Drug Trials Snapshots: INQOVI
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race, and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT:
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your health provider about the risks and benefits of a drug. Refer to INQOVI Prescribing Information for complete information.
INQOVI (decitabine and cedazuridine)
In KOE' VEE
Taiho Oncology, Inc.
Approval date: July 7, 2020
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
INQOVI is used to treat adults with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) including chronic myelomonocytic leukemia.
MDS is a type of blood cancer in which blood cells in the bone marrow are defective leading to a low number of one or more types of blood cells.
How is this drug used?
INQOVI is a tablet taken once a day on Days 1 through 5 of each 28 day cycle.
What are the benefits of this drug?
In Trial 1, 18% of patients treated with INQOVI experienced complete response (specific improvements in bone marrow and blood cells) that lasted about 9 months. In Trial 2, 21% of patients treated with INQOVI, experienced complete response that lasted about 7.5 months.
Additionally, about half of the patients who were formerly dependent on transfusions were able to no longer require transfusions during an 8-week period.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
The tables below summarize efficacy results established on the basis of complete response for individual trials.
Table 1. Efficacy Results in Patients with MDS or CMML from Trial 1
|
Efficacy Endpoint |
INQOVI |
|
Complete Response (%) (95% CI) |
18 (10, 28) |
|
Median Duration of CR - months (range)* |
8.7 (1.1, 18.2) |
|
Median Time to CR - months (range) |
4.8 (1.7, 10.0) |
* From start of CR until relapse or death.
| Among the 41 patients who were dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 20 (49%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any consecutive 56-day post-baseline period. Of the 39 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 25 (64%) remained transfusion-independent during any consecutive 56-day post-baseline period. |
Table 2. Efficacy Results in Patients with MDS or CMML from Trial 2
|
Efficacy Endpoints |
INQOVI |
|
Complete Response (%) (95% CI) |
21 (15, 29) |
|
Median Duration of CR - months (range)* |
7.5 (1.6, 17.5) |
|
Median Time to CR - months (range) |
4.3 (2.1, 15.2) |
* From start of CR until relapse or death.
|
Among the 57 patients who were dependent on RBC and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 30 (53%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post-baseline period. Of the 76 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 48 (63%) remained transfusion-independent during any 56-day post-baseline period. |
INQOVI Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: INQOVI worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: Most of the patients were White. Differences in how well the drug worked among races could not be determined because of the small number of patients in other races.
- Age: INQOVI worked similarly in patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes efficacy results by demographic subgroups. These analyses were exploratory and therefore should be interpreted with caution.
Table 3. Subgroup Analyses of Complete Response Rate by Sex, Race and Age- Trial 1
|
|
Sex |
Race |
Age |
|||
|
Type of Response |
Men |
Women |
White |
Other |
<65 y |
≥65 y |
|
Complete Response (CR) |
12 (20.0%) |
2 (11%) |
14 (19%) |
0 (0%) |
3 (18%) |
11 (17%) |
Table 4. Subgroup Analyses of Complete Response Rate by Sex, Race and Age-Trial 2
|
|
Sex |
Race |
Age |
|||
|
Type of Response |
Men |
Women |
White |
Other |
<65 y |
≥65 y |
|
Complete Response (CR) |
19 (22%) |
9 (20%) |
25 (21%) |
3 (25%) |
8 (22%) |
20 (21%) |
FDA Review
What are the possible side effects?
INQOVI may cause serious and life-threatening bone marrow suppression. Most common side effects of INQOVI are low cell counts, fatigue, constipation, bleeding, muscle pain, oral pain or sores, joint pain, nausea, shortness of breath, diarrhea, rash, dizziness, febrile neutropenia, swelling of arms or legs, and headache.
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes adverse reactions in the clinical trial.
