Drug Trials Snapshot: Jublia (efinaconazole)
Disclaimer: The Drug Trials Snapshot provides information about who was in the clinical trials that led to the FDA approval of this drug. This website shows who participated in these studies by sex, race, and age groups. You can get more information about this drug from JUBLIA Drug Label and your doctor or health care professional.
JUBLIA (efinaconazole)
(joo-blee-uh)
Dow Pharmaceutical Sciences
NDA 203567
Approval date: June 6, 2014
DRUG TRIALS SUMMARY
What is the drug for?
JUBLIA treats fungal infection of the toenails (onychomycosis) due to two common forms of fungi (Trichophyton rubrum or Trichopyton mentagrophytes.)
How do I use this drug?
JUBLIA is painted on the affected toenail much like a nail polish. It should be applied to the entire toenail surface and under the tip of each nail being treated once a day for 48 weeks.
What are the benefits of this drug?
Clinical study results showed that JUBLIA was better than the placebo at clearing the nail of the infection.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
Subgroup analyses were conducted for sex, race and age.
- Sex: A trend towards greater efficacy was observed in women than men taking JUBLIA.
- Race: A trend towards greater efficacy was observed in Asians than in Whites or Black/African Americans taking JUBLIA.
- Age: JUBLIA is similarly effective among those above and below 65 years of age.
What are the possible side effects?
The most common side effects that occurred during the clinical trials included ingrown toenail, itchy skin, inflammation, rash, and pain.
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
Subgroup analyses were not conducted for sex and race but were evaluated for age.
- Sex: The difference in side effects by sex was not evaluated.
- Race: The difference in side effects by race was not evaluated.
- Age: No differences in side effects were observed between those above and below 65 years of age.
WHO WAS IN THE STUDY?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved JUBLIA based on evidence from two studies of 1,651 patients with toenail fungus infections. The studies were conducted in the United States, Canada, and Japan.
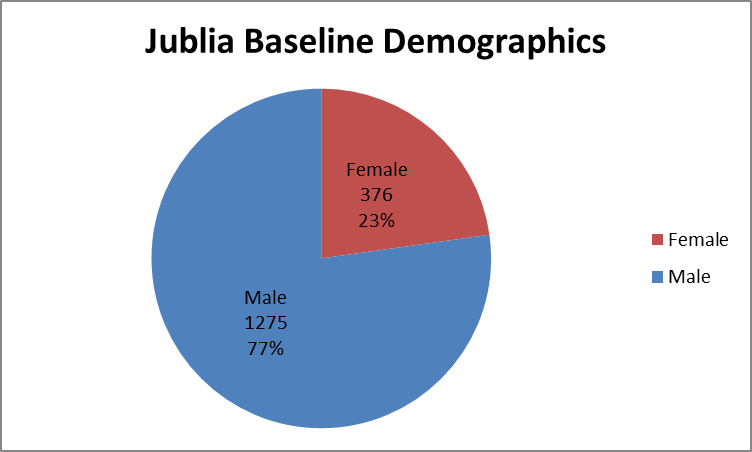
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Source: Adapted from FDA Medical Review, Table 7
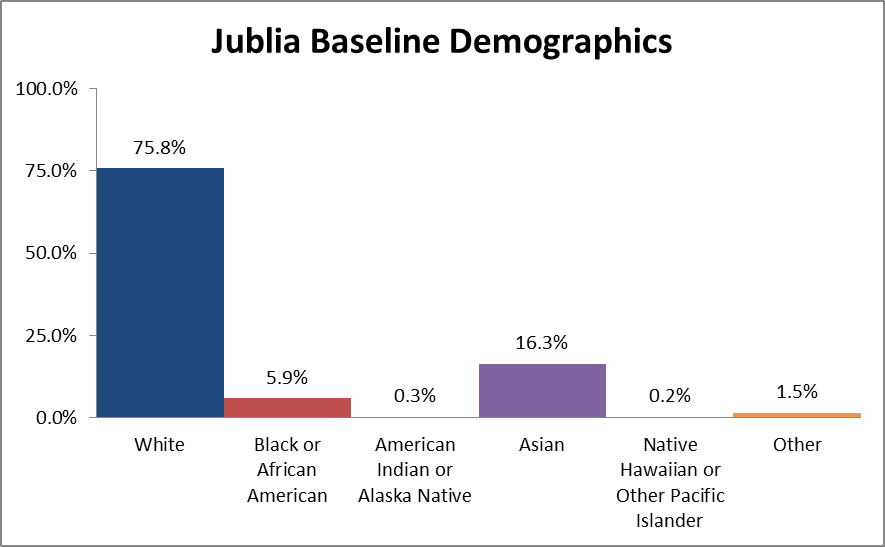
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
Source: Adapted from FDA Medical Review, Table 7
Table 1. Baseline Demographics by Race for the Intent to Treat (ITT) Population
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 1251 | 75.8% |
| Black or African American | 98 | 5.9% |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 5 | 0.3% |
| Asian | 269 | 16.3% |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 3 | 0.2% |
| Other | 25 | 1.5% |
How was the study designed?
JUBLIA was approved by the FDA based on two clinical studies of 1655 patients with toenail fungal infections. Chosen at random, 1236 patients painted JUBLIA on their toenails while 415 used a placebo once daily for 48 weeks. Neither the patients nor the health care professionals administering the drug knew which patients were using JUBLIA and which ones were using the placebo until after the drug trial was complete. All patients were evaluated 52 weeks after beginning the study.
What are the results of the efficacy study?
JUBLIA worked better than the placebo at clearing the nail of infection.
What are the results of the safety study?
Most common side effects (ingrown toenail, itchy skin, inflammation, rash, and pain) occurred in 1-2% of patients using JUBLIA compared to 1% of patients using a control.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
MEDICAL REVIEW (PDF - 6.18MB)
DRUG LABEL (PDF - 330KB)