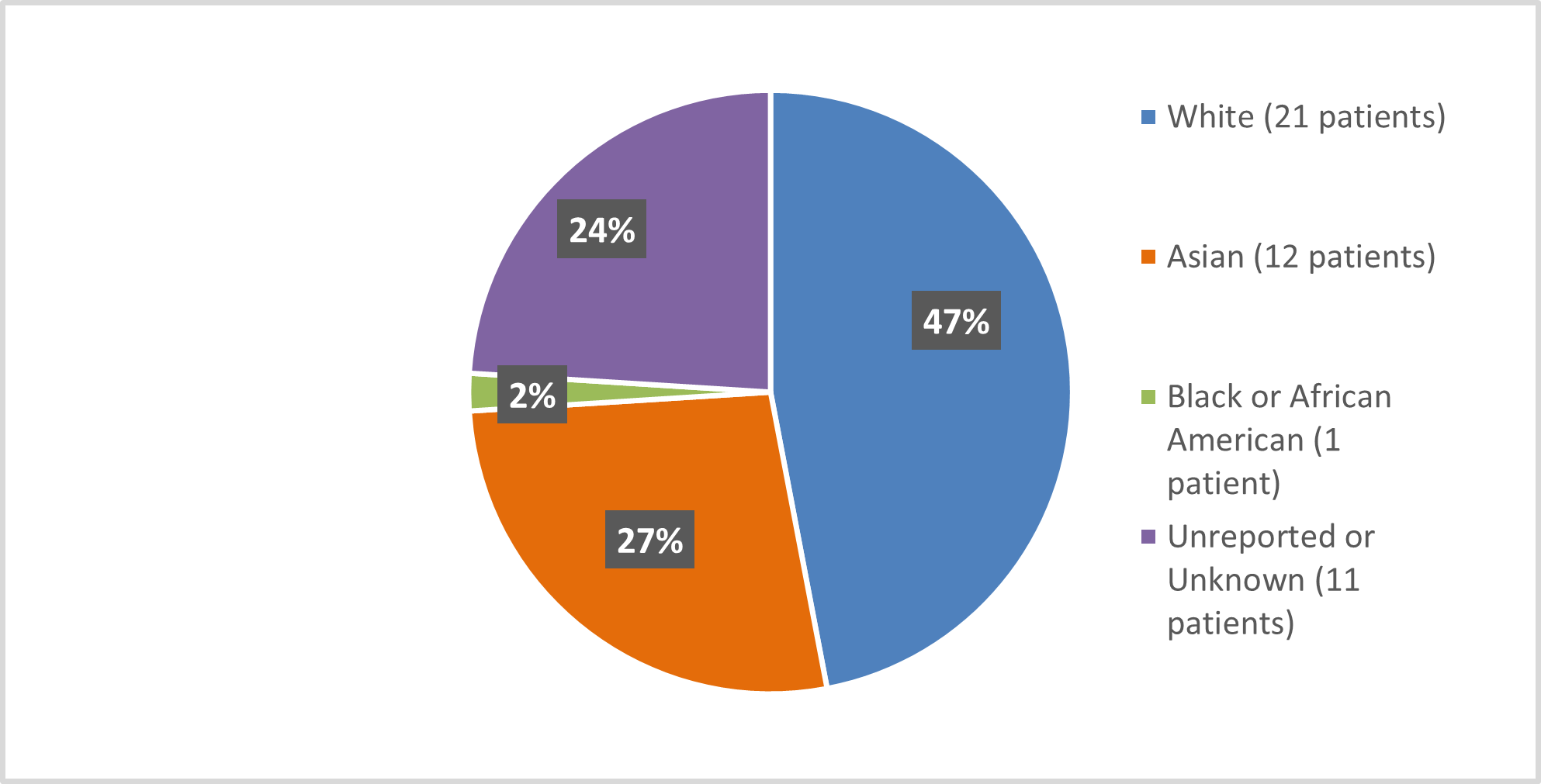
Figure 2 and Table 8 summarize the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trial used to evaluate the efficacy of SCEMBLIX.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race (efficacy population*)
*The Safety Population included two more white and one more patient with unknown or unreported race
Table 8. Baseline Demographics by Race (efficacy population*)
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage of Patients |
|---|---|---|
| White | 21 | 47% |
| Asian | 12 | 27% |
| Black or African American | 1 | 2% |
| Unreported/Unknown | 11 | 24% |
*The Safety Population included two more white and one more patient with unknown or unreported race
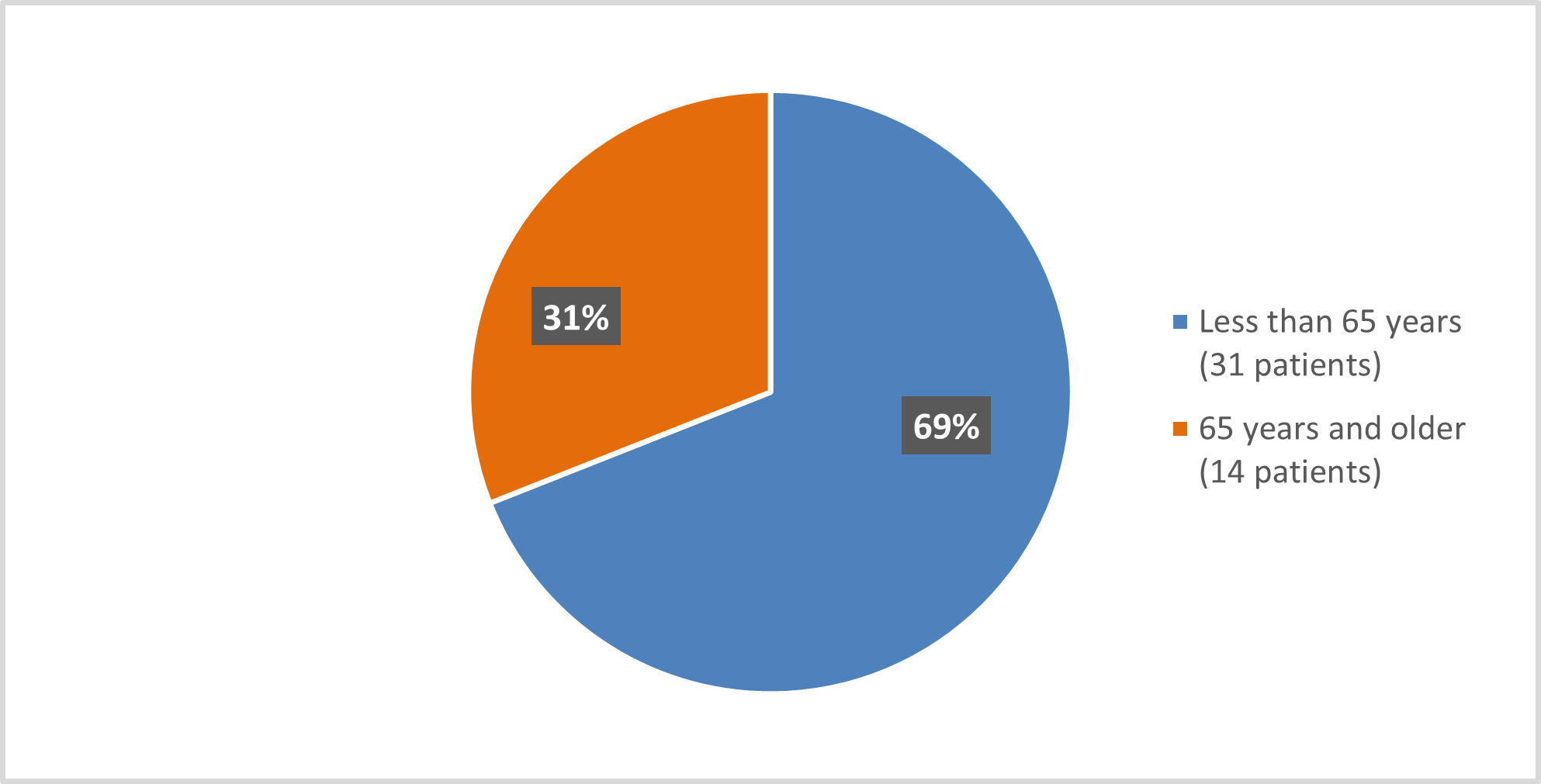
Figure 3 below summarizes how many patients of certain age were enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age (efficacy population*)
*The Safety Population included one more < 65 years old and two more ≥ 65 years old patients
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes demographics of all patients with CML-CP with T315I mutation enrolled in the clinical trial who received SCEMBLIX.
Table 9. Baseline Demographics (safety population)
| SCEMBLIX 200 mg BID |
|
|---|---|
| Demographic Parameter | N=48 |
| Age (years) | |
| Mean | 55 |
| Median | 56.5 |
| Minimum | 26 |
| Maximum | 86 |
| Age category (years) -n (%) | |