Table 5. Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 10% of Patients Who Received INQOVI in Pooled Safety Population
|
Adverse Reactions |
INQOVI |
Intravenous Decitabine |
INQOVI† |
|||
|
All Grades (%) |
Grades 3-4 |
All Grades (%) |
Grades 3-4 |
All Grades (%) |
Grades 3-4 |
|
|
General disorders and administration site conditions |
||||||
|
Fatigue1 |
29 |
2 |
25 |
0 |
55 |
5 |
|
Hemorrhage2 |
24 |
2 |
17 |
0 |
43 |
3 |
|
Edema3 |
10 |
0 |
11 |
0 |
30 |
0.5 |
|
Pyrexia |
7 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
19 |
1 |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
||||||
|
Constipation4 |
20 |
0 |
23 |
0 |
44 |
0 |
|
Mucositis5 |
18 |
1 |
24 |
2 |
41 |
4 |
|
Nausea |
25 |
0 |
16 |
0 |
40 |
0.5 |
|
Diarrhea6 |
16 |
0 |
11 |
0 |
37 |
1 |
|
Transaminase increased7 |
12 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
21 |
3 |
|
Abdominal pain8 |
9 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
19 |
1 |
|
Vomiting |
5 |
0 |
5 |
0 |
15 |
0 |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders |
||||||
|
Myalgia9 |
9 |
2 |
16 |
1 |
42 |
3 |
|
Arthralgia10 |
9 |
1 |
13 |
1 |
40 |
3 |
|
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders |
||||||
|
Dyspnea11 |
17 |
3 |
9 |
3 |
38 |
6 |
|
Cough12 |
7 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
28 |
0 |
|
Blood & lymphatic system disorders |
||||||
|
Febrile neutropenia |
10 |
10 |
13 |
13 |
33 |
32 |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
||||||
|
Rash13 |
12 |
1 |
11 |
1 |
33 |
0.5 |
|
Nervous system disorders |
||||||
|
Dizziness14 |
16 |
1 |
11 |
0 |
33 |
2 |
|
Headache15 |
22 |
0 |
13 |
0 |
30 |
0 |
|
Neuropathy16 |
4 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
13 |
0 |
|
Metabolism and nutritional disorders |
||||||
|
Decreased appetite |
10 |
1 |
6 |
0 |
24 |
2 |
|
Infections and infestations |
||||||
|
Upper respiratory tract infection17 |
6 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
23 |
1 |
|
Pneumonia18 |
7 |
7 |
7 |
5 |
21 |
15 |
|
Sepsis19 |
6 |
6 |
2 |
1 |
14 |
11 |
|
Cellulitis20 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
12 |
5 |
|
Investigations |
||||||
|
Renal impairment21 |
9 |
0 |
8 |
1 |
18 |
0 |
|
Weight decreased |
5 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
10 |
1 |
|
Injury, poisoning, and procedural complications |
||||||
|
Fall |
4 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
12 |
1 |
|
Psychiatric disorders |
||||||
|
Insomnia |
6 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
12 |
0.5 |
|
Vascular disorders |
||||||
|
Hypotension22 |
4 |
0 |
6 |
1 |
11 |
2 |
|
Cardiac Disorders |
||||||
|
Arrhythmia23 |
3 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
11 |
1 |
†Includes adverse reactions that occurred during all cycles, including during treatment with 1 cycle of intravenous decitabine.
