Aquacultured Seafood

Aquaculture is the farming of aquatic organisms, such as fish, shellfish (bivalves and crustaceans), amphibians, reptiles, turtles and aquatic plants. Aquaculture is described as farming because of interventions with breeding and the growing process, improving aquatic animal health and production. Aquaculture farms can be built in freshwater, coastal and marine environments. There are several types of farming systems, including:
- water-based systems (cages and pens offshore, in coastal areas or in freshwater lakes, rivers).
- land-based systems (ponds, irrigated or flow-through or single-pass systems, tanks and raceways).
- recirculation (or closed) systems (high control enclosed systems, more open pond-based recirculation).
- integrated multi-trophic farming systems (e.g. agriculture and fish dual use aquaculture and irrigation ponds).
About 580 aquatic species are currently farmed all over the world. Aquaculture production contributes to the overall global seafood supply. Globally, aquaculture supplies more than 50 percent of all seafood produced for human consumption—and that percentage will continue to rise. Aquacultured and wild-caught seafood is an excellent source of low-fat proteins, omega-3 fatty acids, and key vitamins and minerals and should be a part of a healthy, well-balanced diet. The U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans encourage Americans to eat more seafood and include seafood as one of the core elements of a healthy dietary pattern to maintain good health. The FDA recommends that women who might become or are pregnant or lactating and young children, eat 2 to 3 servings a week of seafood that are lower in mercury (Advice about Eating Fish).
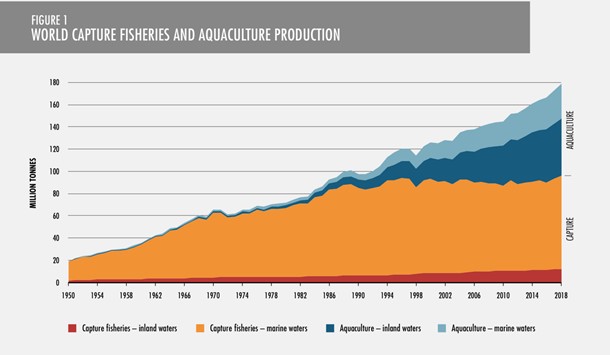
Aquaculture production helps sustain wild-captured fisheries, making seafood more accessible and affordable for consumers. It also helps restore threatened and endangered species populations and sustain wild stock populations, and habitat restoration. The graph below shows the rapid growth in aquaculture production compared to wild-caught fisheries (Food and Agriculture Organization, State of the World Fisheries, 2020)
Domestic and imported aquacultured fish and shellfish are held to the same FDA food safety standards and regulatory requirements as wild-caught seafood to help ensure that only safe and wholesome products are offered to consumers. The agency uses every available tool to identify immediate or potential threats as well as the best course of action to protect public health.
Animal Drug Residues in Aquacultured Seafood:
A primary food safety hazard of concern in aquaculture products are animal drug residues which are used to treat or mitigate disease on an aquaculture farm. The use of animal drugs in aquaculture is strictly regulated in the United States. Only medicinal products approved by the FDA may be administered to aquatic animals, and withdrawal periods and testing are enforced to ensure that when fish is sold to consumers no drug residues are present for animal drugs not approved in the United States and no drug residues for approved drugs exceed the FDA established tolerance. The list of animal drugs approved for aquatic animals by the FDA is available at the Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM) website, Approved Aquaculture Drugs. The agency does not publish a list of unapproved drugs. In the United States any animal drug not approved by the FDA is considered an unapproved animal drug. The FDA has a routine surveillance testing program for animal drugs, referred to as chemotherapeutic agents, in domestic and imported aquaculture seafood. The program is an integral part of the comprehensive, prevention-oriented food safety system for all fish and fishery products. It is a verification tool which provides information on the degree of good practices and controls application and their effectiveness within the entire production system. The program incorporates a risk-based approach to identify types of commodities, specific drugs to test and countries of interest.
If a seafood product tests positive for the presence of residues of animal drugs that are not approved in the United States or residues of approved drugs that exceed the FDA established tolerance level, the agency may take regulatory action against the firm and the product. If the contaminated product was offered for import into the United States, it is refused entry and future entries may be subject to detention without physical examination (import alert). For additional information on preventive measures and controls of food safety hazards in aquaculture products refer to FDA’s Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Control Guide.