| 18 - <65 years | 32 (67) |
| ≥ 65 years | 16 (33) |
| Sex - n (%) | |
| Male | 37 (77) |
| Female | 11 (23) |
| Race - n (%) | |
| Black or African American | 1 (2.1) |
| White | 23 (48) |
| Asian | 12 (25) |
| Unknown/Unreported | 12 (25) |
| Ethnicity -n (%) | |
| Hispanic or Latino | 3 (6) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 28 (58) |
| Not Reported | 14 (29) |
| Unknown | 3 (6) |
How were the trials designed?
SCEMBLIX was evaluated in one clinical trial that included 48 patients with Ph+ CML with the T315I mutation.
Patients received SCEMBLIX twice daily until disease worsened or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
The benefit of SCEMBLIX was evaluated in Ph+ CML patients with the T315 mutation by measuring the reduction of abnormal cells in patients’ blood to a very low level after 96 weeks of treatment.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of SCEMBLIX in the treatment of patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase (Ph+ CML-CP) with the T315I mutation was evaluated in the multi-center open-label study CABL001X2101 (NCT 02081378).
In this study, 48 patients with CML-CP with T315I mutation were given SCEMBLIX 200 mg twice daily.
The efficacy was established based on major molecular response (MMR) by 24 or 96 weeks of treatment.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP:A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.