1 Includes fatigue, asthenia, and lethargy
2 Includes contusion, epistaxis, petechiae, hematuria, conjunctival hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, purpura, angina bullosa hemorrhagica, gingival bleeding, hematoma, hemoptysis, eye contusion, hemorrhagic diathesis, increased tendency to bruise, vaginal hemorrhage, abdominal wall hematoma, blood blister, bone contusion, catheter site bruise, ecchymosis, genital hemorrhage, intra-abdominal hematoma, oral mucosa hematoma, periorbital hemorrhage, procedural hemorrhage, pulmonary alveolar hemorrhage, retinal hemorrhage, scleral hemorrhage, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, tongue hemorrhage, and vessel puncture site hemorrhage
3 Includes edema peripheral, peripheral swelling, swelling face, fluid overload, localized edema, face edema, edema, eye swelling, eyelid edema, fluid retention, periorbital swelling, scrotal edema, scrotal swelling, and swelling
4 Includes constipation and feces hard
5 Includes oropharyngeal pain, stomatitis, mouth ulceration, proctalgia, oral pain, gingivitis, oral disorder, gingival pain, colitis, glossodynia, mouth swelling, pharyngitis, proctitis, duodenitis, enteritis, gingival discomfort, gingival swelling, lip disorder, lip ulceration, mucosal ulceration, nasal ulcer, noninfective gingivitis, oral mucosal blistering, oral mucosal erythema, pharyngeal erythema, pharyngeal ulceration, tongue ulceration, and vulvitis
6 Includes diarrhea and feces soft
7 Includes alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, gamma-glutamyltransferase increased, liver function test increased, and transaminases increased
8 Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, epigastric discomfort, and abdominal discomfort
9 Includes myalgia, pain in extremity, muscle spasms, pain, musculoskeletal pain, non-cardiac chest pain, muscular weakness, musculoskeletal chest pain, flank pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, muscle strain, and musculoskeletal discomfort
10 Includes arthralgia, back pain, neck pain, joint stiffness, pain in jaw, joint swelling, bursitis, joint range of motion decreased, and joint injury
11 Includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, hypoxia, wheezing, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and tachypnoea
12 Includes cough and productive cough
13 Includes maculo-papular rash, rash, erythema, skin lesion, folliculitis, dermatitis, dermatitis acneiform, eczema, erythema multiforme, rash erythematous, seborrheic keratosis, skin ulcer, dermatitis allergic, dermatitis contact, eczema nummular, genital erythema, rash papular, rash pruritic, rash pustular, seborrheic dermatitis, skin exfoliation, skin irritation, stasis dermatitis, and ulcerative keratitis
14 Includes dizziness, vertigo, postural dizziness, and positional vertigo
15 Includes headache, sinus pain, and sinus headache
16 Includes hypoesthesia, paresthesia, neuropathy peripheral, gait disturbance, peripheral sensory neuropathy, ataxia, balance disorder, brachial plexopathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, and radicular pain
17 Includes upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, sinusitis, and viral upper respiratory tract infection
18 Includes pneumonia, pneumonitis, atypical pneumonia, and lung infection
19 Includes sepsis, bacteremia, septic shock, endocarditis, pseudomonal bacteremia, and staphylococcal bacteremia
20 Includes cellulitis, catheter site cellulitis, and infected bite
21 Includes blood creatinine increased, acute kidney injury, blood urea increased, blood creatine increased, and renal failure
22 Includes hypotension, blood pressure decreased, and cardiogenic shock
23 Includes sinus tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, tachycardia, atrial flutter, sinus bradycardia, and conduction disorder
INQOVI Prescribing Information
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in men and women.
- Race: Most of the patients were White. Differences in the occurrence of side effects among races could not be determined because of the small number of patients in other races.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar in patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
Tables below summarize selected adverse events by sex, age and race subgroup. Presented is pooled safety population.
Table 6. Selected Adverse Events in ≥10% of Patients by Subgroup
|
Adverse Event |
Sex |
Race |
Age |
||||
|
Men N=144 |
Women N=64 |
White |
Other |
<65 y |
65-75y |
≥75 y |
|
|
Any AEs, (%) |
97 |
100 |
97 |
100 |
94 |
100 |
97 |
|
Febrile neutropenia |
24 |
22 |
23 |
33 |
35 |
21 |
19 |
|
Fatigue |
33 |
34 |
36 |
11 |
27 |
31 |
42 |
|
Constipation |
24 |
28 |
27 |
11 |
25 |
26 |
26 |
Adapted from Clinical Trial Report
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved INQOVI based on evidence from two clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT02103478 and Trial 2/NCT03306264) of 213 patients with MDS or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). The trials were conducted at 51 sites in the United States and Canada.