All processors of fish and fishery products, aquacultured or wild-caught, are subject to the FDA’s regulations that describe the procedures for the safe and sanitary processing and importing of fish and fishery products. 21 CFR Part 123 (Fish and Fishery Products), commonly known as the Seafood HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) Regulation, requires both domestic and foreign processors of fish and fishery products to understand the food safety hazards associated with their process and products and, through a system of preventive measures, to implement appropriate controls to keep those hazards from occurring.
Aquaculture production of bivalve shellfish (oysters, clams, mussels and whole or roe-on scallops) is unique in that it is regulated through a Federal-state cooperative program called the National Shellfish Sanitation Program (NSSP) which is recognized by the FDA through the Interstate Shellfish Sanitation Conference (ISSC). The ISSC is a cooperative body that establishes food safety measures that can be adopted and enforced by the individual states. Participants include Federal agencies (the FDA, the Environmental Protection Agency and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration), state agencies (public health, environmental and public safety) from shellfish producing and non-producing states, academia and representatives of the shellfish industry.
The FDA has a variety of tools to ensure compliance with seafood safety requirements, including inspections of domestic and foreign processing facilities, examination and sampling of domestic seafood and seafood offered for import into the United States, domestic surveillance sampling of imported products, inspections of seafood importers, evaluations of filers of seafood products offered for import, and foreign country program assessments. See Imported Seafood Safety Program for additional information on how the FDA ensures the safety of imported seafood products.
Aquaculture in the United States is a diverse industry that includes the production of a variety of fish, crustaceans, bivalves, and plants. The primary aquaculture species in the United States are catfish, trout, tilapia and crawfish, as well as bivalve shellfish. Aquaculture production is distributed throughout the United States but the major productions in terms of value and volume come from the southern and coastal regions of the country.
The FDA regulates fish and fishery products that enter interstate commerce. These products must meet the requirements of the Seafood HACCP regulation or the NSSP (for bivalve shellfish). Under the NSSP, all aquacultured shellfish entering interstate commerce must be grown in and harvested from approved shellfish growing areas, handled by state-certified dealers, be tagged and tracked and processed in plants that meet NSSP sanitation requirements.
Approximately 90 percent of the seafood eaten in the United States comes from abroad, with more than half of it from aquaculture. The most frequently eaten aquacultured products, shrimp, salmon, and tilapia, alone make up 50 percent of the total seafood eaten in the United States.
The FDA has a robust import program to ensure the safety of seafood offered for import into the United States. All imported seafood shipments are screened before entering the U.S. The FDA utilizes electronic import systems to review and validate entry data and information and to determine the admissibility of the product. The import review process helps prevent the entry of adulterated, misbranded, or otherwise violative products and allows seafood processors to expedite the entry of non-violative products. The systems use various sources of information to assess risk, detect trends, investigate patterns and identify products and countries for physical inspection and examination at the border.
The FDA prioritizes these import-related activities based on the products with the greatest potential for contamination and impact on public health. High-risk products, and foreign processors or importers of high-risk products, are of greater importance and are assigned higher priority for surveillance activities.
Another key tool for ensuring the safety of imported seafood are import alerts which inform the FDA field personnel that the Agency has sufficient evidence or other information about a particular product, producer, shipper, or importer to believe that future shipments of an imported product may be violative. Based on that evidence, the FDA may detain articles that are being offered for import into the U.S. without physically examining the product. Further, the FDA works closely with our foreign, federal, state, local, and tribal partners to share relevant information to ensure that products in U.S. commerce meet the applicable FDA requirements.
In the FY21 Appropriations Bill H.R. 133, Section 787 Congress directed FDA to develop and implement options for regulating the export of shrimp to the United States from other countries. The Bill directed FDA to consider a number of options including increasing inspections and sample collection and testing.
In addition, the FDA was directed to explore and implement formal seafood arrangements with foreign competent authorities with a priority to assure appropriate controls are applied throughout the entire supply chain and dedicate inspectional effort to determine compliance with arrangements. FDA developed and implemented a process to establish Regulatory Partnership Arrangements with foreign governments to enhance the safety of shrimp exports to the United States.
