2023 FDA Science Forum
Metabolomic analysis reveals a novel immunomodulatory role of lysophosphatidylcholines in immunization with a genetically modified live attenuated parasitic vaccine
- Authors:
- Center:
-
Contributing OfficeCenter for Biologics Evaluation and Research
Abstract
Background:
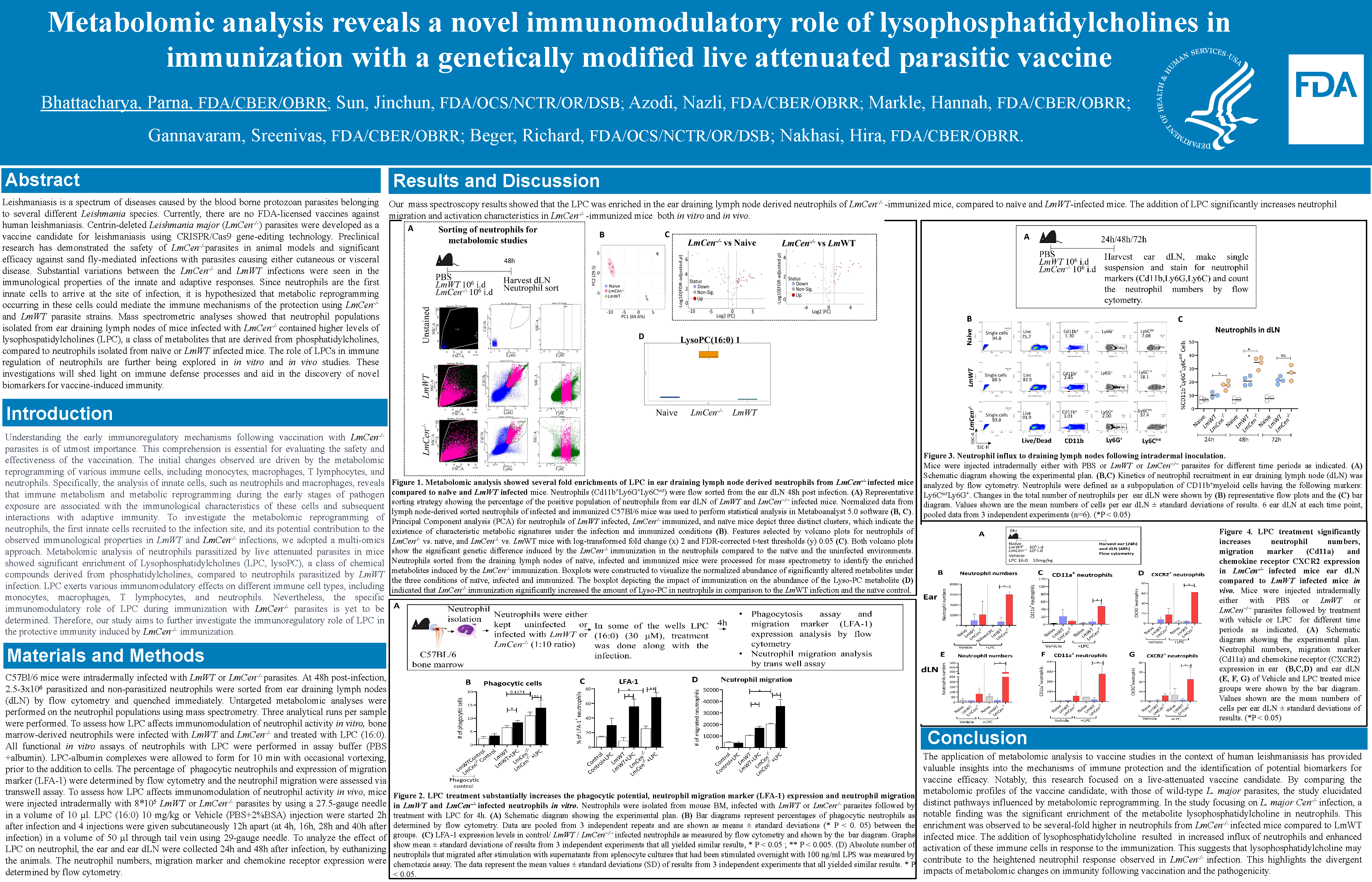
Leishmaniasis is a spectrum of diseases caused by the blood borne protozoan parasites belonging to several different Leishmania species. Currently, there are no FDA-licensed vaccines against human leishmaniasis. Centrin-deleted Leishmania major (LmCen-/-) parasites were developed as a vaccine candidate for leishmaniasis using CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology. Preclinical research has demonstrated the safety of LmCen-/- parasites in animal models and significant efficacy against sand fly-mediated infections with parasites causing either cutaneous or visceral disease. Substantial variations between the LmCen-/- and LmWT infections were seen in the immunological properties of the innate and adaptive responses.
Purpose:
Since neutrophils are the first innate cells to arrive at the site of infection, it is hypothesized that metabolic reprogramming occurring in these cells could mediate the immune mechanisms of the protection using LmCen-/- and LmWT parasite strains.
Methods:
C57Bl/6 mice were intradermally infected with LmWTmCherry or LmCen-/-mCherry parasites. At 48 h post-infection, parasitized and non-parasitized neutrophils were sorted by flow cytometry and quenched immediately. Untargeted metabolomic analyses were performed on the neutrophil populations using mass spectrometry. Three analytical runs per sample were performed.
Results:
Mass spectrometric analyses showed that neutrophil populations isolated from ear draining lymph nodes of mice infected with LmCen-/- contained higher levels of lysophospatidylcholines (LPC), a class of metabolites that are derived from phosphatidylcholines, compared to neutrophils isolated from naïve or LmWT infected mice. The role of LPCs in immune regulation of neutrophils are further being explored using a LPC receptor antagonist in in vitro and in vivo studies.
Conclusion:
These investigations will shed light on immune defense processes and aid in the discovery of novel biomarkers for vaccine-induced immunity.
Download the Poster (PDF; 3.52 MB)