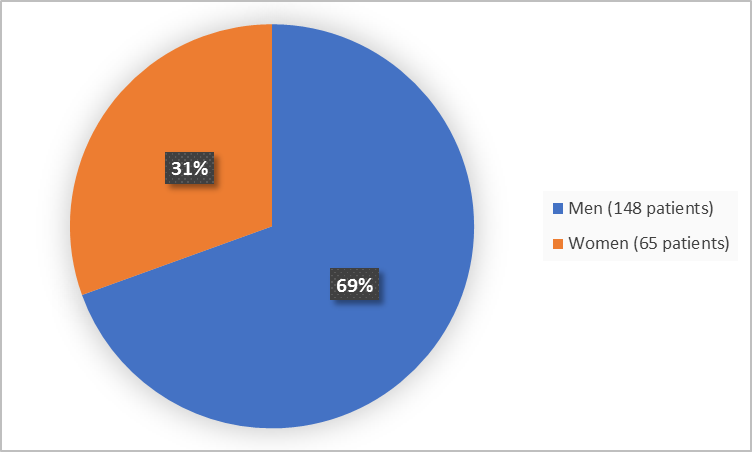
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were in the clinical trials.
Figure 1. Demographics by Sex
Adapted from FDA Review
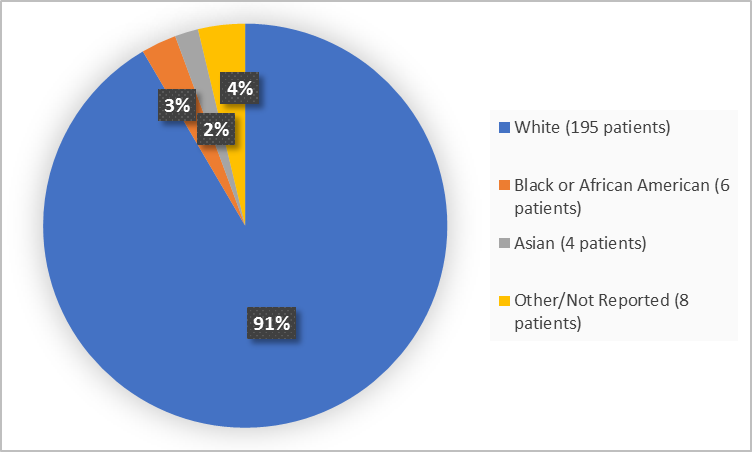
Figure 2 below summarizes the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trials.
Figure 2. Demographics by Race
Adapted from FDA Review
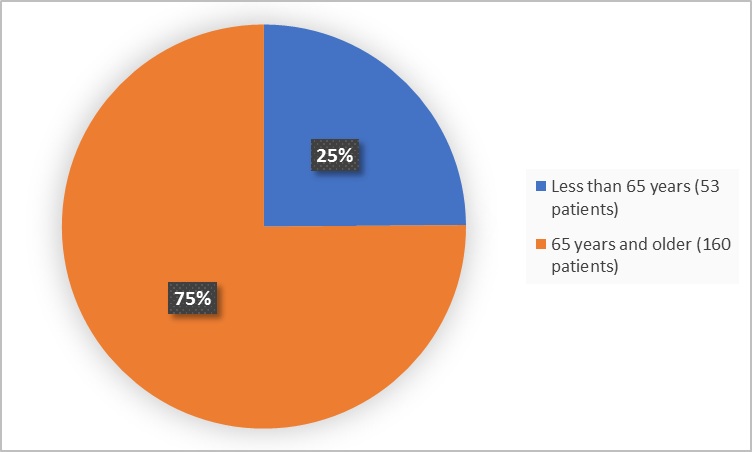
Figure 3 summarizes how many patients of certain age were in the clinical trials.