The Regulatory Partnership will allow the FDA and our foreign counterparts to work closer together, share non-public information, and enforce food safety practices along the entire supply chain. Prior to signing a Regulatory Partnership Arrangement, the FDA will conduct a rigorous assessment of the countries aquaculture food safety system, examine key elements and ongoing processes to ensure there are preventive controls, and competent oversight throughout the aquacultured shrimp supply chain.
The FDA conducts foreign country assessments to provide the agency with a broad view of a foreign country’s regulatory infrastructure and industry capacity to meet FDA’s HACCP requirements and other relevant regulations to control risks and reduce potential hazards, e.g., animal drug residues, of aquaculture products imported into the United States. Assessments support the FDA’s enforcement activities and help the agency determine the effectiveness of established operational criteria. These activities are also instrumental in building relationships with the foreign country’s regulatory partners.
Aquacultured shellfish may be imported into the United States through an international agreement between the FDA and the regulatory authority of the country in which the shellfish are produced. The FDA periodically assesses the country’s shellfish safety program in accordance with the agreement. The FDA has international food safety programs including trade agreements with foreign governments and the global public health community to enhance internationally the understanding of food safety.
Aquaculture is vulnerable to the impact of constantly changing environmental conditions and stress factors that make fish more susceptible to diseases. Diseases pose one of the most significant constraints to aquaculture development. Good aquaculture management practices that improve safety and optimize production parameters are necessary to prevent and minimize the impact of diseases on aquaculture seafood.
International Farming Resources and Training:
The FDA, in conjunction with the Joint Institute for Food Safety and Nutrition (JIFSAN), developed Good Aquaculture Practices (GAqP); a scientifically based food safety prevention training program that integrates disease prevention and food safety. The GAqP training program is designed for aquaculture farm operators, seafood processors, academia, and government or third parties that provide aquaculture training, technical assistance, or conduct verification audits.
The primary objectives are to:
- train farm operators on how to minimize the risk of diseases in order to reduce the need for interventions such as the use of antimicrobials or chemicals,
- teach farm operators and processors how to verify that only approved drugs and chemicals were properly used on the products they sell or process,
- inform farm operators and processors about seafood HACCP regulations and requirements for exporting seafood products to the United States.
In addition to the FDA, federal agencies with primary responsibility in aquaculture oversight include the Environmental Protection Agency, the Fish and Wildlife Service, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the United States Department of Agriculture and the Army Corp of Engineers. These agencies govern a number of public health concerns, including food safety, use of medicines and feed ingredients, water discharge and environmental concerns, disease management, protection and preservation of tidal and navigable waters and habitat protection.
- Environmental Protection Agency - National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Aquaculture Permitting
- Department of Interior’s Fish and Wildlife Service - National Fish Hatchery System
- National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration - National Marine Fisheries
- Army Corp of Engineers - Federal Aquaculture Regulatory Fact Sheet
- The Department of Agriculture
- Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service - certifies aquatic animal health for export
- Natural Resources Conservation Service - Soils - assists with fish pond design and construction
- Agriculture Research Service - conducts research in aquaculture production and diseases
- Agricultural Research and Extension Services - research funds and technical information
- Food Safety Inspection Services – information for catfish inspection services
Additional Information
- FDA/CVM Aquaculture
- FDA/CVM Key Antimicrobial Resistance and Judicious Use of Antimicrobials
- FDA/CVM Judicious Use of Antimicrobials
- Fish and Fishery Products Hazards Control Guide
- FDA Seafood Imports and Exports
- FDA Import Alerts for Industry Fishery and Seafood Products
- NOAA Aquaculture
- USDA Aquaculture
- US Fish and Wildlife Service – Aquatic Animal Approval Partnership
- FAO the State of the World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020
- FAO Antimicrobial Resistance
Please contact us at:
United States Food and Drug Administration
Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition
Office of Food Safety, Division of Seafood Safety
5001 Campus Drive, HFS-325
College Park, MD 20740
Phone: 240-402-2300