Figure 3. Demographics by Age
Adapted from FDA Review
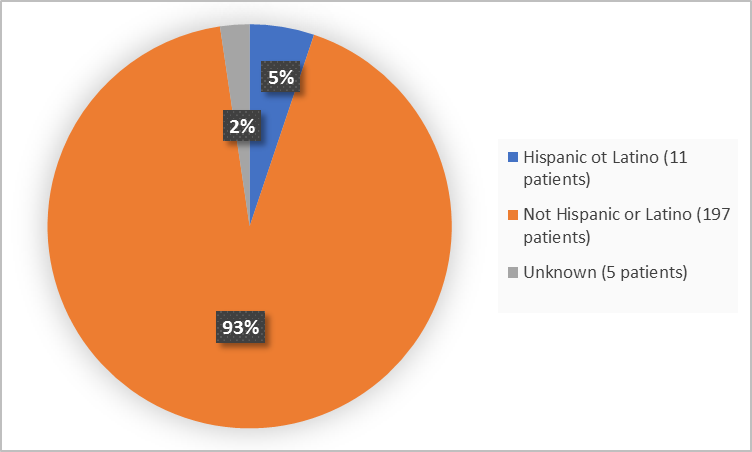
Figure 4 summarizes the percentage of patients by ethnicity in the clinical trials.
Figure 4. Demographics by Ethnicity
Adapted from FDA Review
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes demographics of all patients who were included in efficacy population.
Table 7. Trial Demograpfics (efficacy population)
|
Demographic Characteristic |
Trial 1 |
Trial 2 |
TOTAL |
|
Sex, n (%) |
|||
|
Men |
61 (76) |
87 (65) |
148 (69) |
|
Women |
19 (24) |
46 (35) |
65 (31) |
|
Race, n (%) |
|||
|
White |
74 (93) |
121 (91) |
195 (92) |
|
Black or African American |
2 (3) |
4 (3) |
6 (3) |
|
Asian |
1 (1) |
3 (2) |
4 (2) |
|
Other or Not Reported |
3 (4) |
5 (4) |
8 (4) |
|
Age (years) |
|||
|
Median (min, max) |
71 (32, 90) |
71 (44, 88) |
71 (32, 90) |
|
Age Group, n (%) |
|||
|
<65 years |
17 (21) |
36 (27) |
53 (25) |
|
≥65 years |
63 (79) |
97 (73) |
160 (75) |
|
Ethnicity, n (%) |
|||
|
Hispanic or Latino |
5 (6) |
6 (5) |
11 (5) |
|
Not Hispanic or Latino |
72 (90) |
125 (94) |
197 (92) |
|
Not Reported/Unknown |
3 (4) |
2 (2) |
5 (2) |
|
Region, n (%) |
|||
|
USA |
64 (80) |
110 (83) |
174 (82) |
|
Canada |
16 (20) |
23 (17) |
39 (18) |
Clinical Trial Data
How were the trials designed?
There were two trials that evaluated the benefit and side effects of INQOVI in patients with MDS or CMML. Patients received INQOVI tablet once a day by mouth in cycle 1 and decitabine (an approved drug for MDS) intravenously in cycle 2 or the reverse sequence. Starting with Cycle 3, all patients received INQOVI orally once daily on Days 1 through 5 of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The benefit of INQOVI was evaluated by measuring how many patients reached complete response (CR) defined as specific improvements in bone marrow and blood cells and how many patients achieved or maintained transfusion independence.
How were the trials designed?
The safety and efficacy of INQOVI was evaluated in two multicenter, open label, randomized, 2-cycle, 2-sequence crossover study trials that included patients with MDS or CMML.
In both trials, patients received INQOVI (35 mg decitabine and 100 mg cedazuridine) orally in Cycle 1 and decitabine 20 mg/m2 intravenously in Cycle 2 or the reverse sequence. Both INQOVI and intravenous decitabine were administered once daily on Days 1 through 5 of the 28 day cycle. Starting with Cycle 3, all patients received INQOVI orally once daily on Days 1 through 5 of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The efficacy was established on the basis of complete response (CR) as per the International Working Group (IWG) 2006 consensus criteria.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.